1) The document discusses renal regulation of sodium, chloride, urea, glucose, amino acids, and calcium. It describes how each of these substances is filtered by the glomerulus and then reabsorbed along different segments of the nephron through various transport mechanisms, primarily active transport and facilitated diffusion.
2) Sodium is 99.6% reabsorbed, mainly through active transport in the proximal tubule, thick ascending limb, and distal convoluted tubule. Chloride largely follows sodium but also uses co-transporters.
3) Urea is freely filtered but also reabsorbed and secreted to help concentrate the medullary interstitium for countercurrent exchange. Glucose


































![Calcium in the plasma:
The total concentration of calcium in plasma is normally 2.2 to 2.7 mM
(8.8-10.6 mg/dl).
Some 40% binds to plasma proteins, mainly albumin, and constitutes the
nonfilterable fraction.
The filterable portion, approximately 60% of total plasma calcium, consists
of two moieties.
1) approximately 15% of the total, complexes with small anions such as
carbonate, citrate, phosphate, and sulfate.
2) approximately 45% of total calcium, is the ionized Ca2+ that one may
measure with Ca2+ -sensitive electrodes or dyes. It is the concentration
of this free, ionized calcium that the body tightly regulates; plasma [Ca2+
] normally is 1.0 to 1.3 mM (4.0-5.2 mg/dl).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cationsandanions-130702025451-phpapp01/85/Cations-and-anions-36-320.jpg)





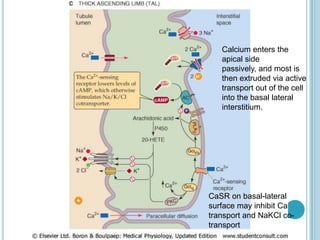

![PARATHYROID HORMONE
The most important regulator of renal Ca2+ reabsorption is PTH, which
stimulates Ca2+ reabsorption in the thick ascending limb, the distal
convoluted tubule, and the connecting tubule.
(PTH does NOT have a proximal action)
PTH appears to increase the open probability of apical Ca2+ channels.
Such an increase in Ca2+ permeability would increase intracellular
[Ca2+]i, which in turn would stimulate basolateral Ca2+ extrusion
mechanisms, increase Ca2+ reabsorption, and raise plasma [Ca2+ ].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cationsandanions-130702025451-phpapp01/85/Cations-and-anions-44-320.jpg)










