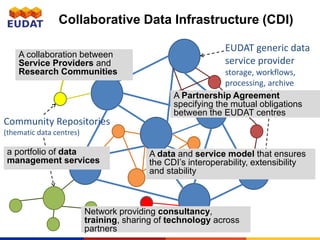
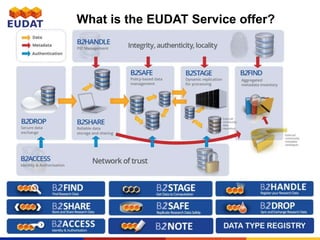
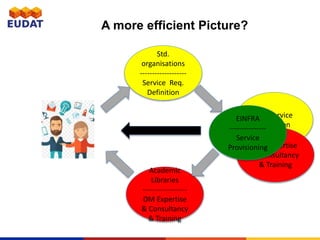
EUDAT, initiated in 2011 and funded by the EU's Horizon 2020, aims to provide comprehensive data management services for research communities facing increasing data complexities. It operates through a collaborative infrastructure involving numerous partners to enhance interoperability and address various data life cycle requirements. EUDAT engages with academic and research libraries for data management expertise while continuously adapting to community needs through outreach, training, and best practices.