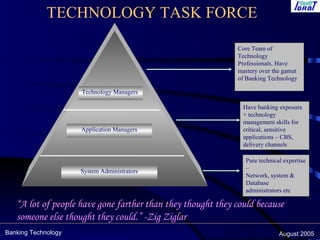
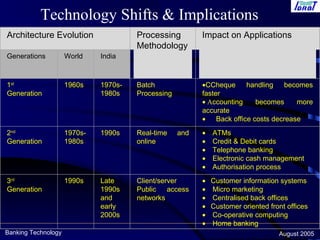
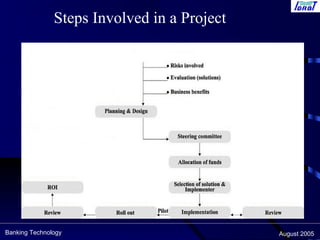
This document discusses key issues, challenges, and best practices for implementing centralized banking systems (CBS). It covers pre-implementation, implementation, and post-implementation phases. Some of the major topics discussed include people issues, change management, legacy systems challenges, infrastructure requirements, and critical success factors like project management skills and top management support. The document provides guidance on technology upgrades, governance, security, and ensuring business continuity during and after a CBS implementation.