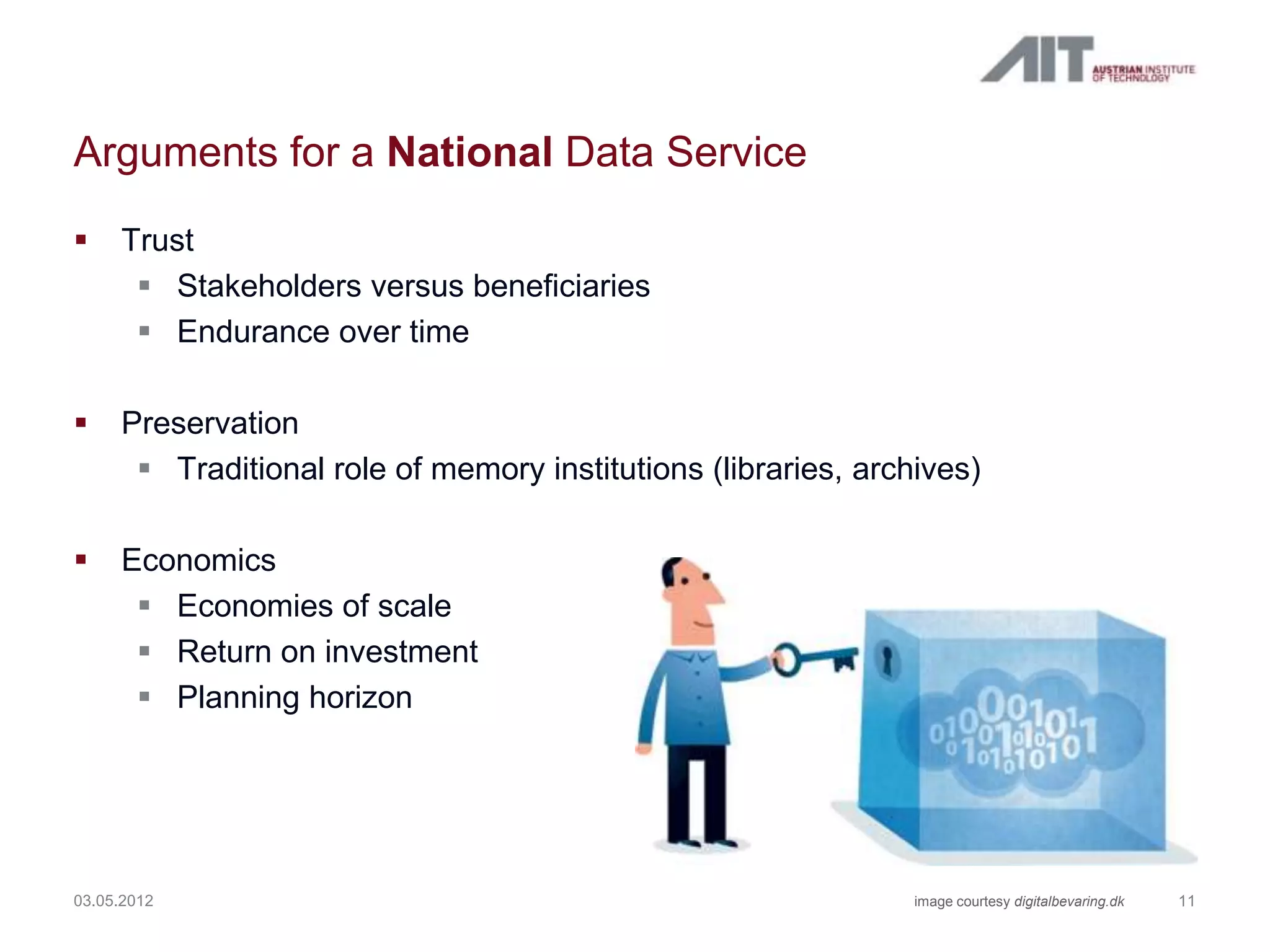
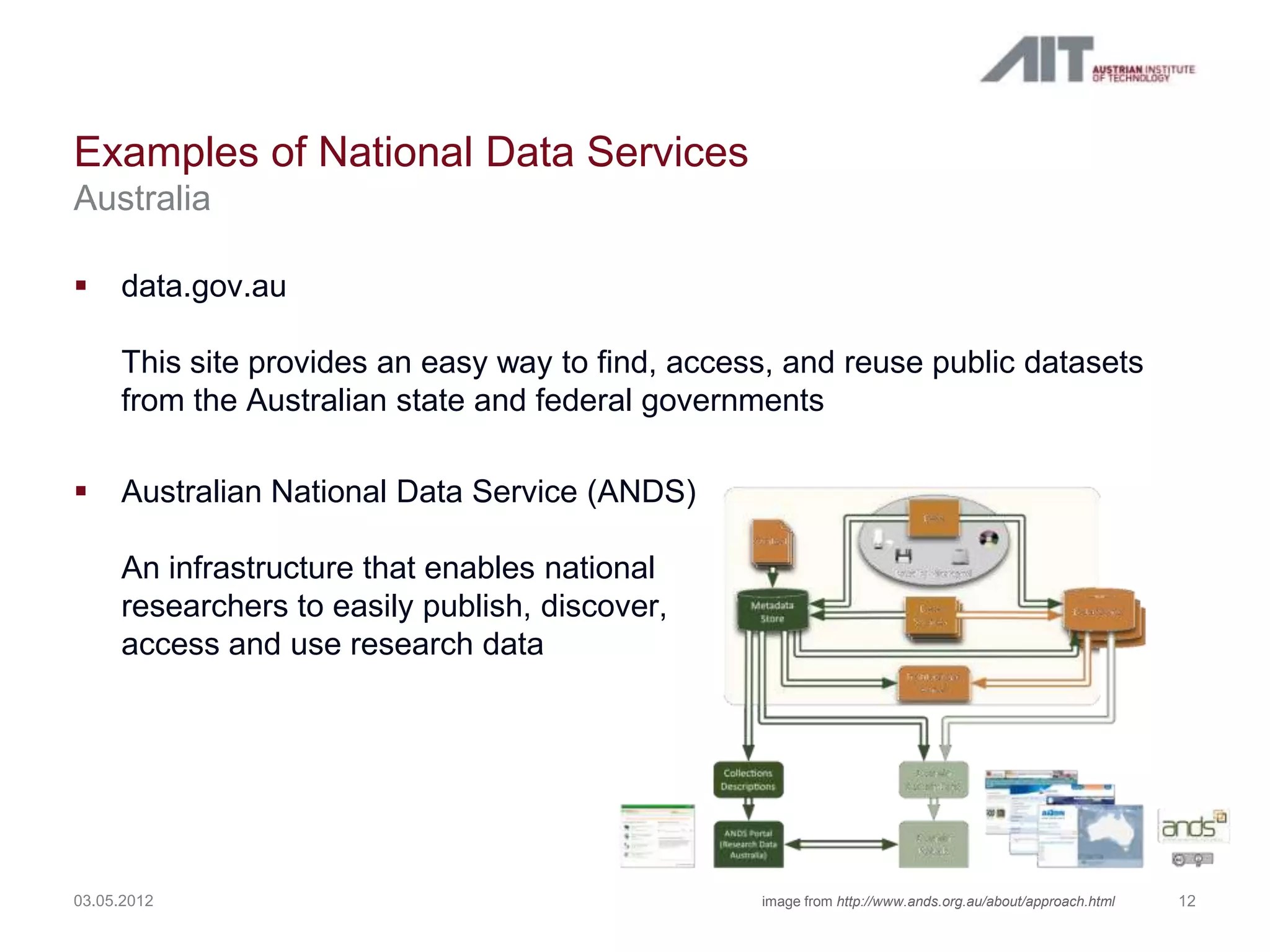
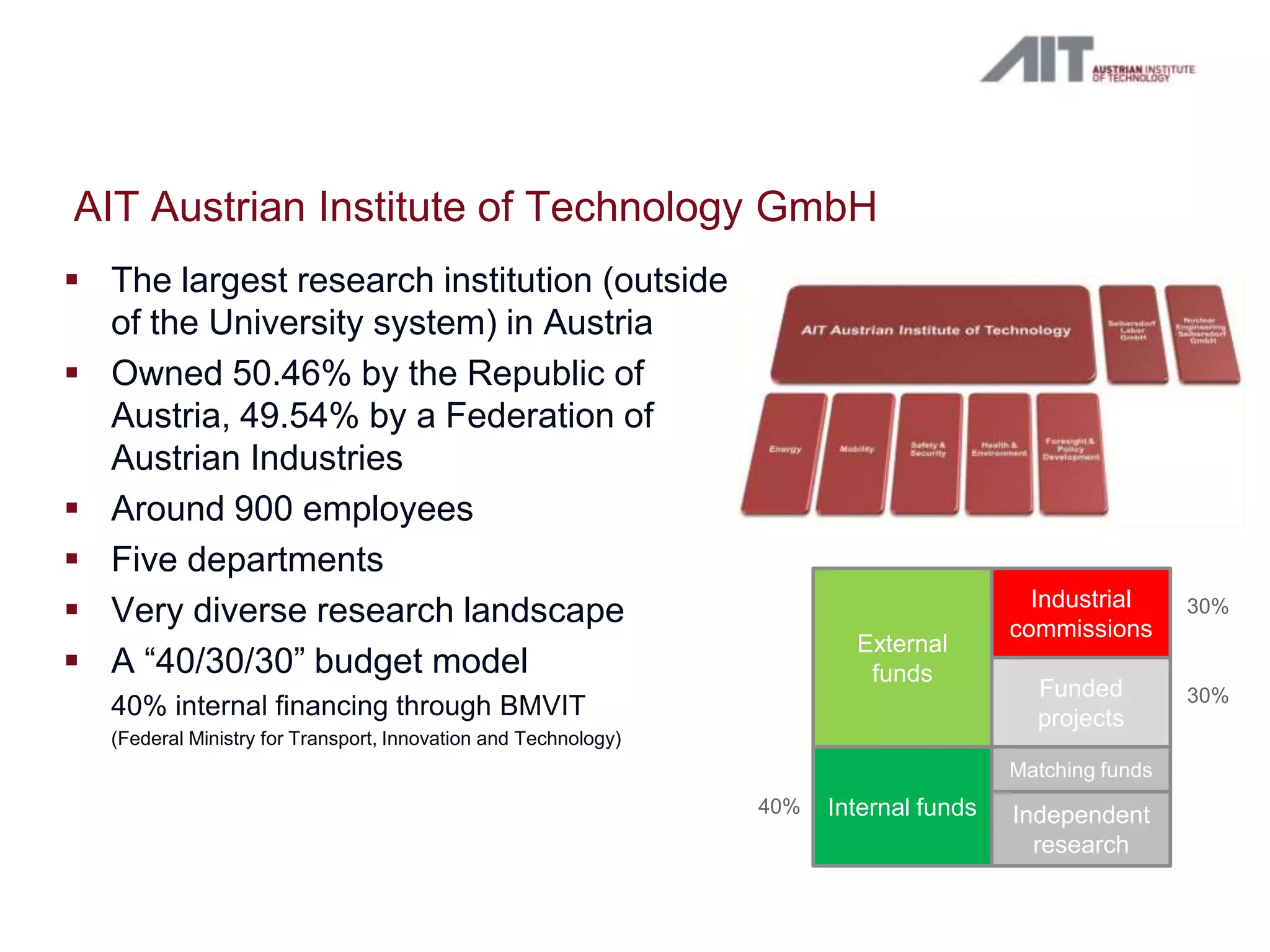
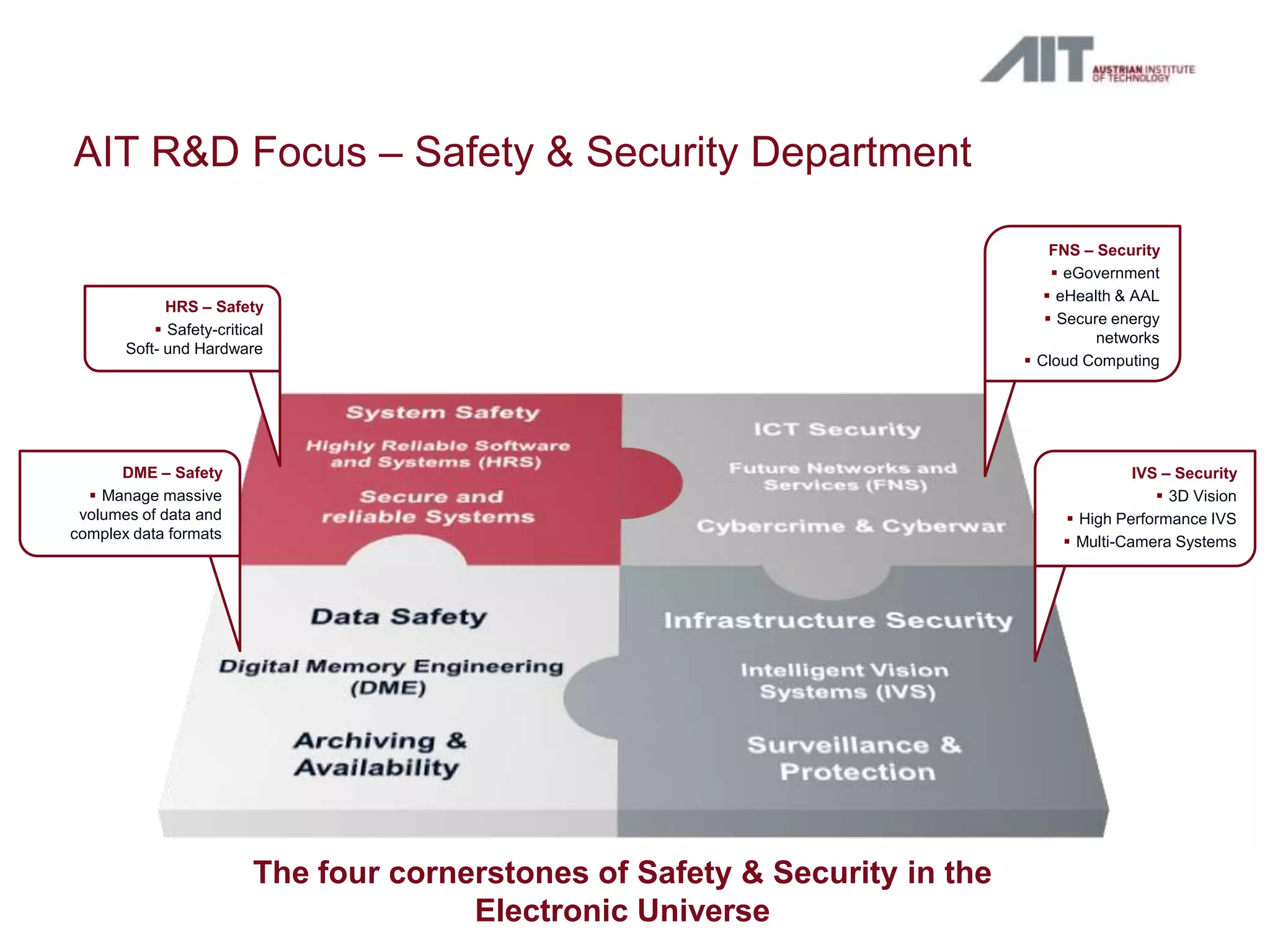
The document summarizes a workshop agenda on open access and preservation in eGovernment. The agenda includes an introduction, general discussion, breakout groups on requirements and policies, and reports from the breakout groups. It also provides background information on the Austrian Institute of Technology (AIT) and its focus on safety and security. AIT has advanced the state of digital preservation through national and international projects. The presentation argues for open access of publicly funded research and data for moral, pragmatic, and economic reasons. It advocates for a national data service in Austria to ensure long-term access, preservation, and return on investment. Examples from Australia, Netherlands, and existing Austrian initiatives are provided. Next steps proposed include defining user requirements, selecting technical





![Arguments for Open Access
Moral Argument
Publically funded research should be publically available
Publically funded government should by publically available
Pragmatic Argument
Open Access improves research efficiency
Open Access improves governmental efficiency
Economic Argument
Open Access and Open Data can be
the foundation of new economic growth
(see for example: Graham Vickery, Review of Recent Studies
on PSI Re-Use and Related Market Developments [2011].)
Is publishing today a value-adding or
a rent-seeking behaviour?
03.05.2012 9
image courtesy digitalbevaring.dk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cedem2012aitworkshoprossking2012-05-03-120504014719-phpapp01/75/Open-Access-Preservation-and-eGovernment-9-2048.jpg)