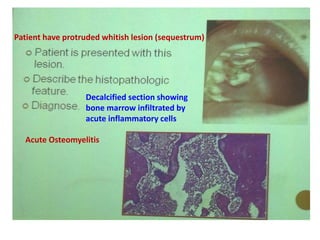
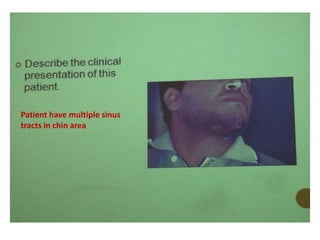
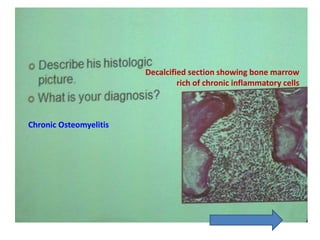
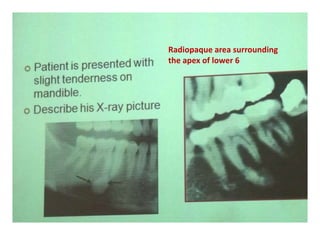
1. The document describes various clinical presentations, radiographic findings, and histopathological features of different dental diseases.
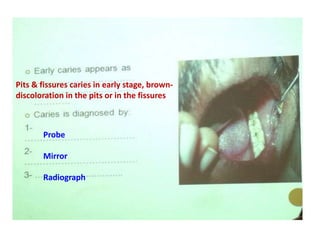
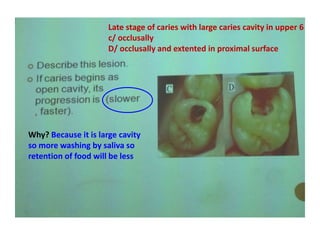
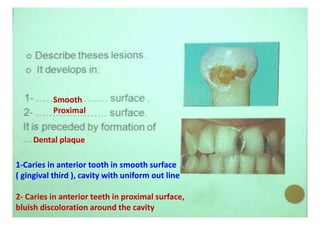
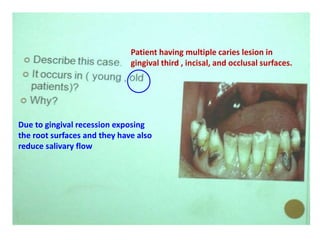
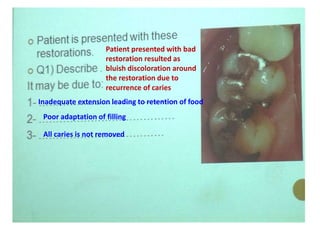
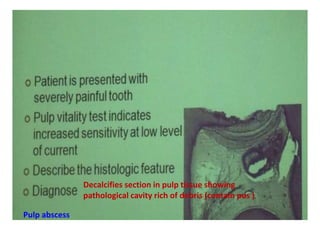
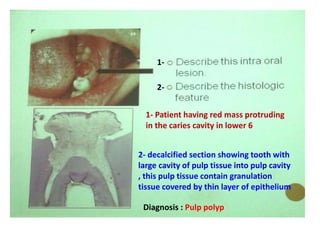
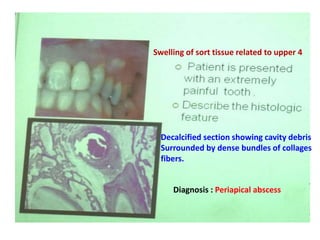
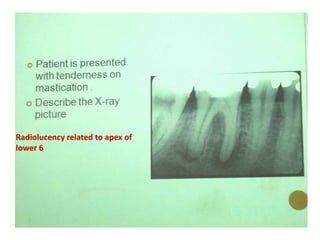
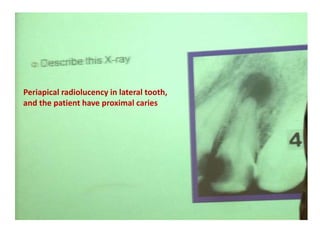
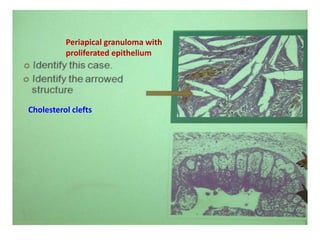
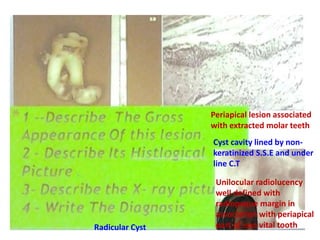
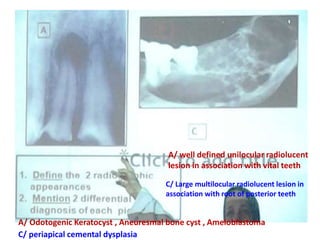
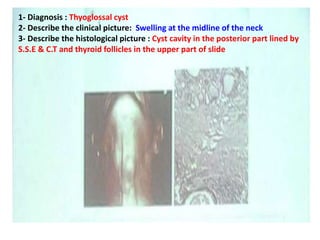
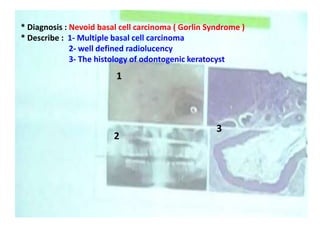
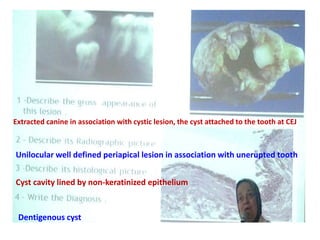
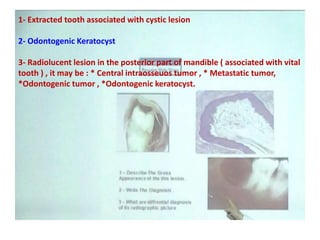
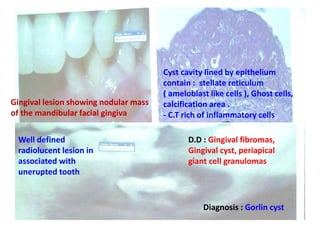
2. Examples include caries lesions at different stages, pulp polyps, periapical abscesses, radicular cysts, dentigenous cysts, and central giant cell granulomas.
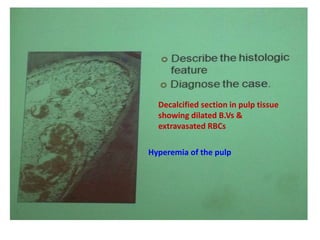
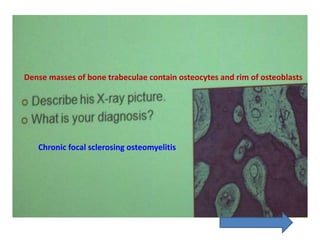
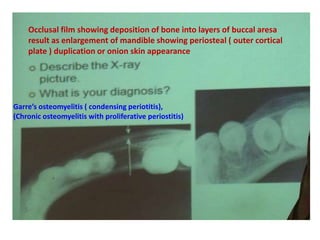
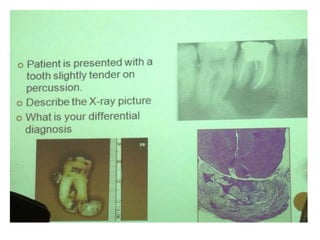
3. Histopathology slides show features like transverse dentinal clefts, pulp tissue with dilated blood vessels, and cyst cavities lined by stratified squamous epithelium.