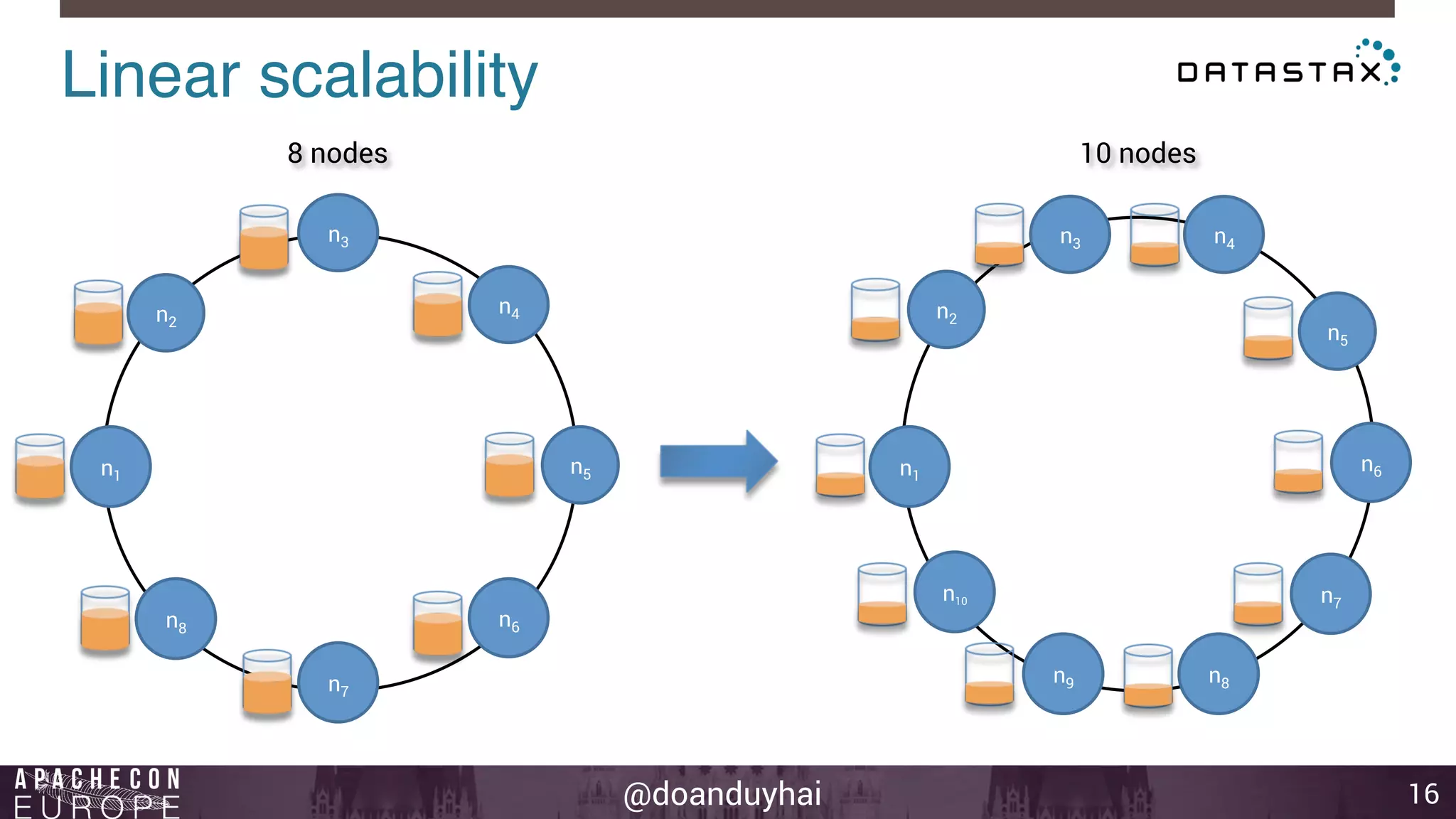
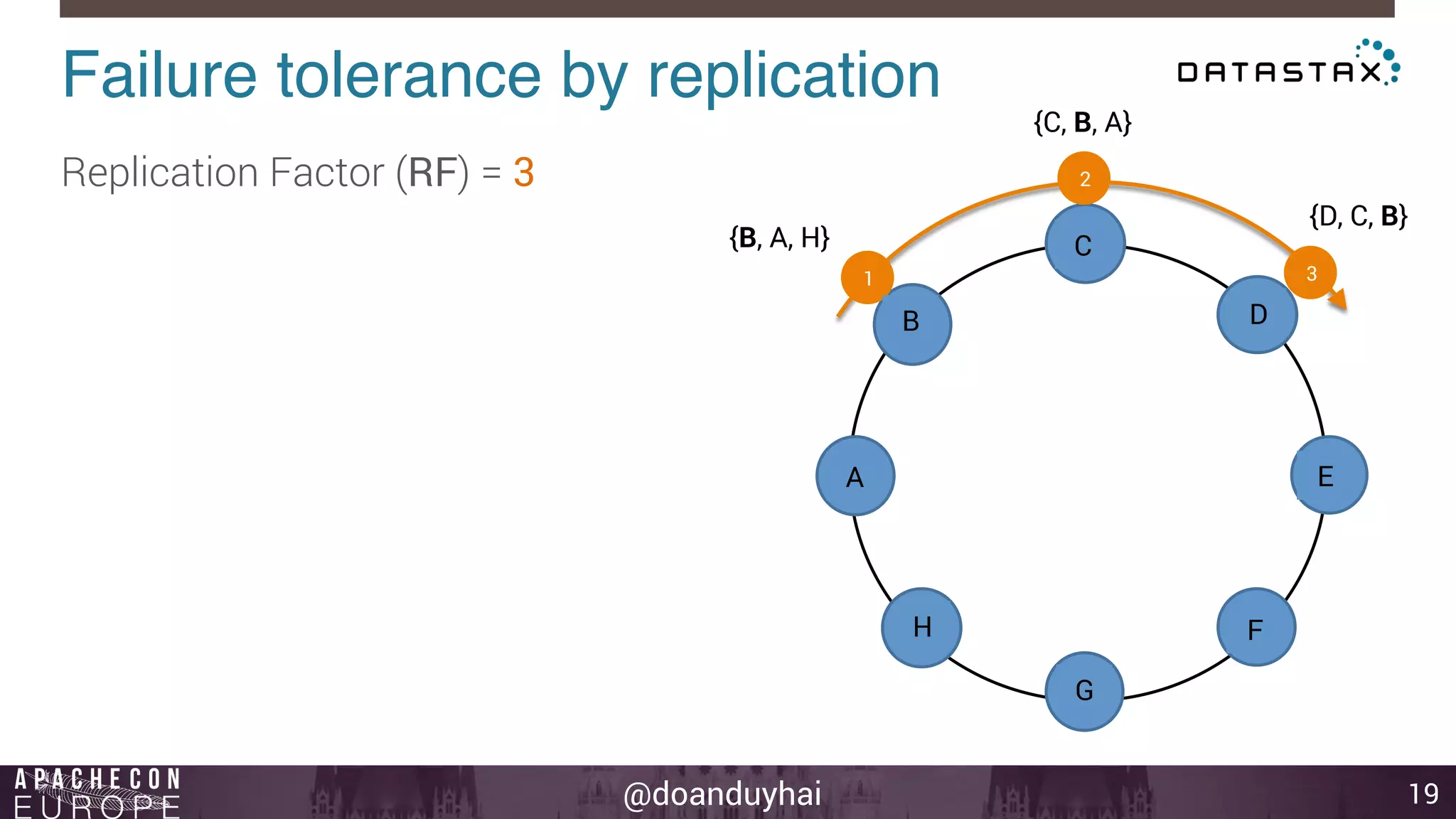
