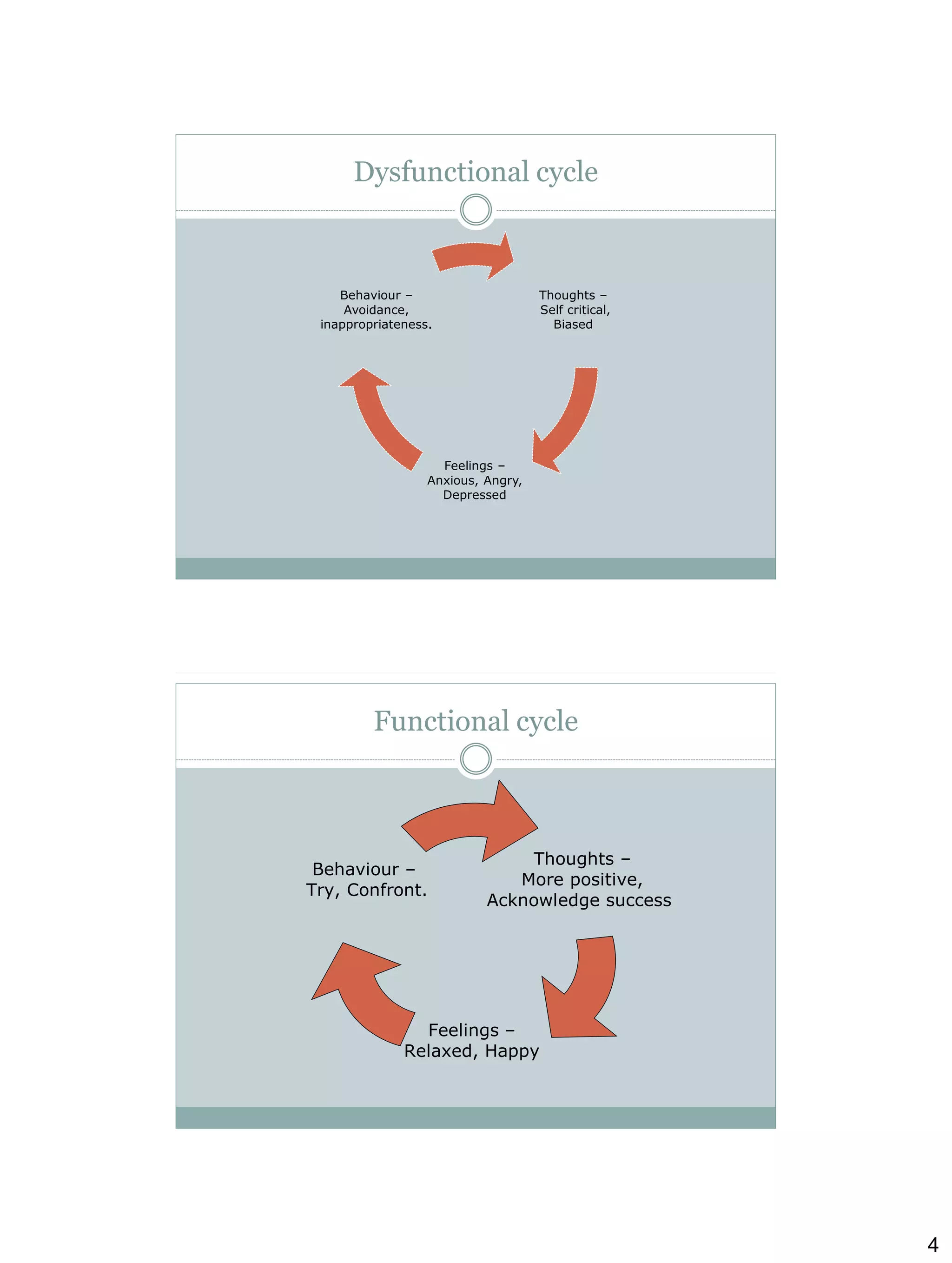
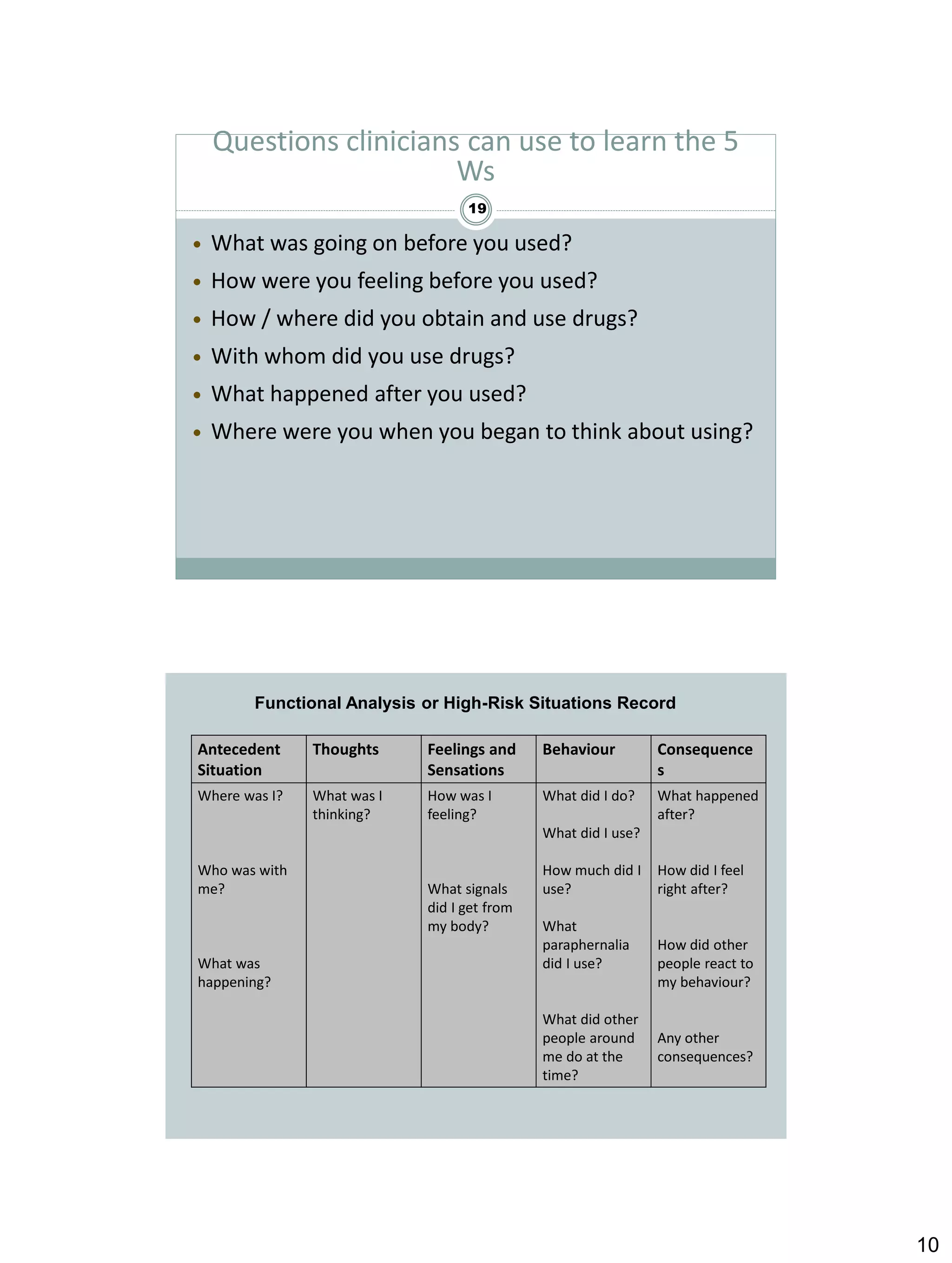
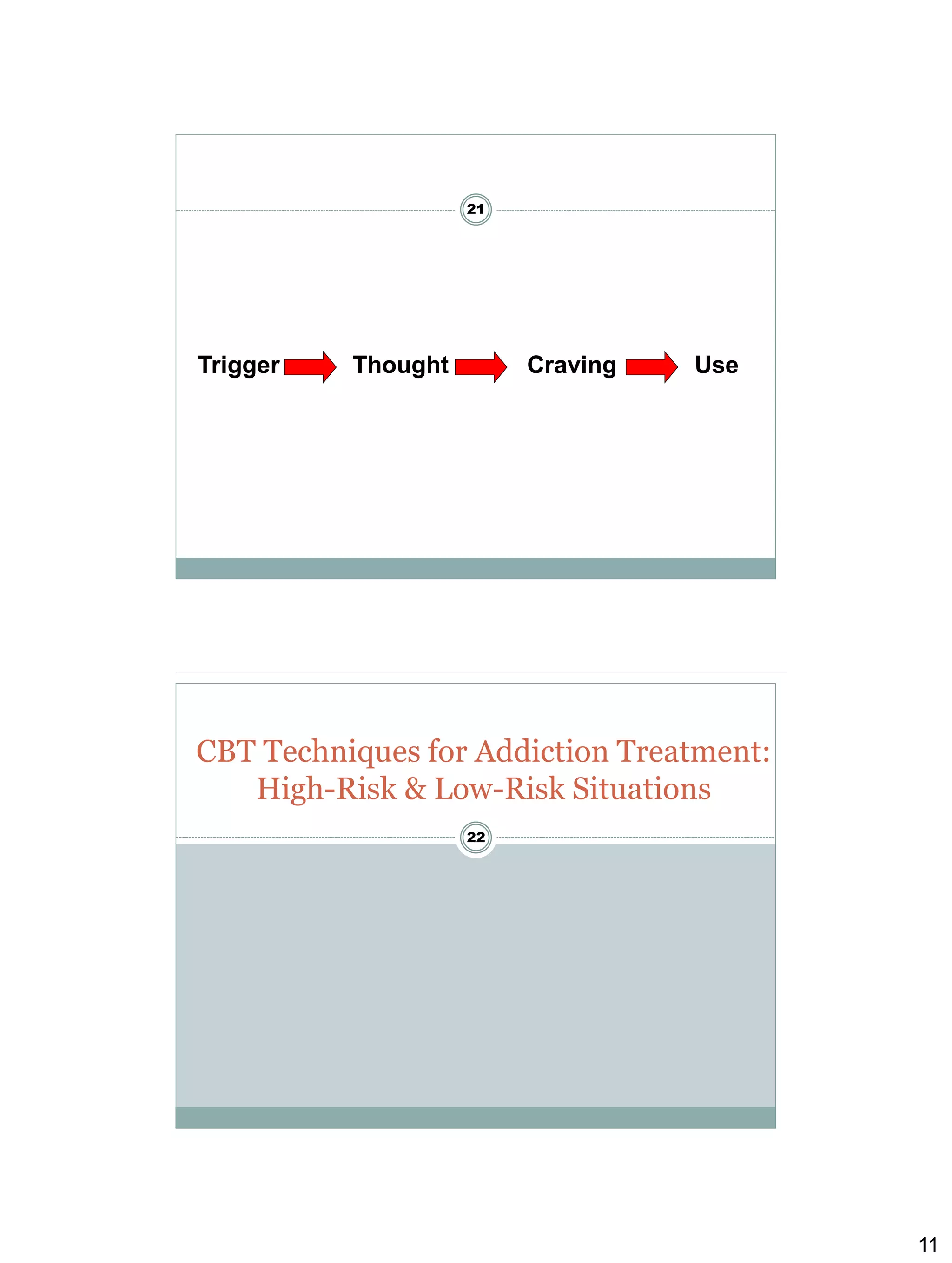
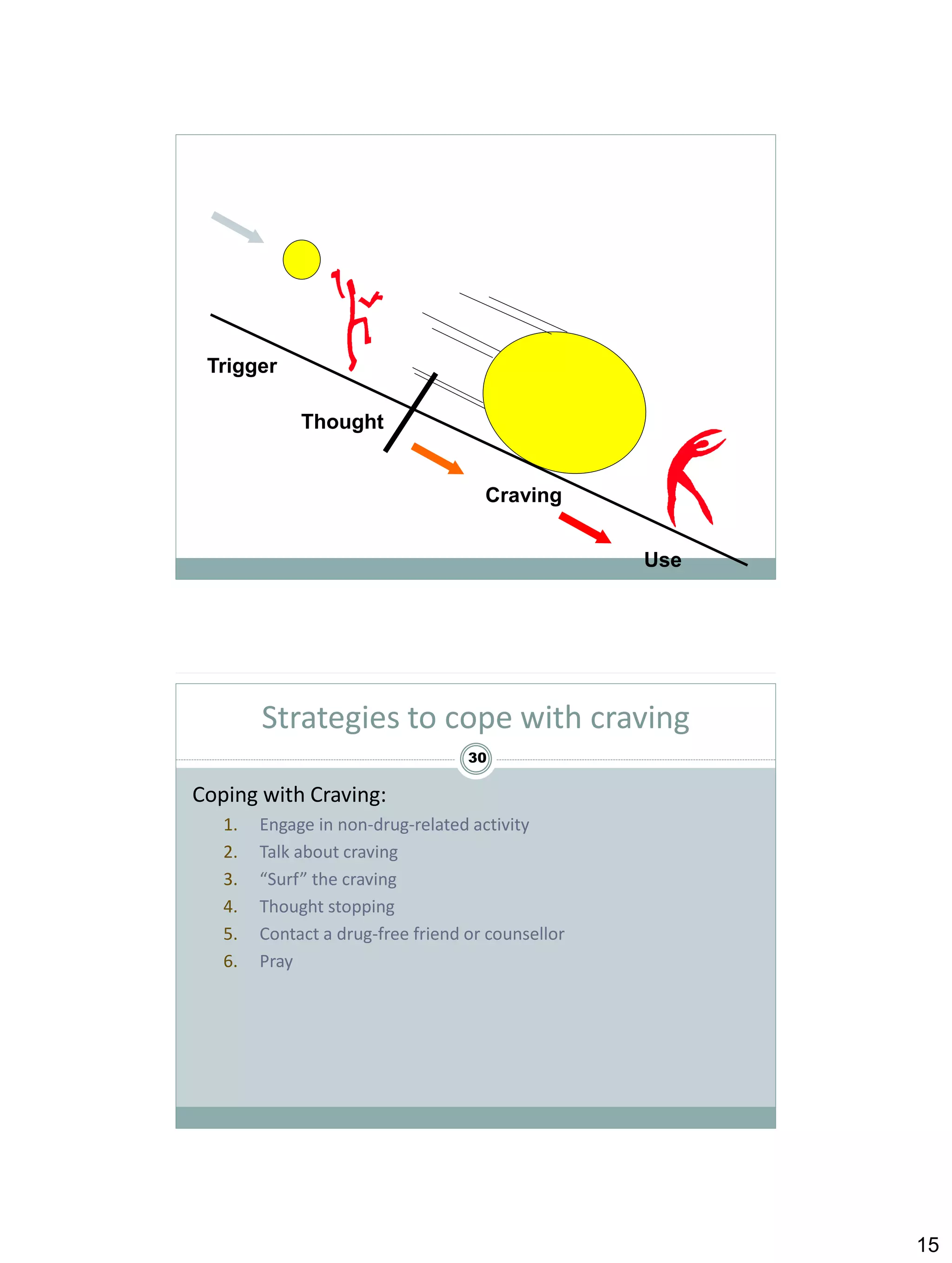
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) aims to reduce psychological distress and maladaptive behaviour by altering cognitive processes. It focuses on the relationship between cognitions, affect, and behaviour. CBT techniques teach clients to identify and change dysfunctional thoughts and beliefs, and develop more adaptive cognitive and behavioural skills. Relapse prevention (RP) applies CBT to help clients maintain abstinence by preventing initial lapses and preventing lapses from becoming full relapses. Key CBT concepts include functional analysis to understand high-risk situations for drug use, coping strategies to manage cravings, and increasing time spent in low-risk situations that don't trigger drug use. The clinician plays an active role in teaching CBT skills and