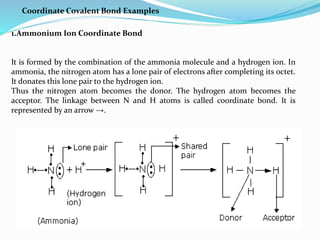
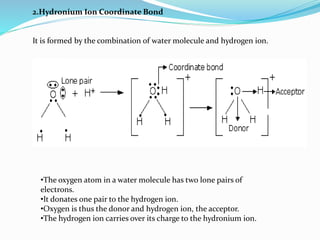
A coordinate bond is a covalent bond where a shared pair of electrons is contributed by only one atom, known as the donor, while the other atom accepts the electrons and is termed the acceptor. Conditions for forming a coordinate bond include the donor having a lone pair of electrons and the acceptor possessing a vacant orbital. Examples include ammonium and hydronium ions, with coordinate compounds exhibiting unique properties like higher melting and boiling points than covalent compounds, semi-polar character, and stability.