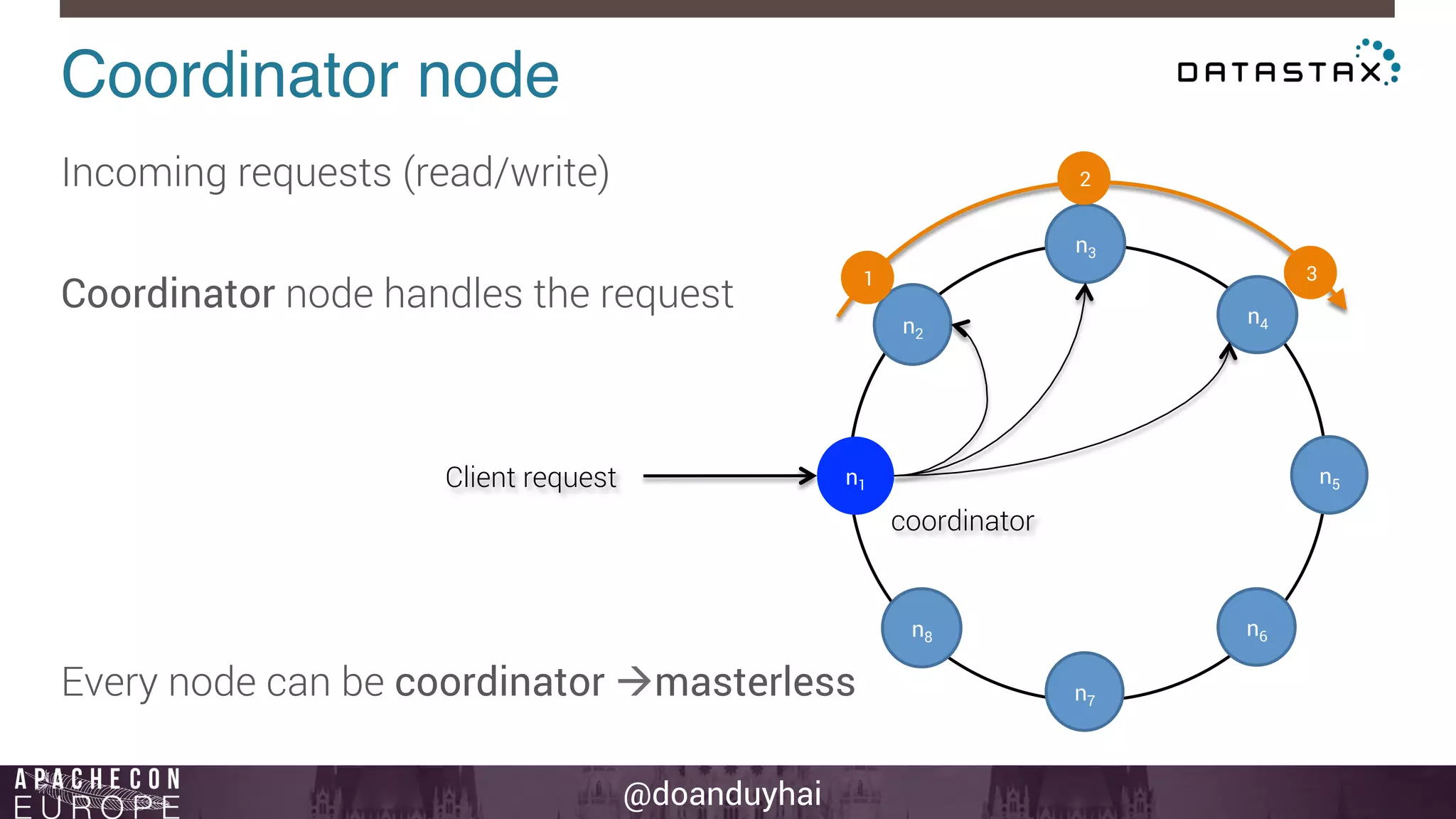
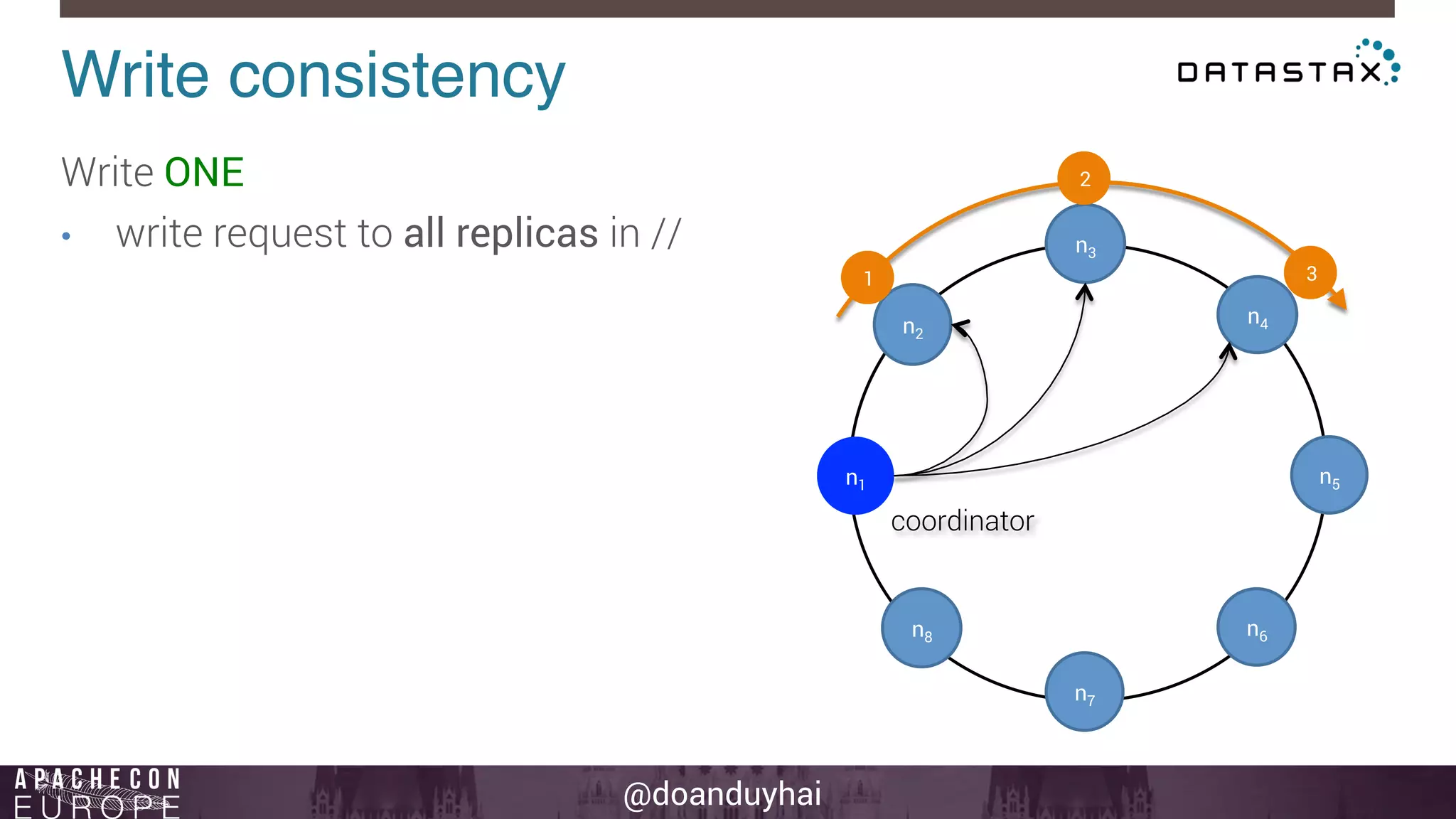
