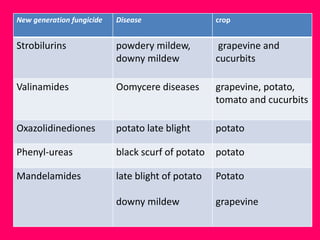
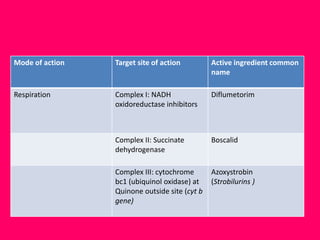
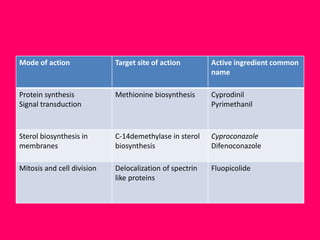
New generation fungicides with novel modes of action have been developed since 2001 that are more targeted and safer for non-target sites. These include fungicides that affect respiration, cell membranes, protein synthesis, signal transduction, and cell mitosis. Many important plant diseases that were previously not well-controlled can now be managed by these new systemic fungicides. The discovery process for fungicides has changed over time from broad-spectrum to more targeted site-specific and novel action chemistries. These new fungicides are more eco-friendly as they can be used at lower doses than earlier compounds.