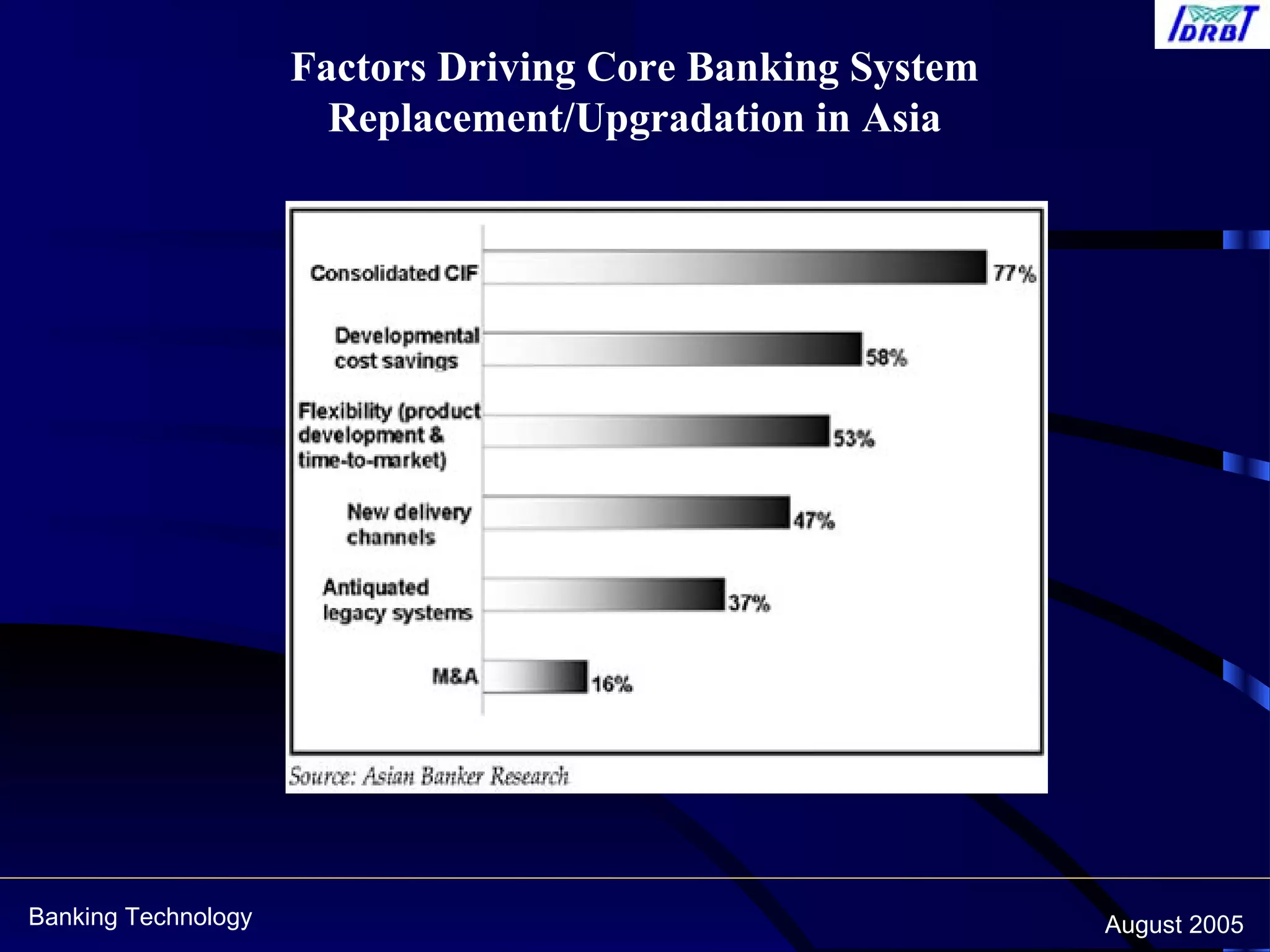
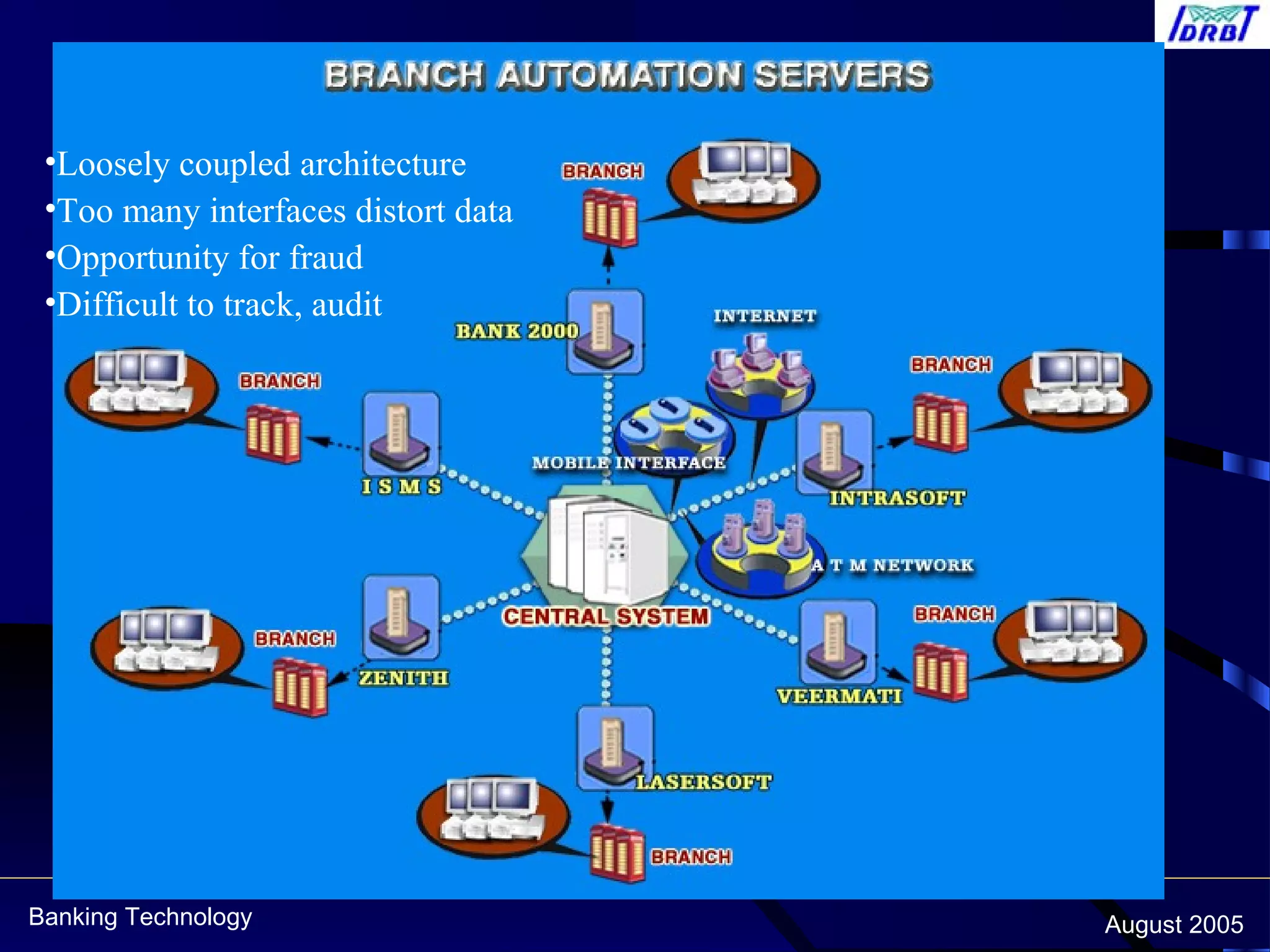
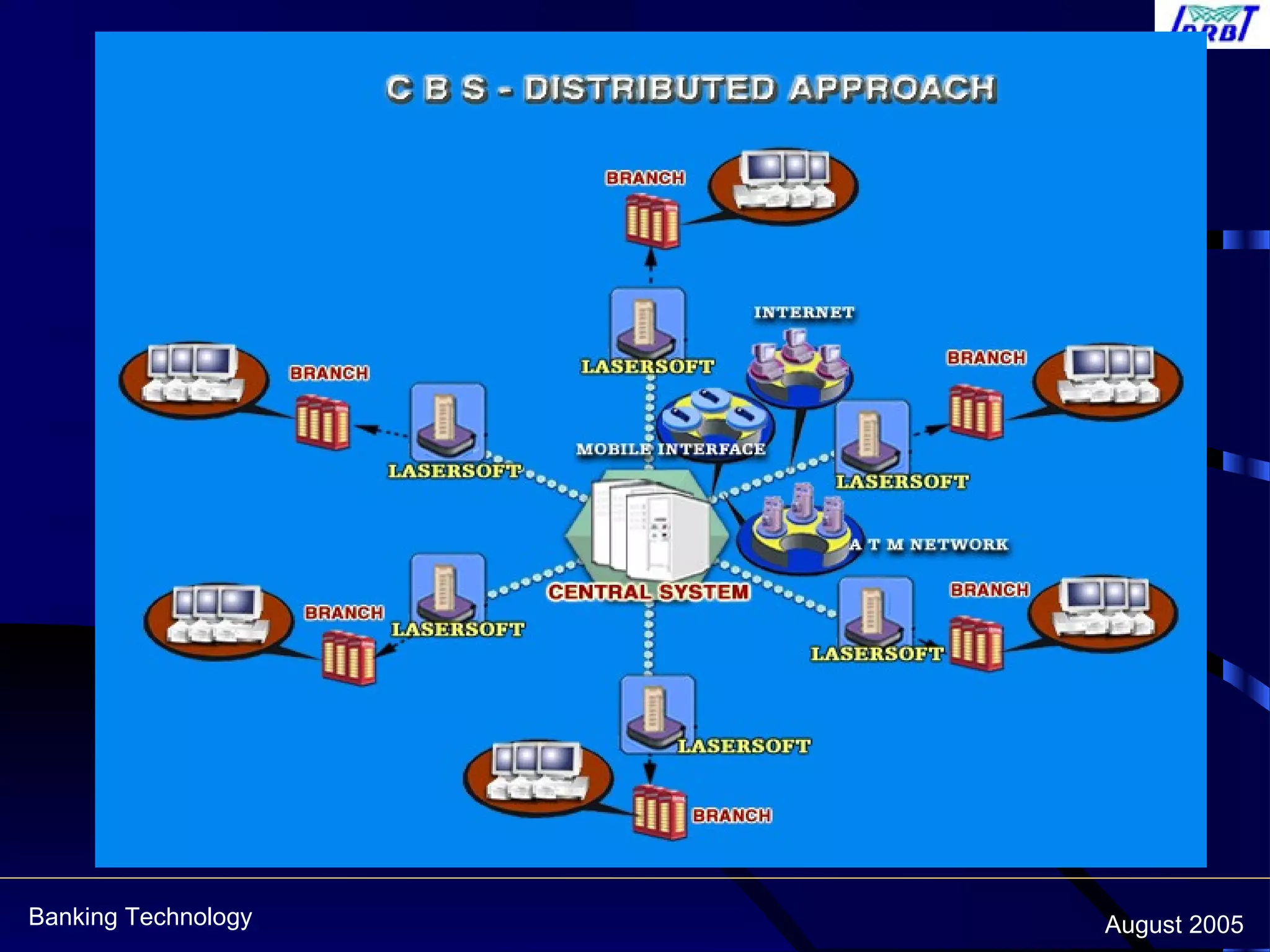
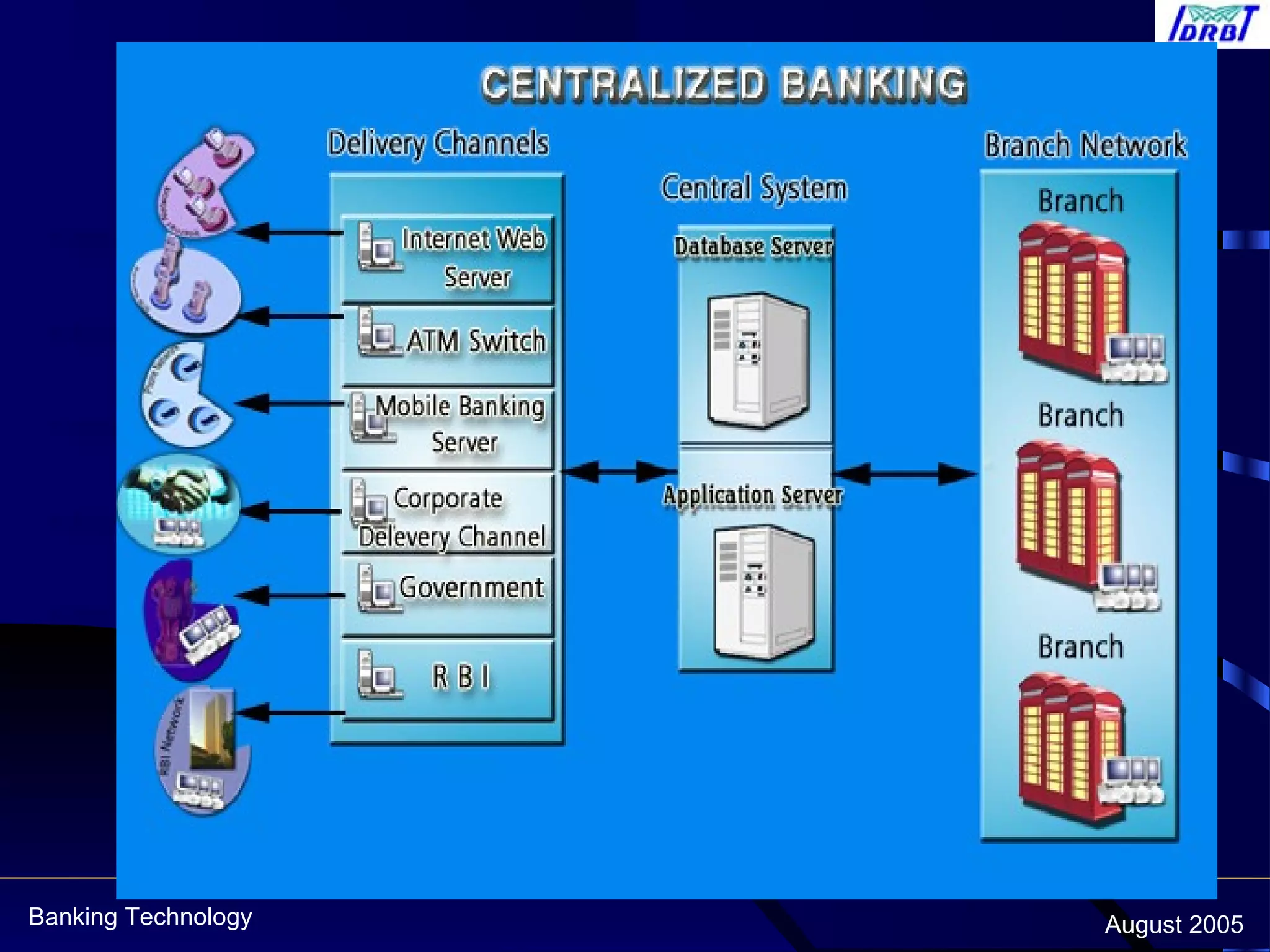
This document discusses centralized banking solutions (CBS), also known as core banking solutions. It defines CBS as a solution that enables banks to offer services from a single location supporting retail and corporate banking across all delivery channels. The key benefits of CBS include offering a single point of management, preparation for current and future requirements, and better integration across software and hardware. The document also outlines some major global and domestic vendors that provide CBS.