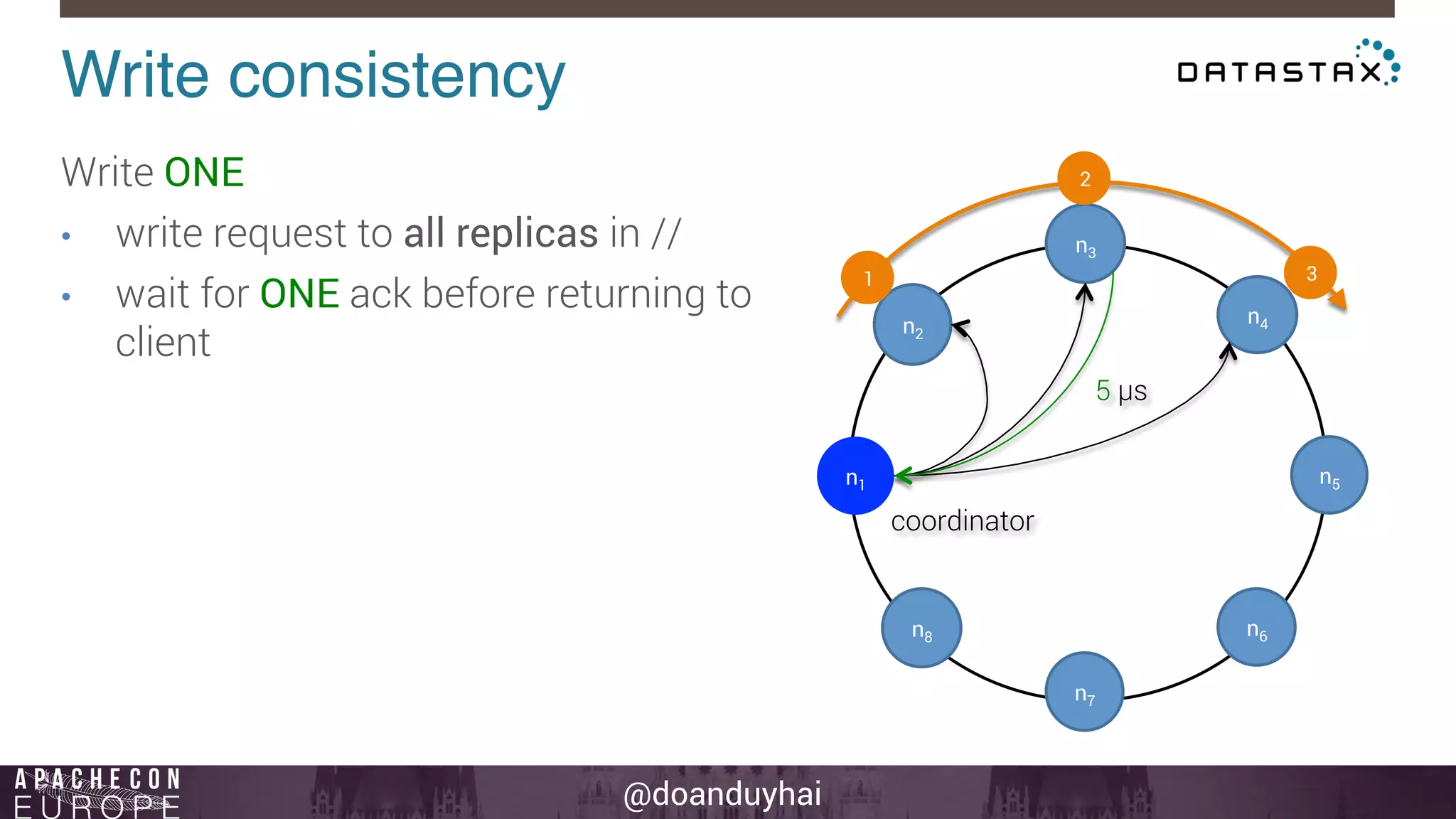
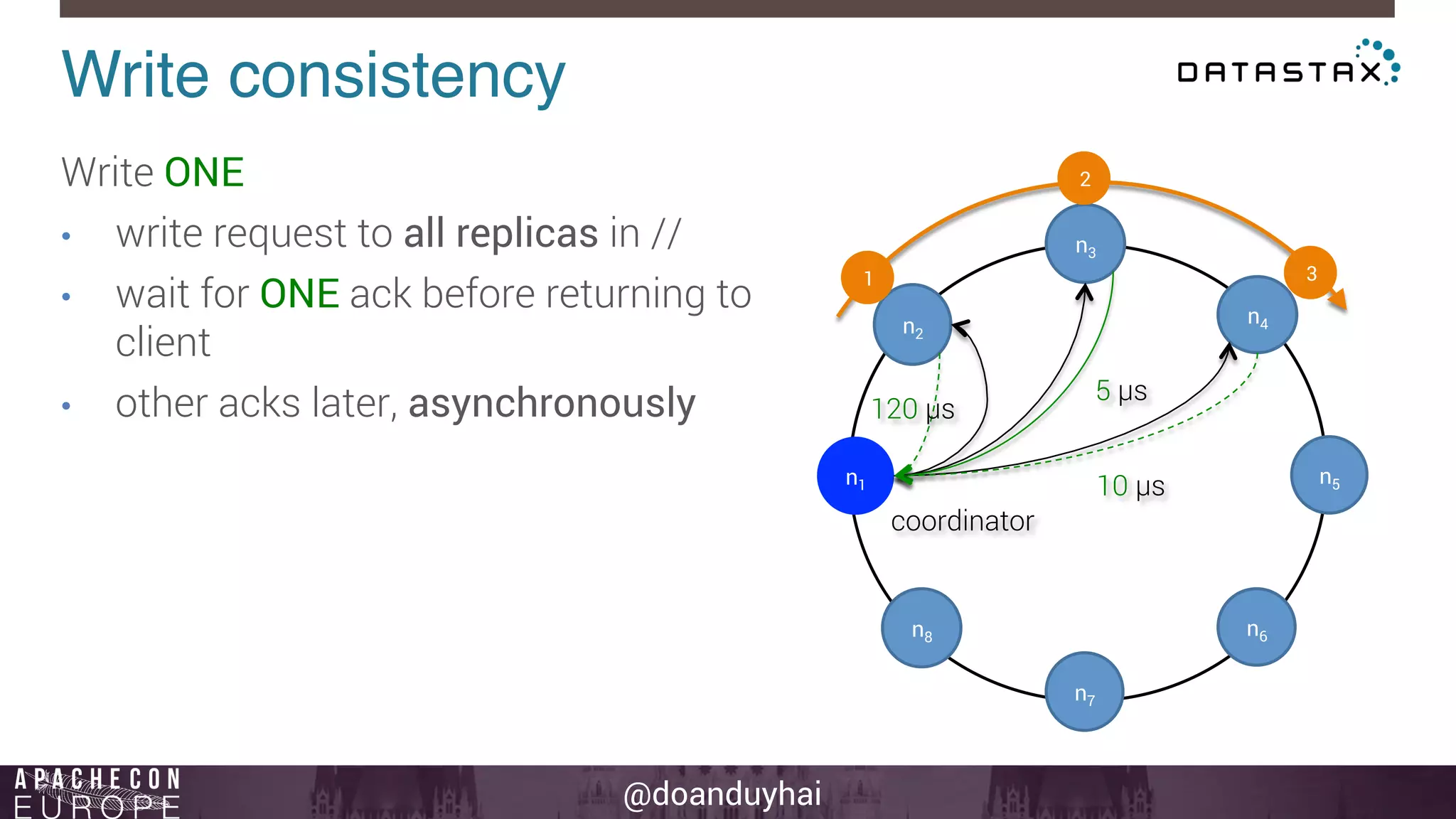
