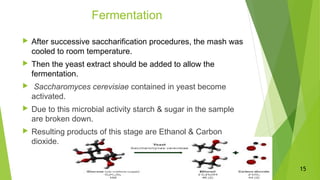
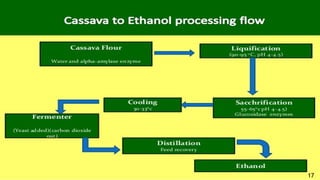
Cassava is the fourth largest source of carbohydrates and is grown in many tropical regions. It can be processed into ethanol biofuel through a multi-step process. The cassava root is ground and mixed with water before enzymes convert its starch into sugars through saccharification. Yeast then ferments the sugars to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide. Distillation separates and purifies the ethanol. While cassava biofuel helps reduce fossil fuel usage, its production has high costs and technical requirements compared to other biofuel feedstocks.