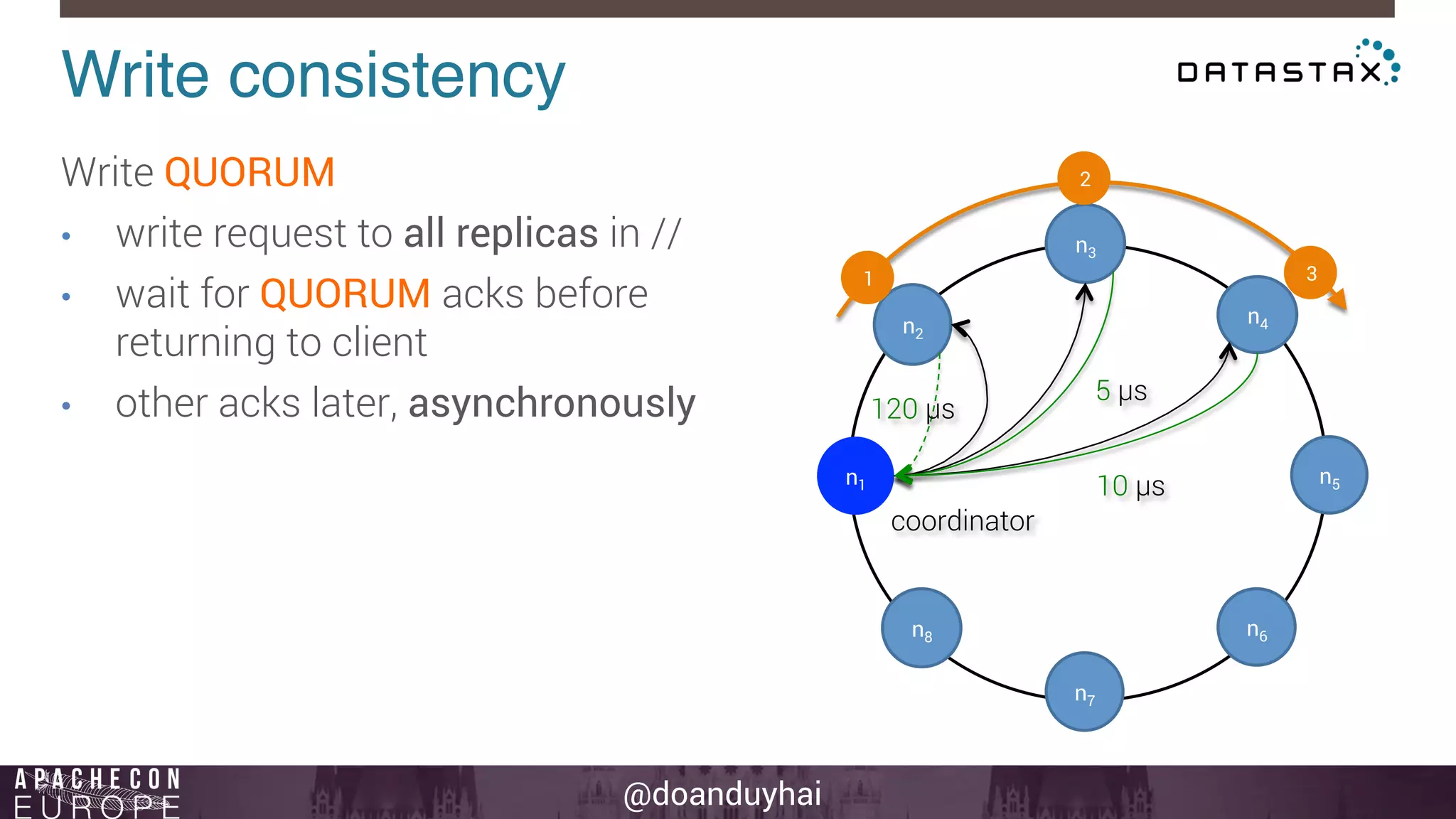
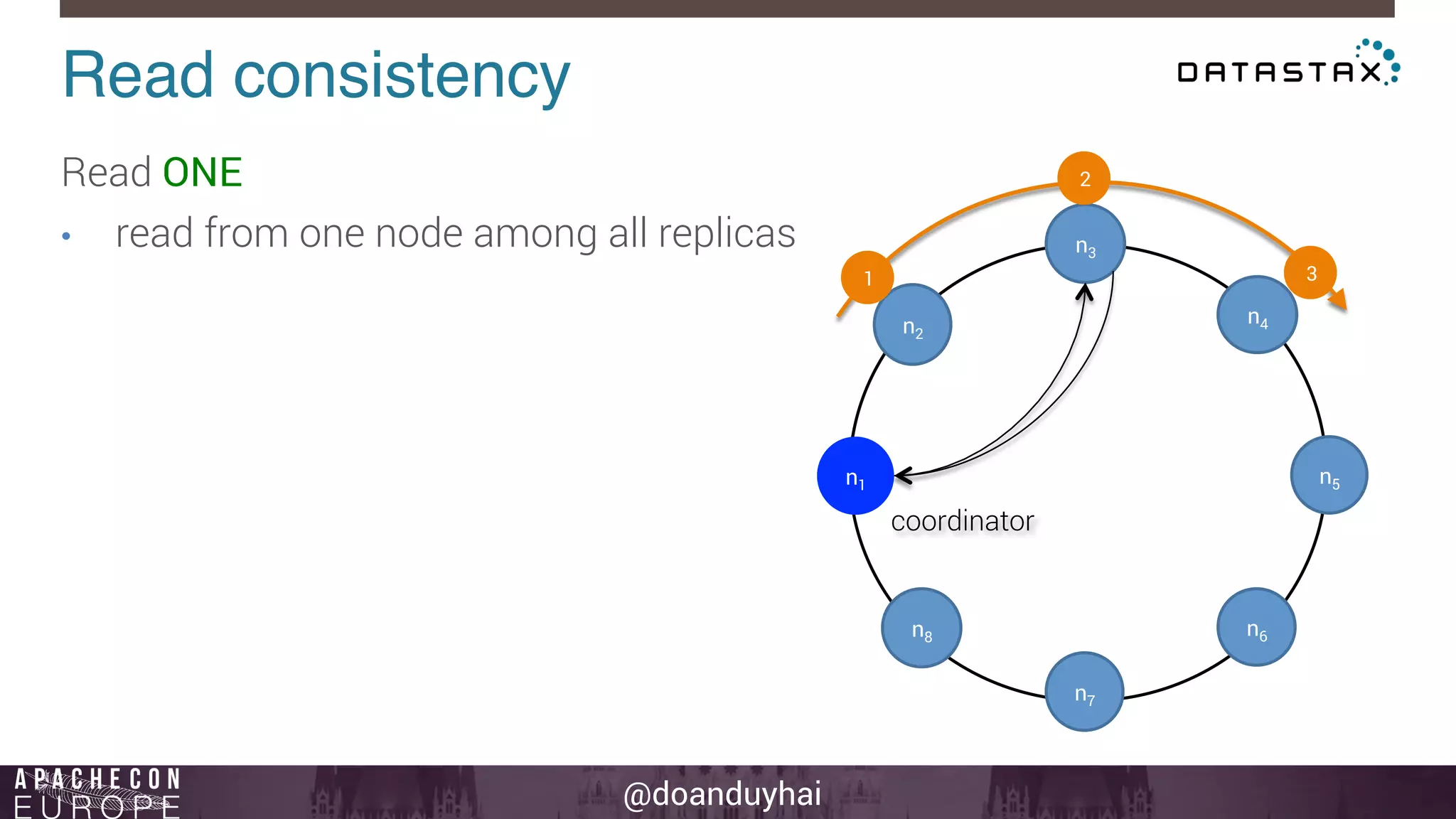
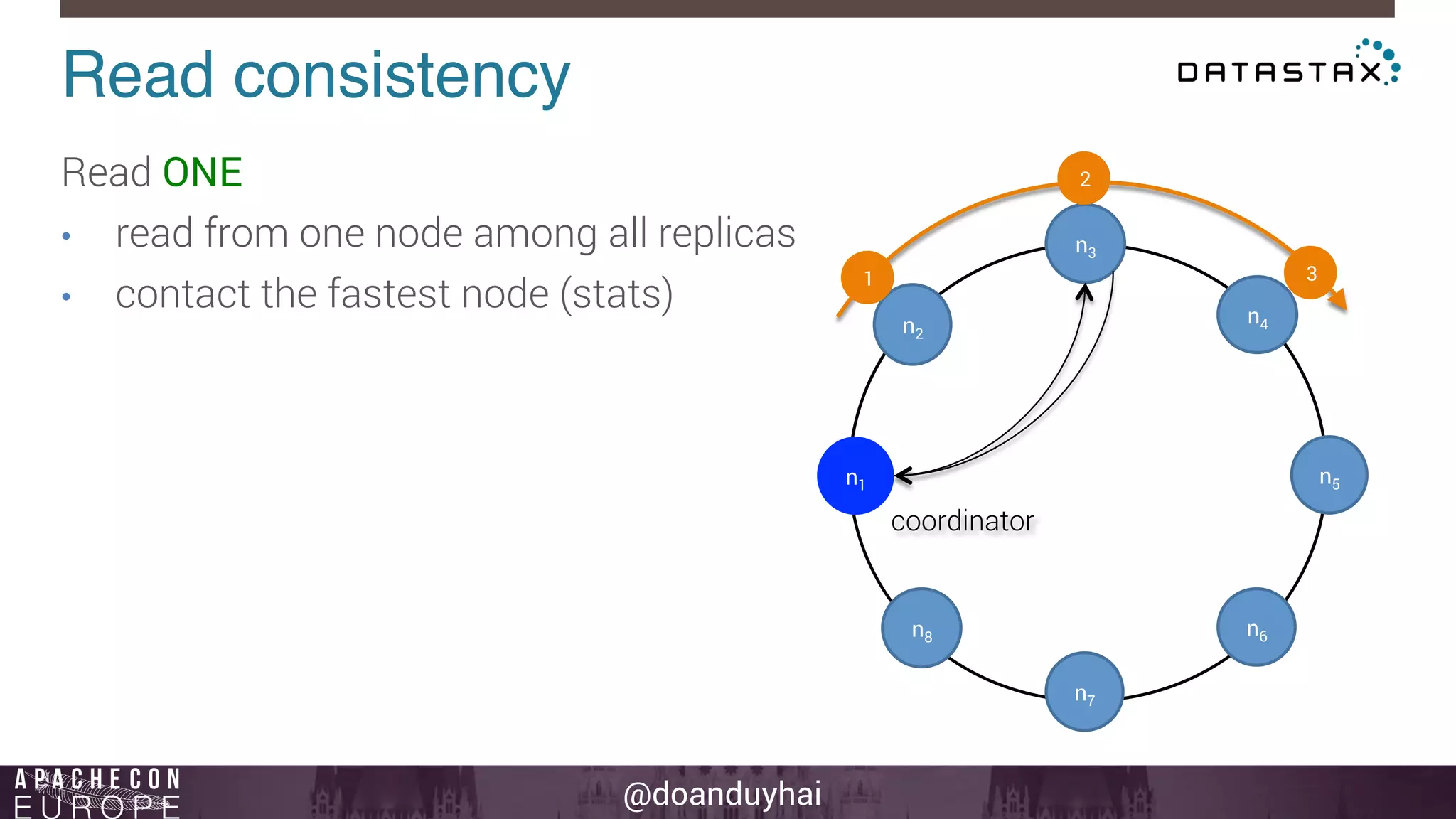
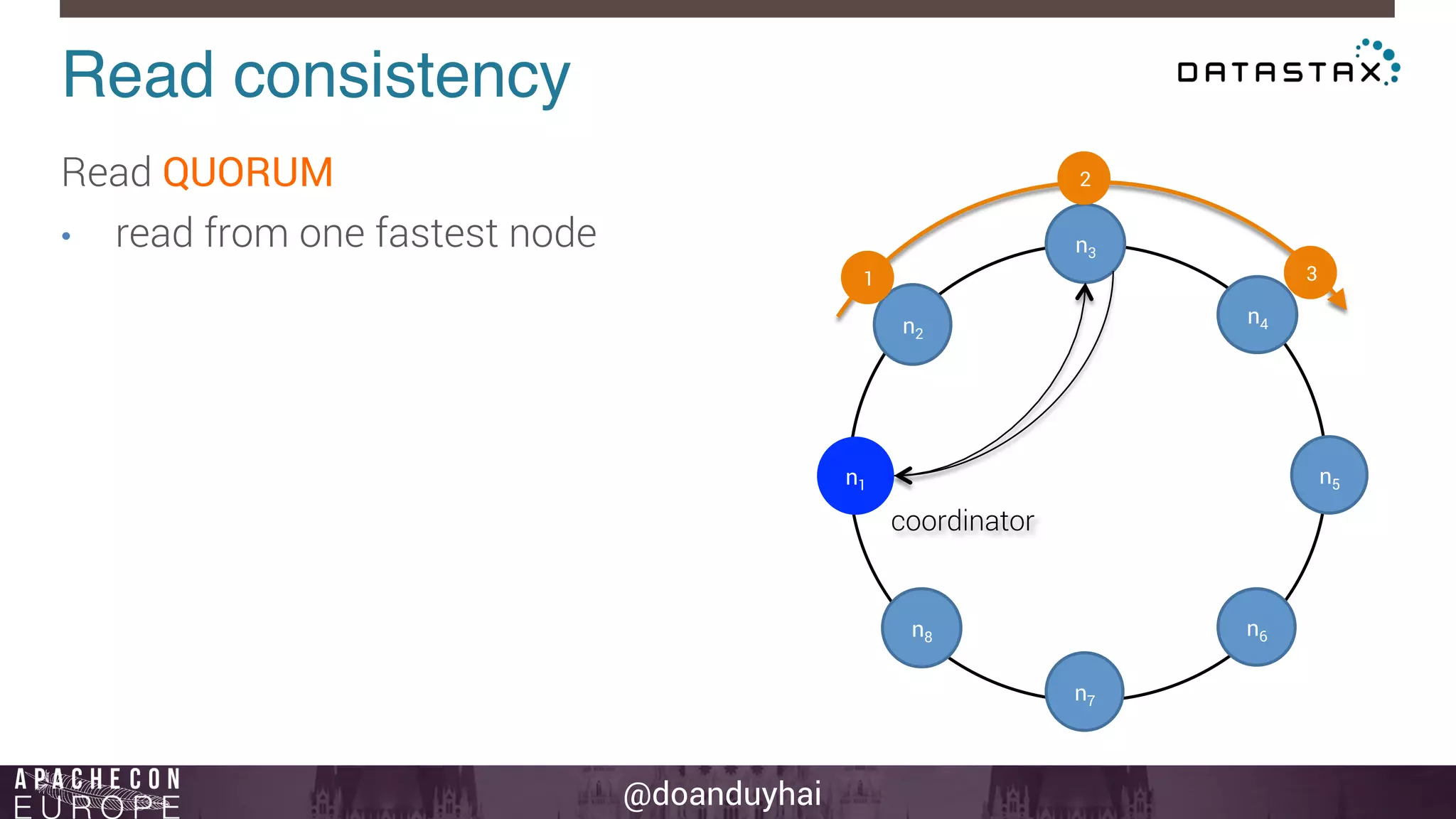
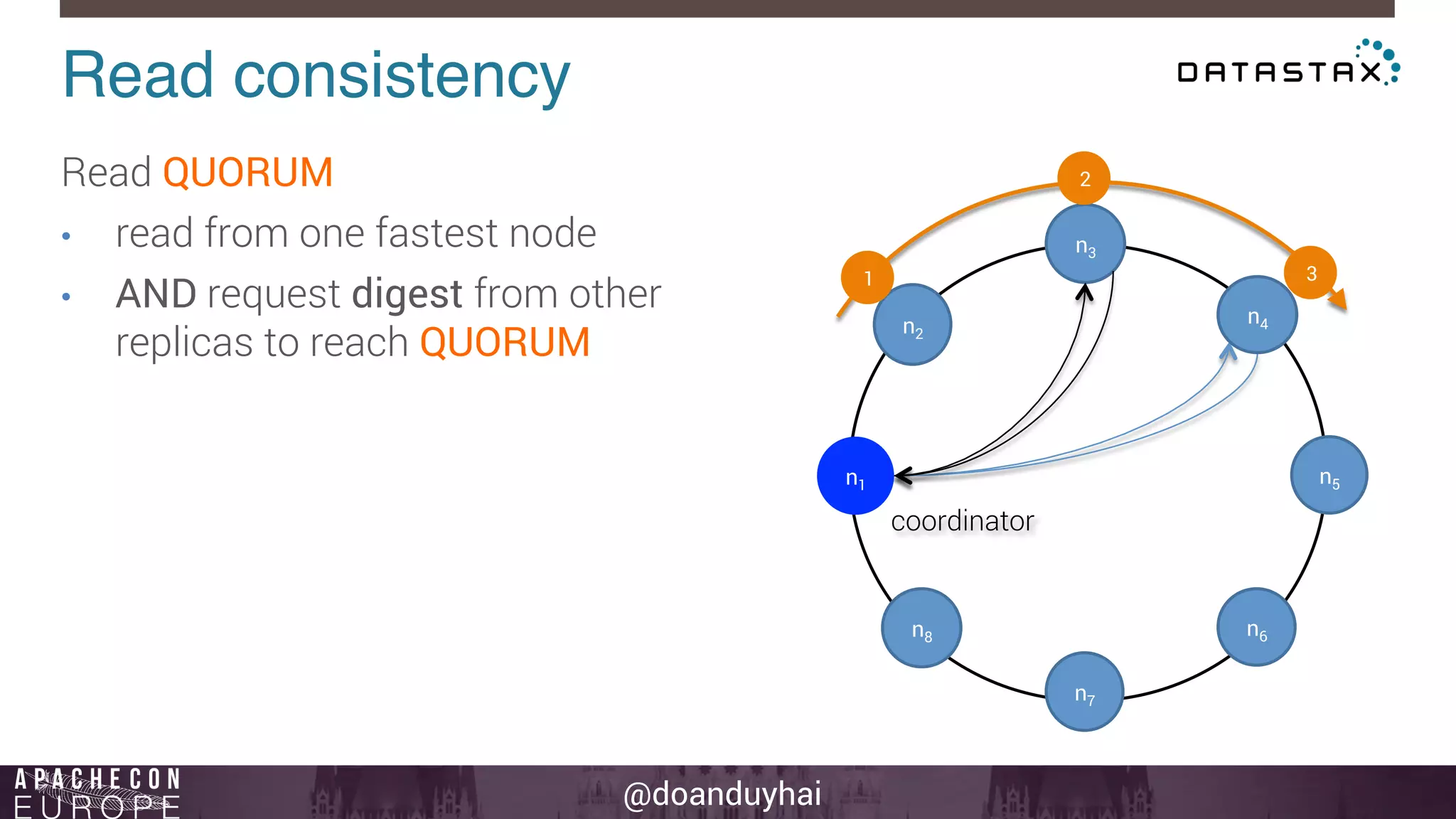
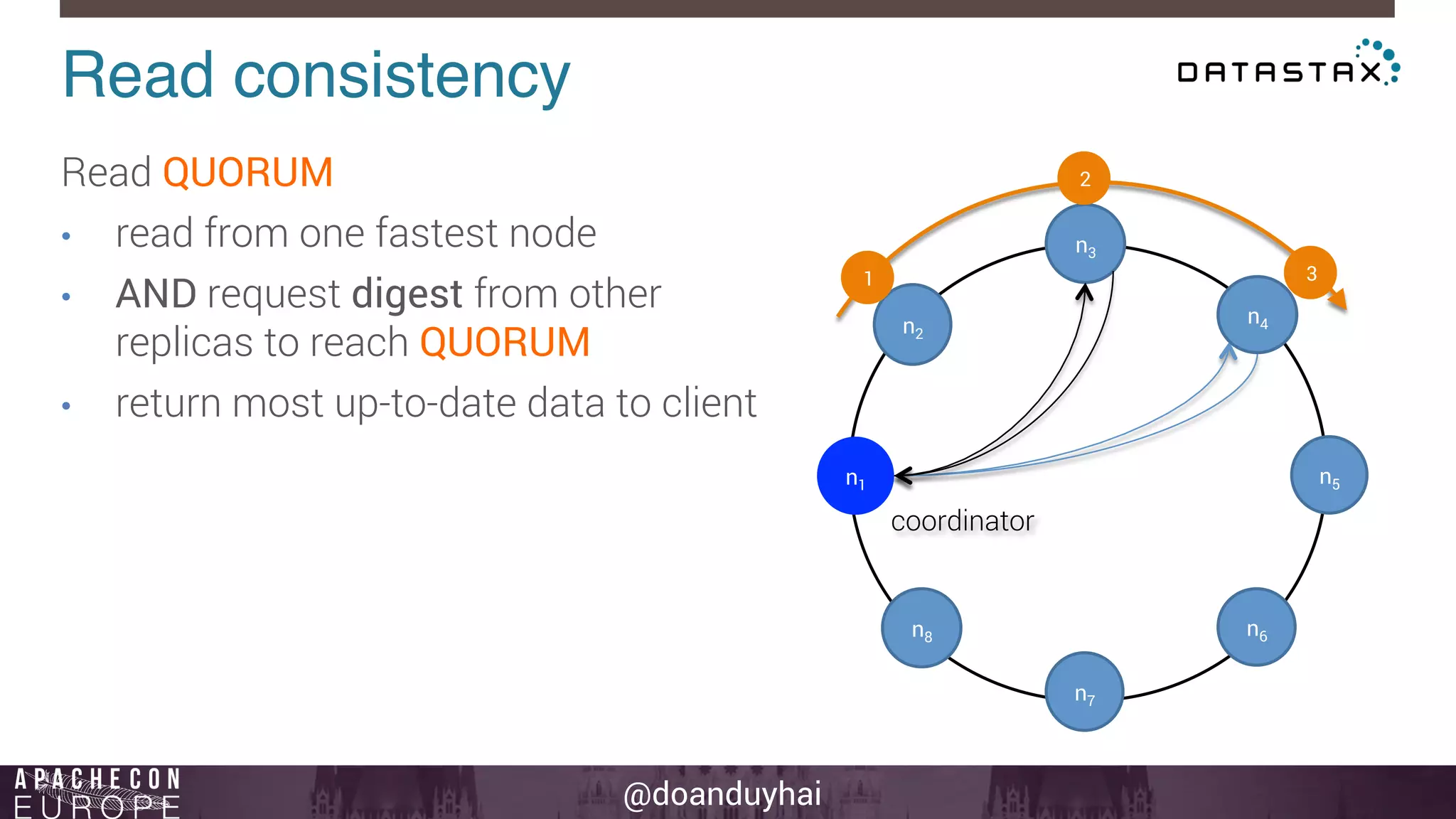
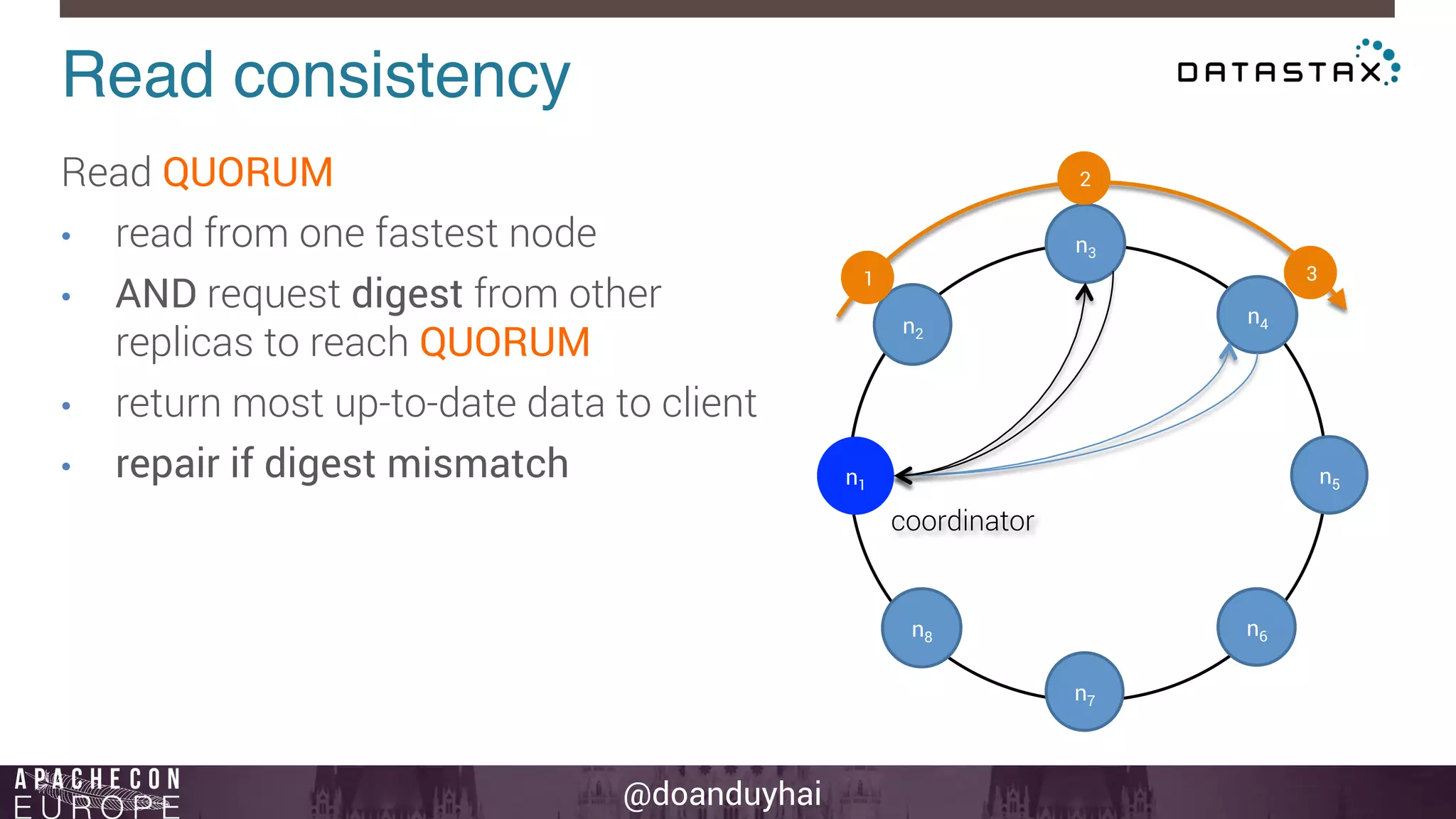
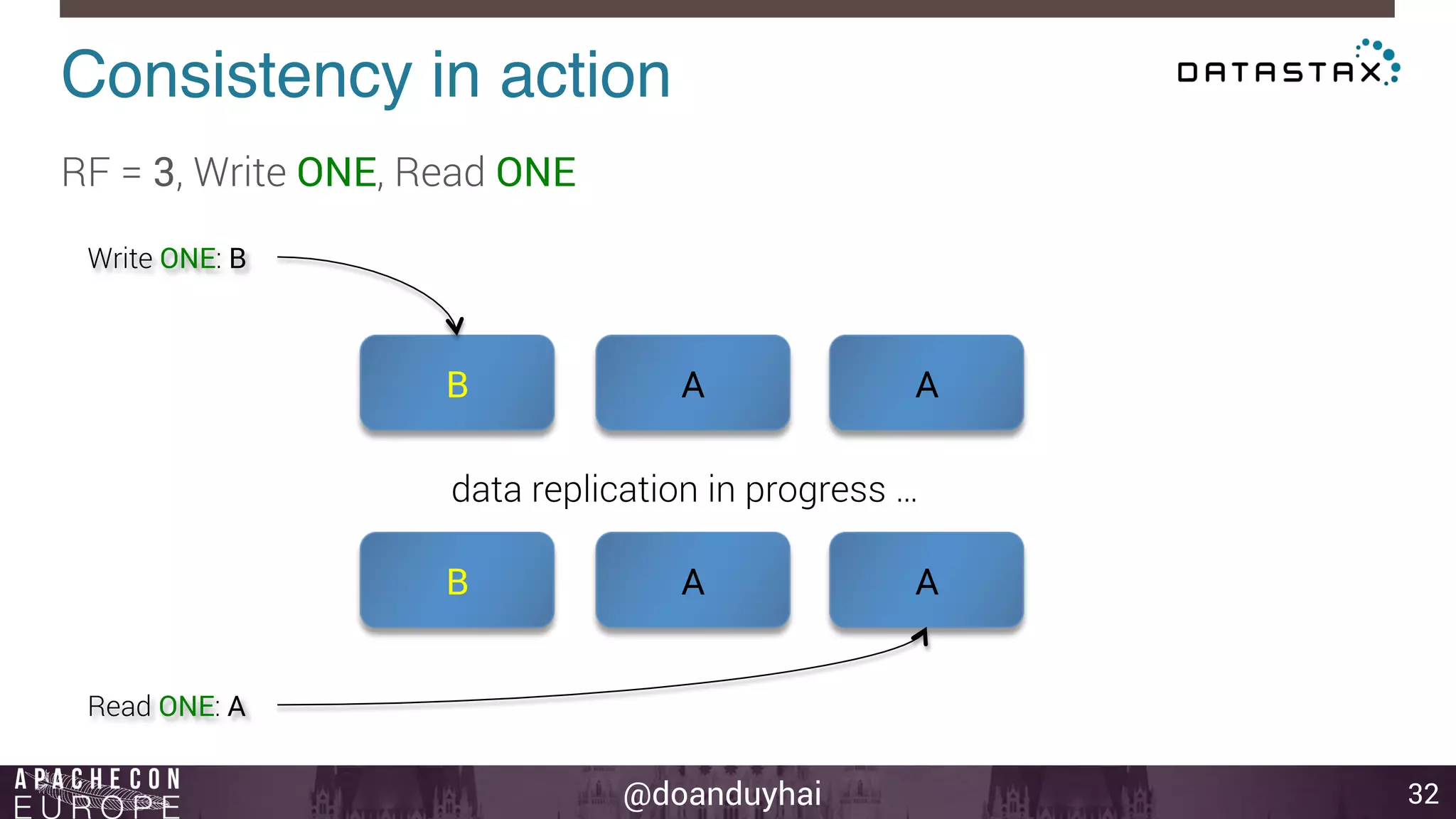
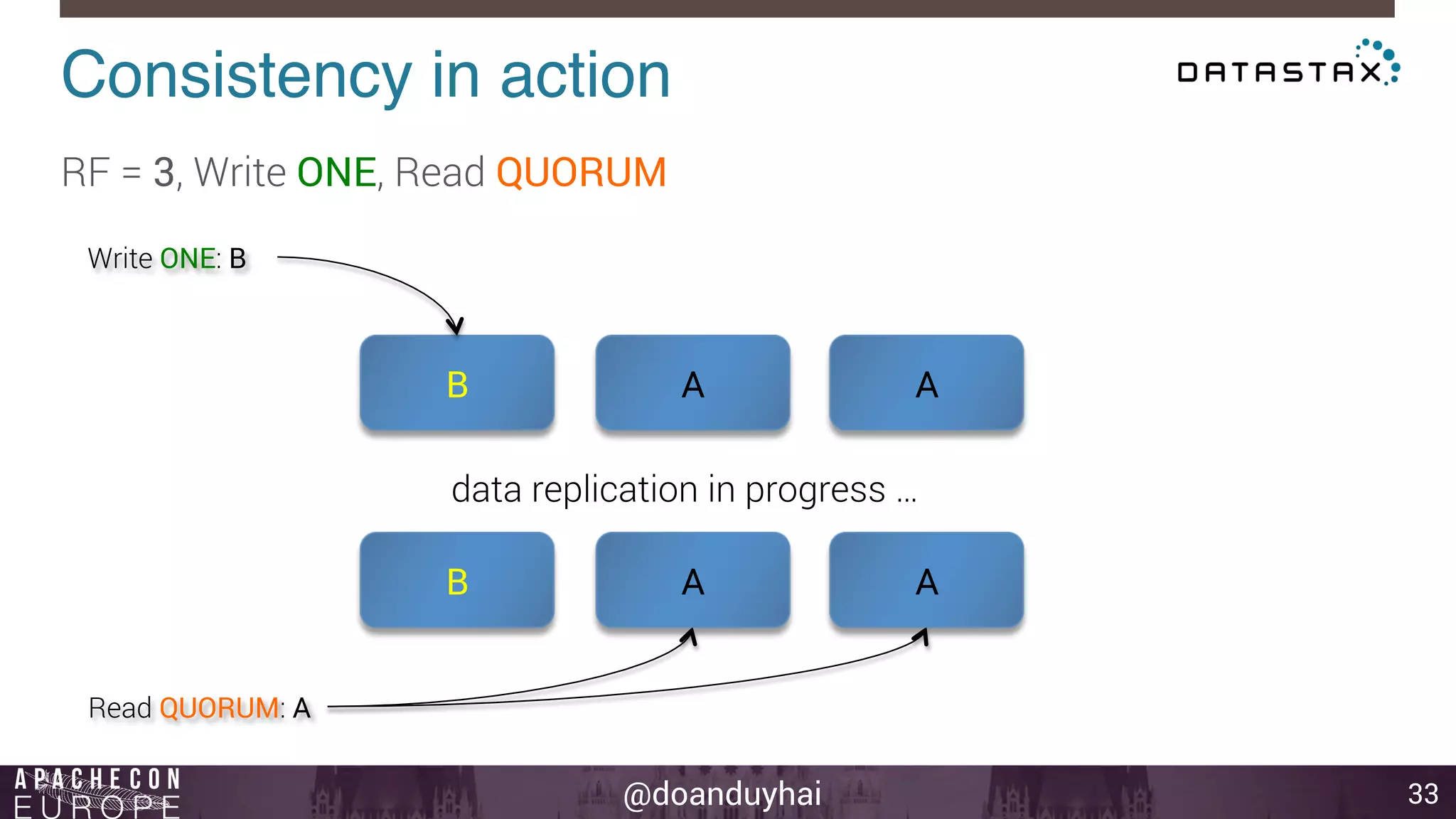
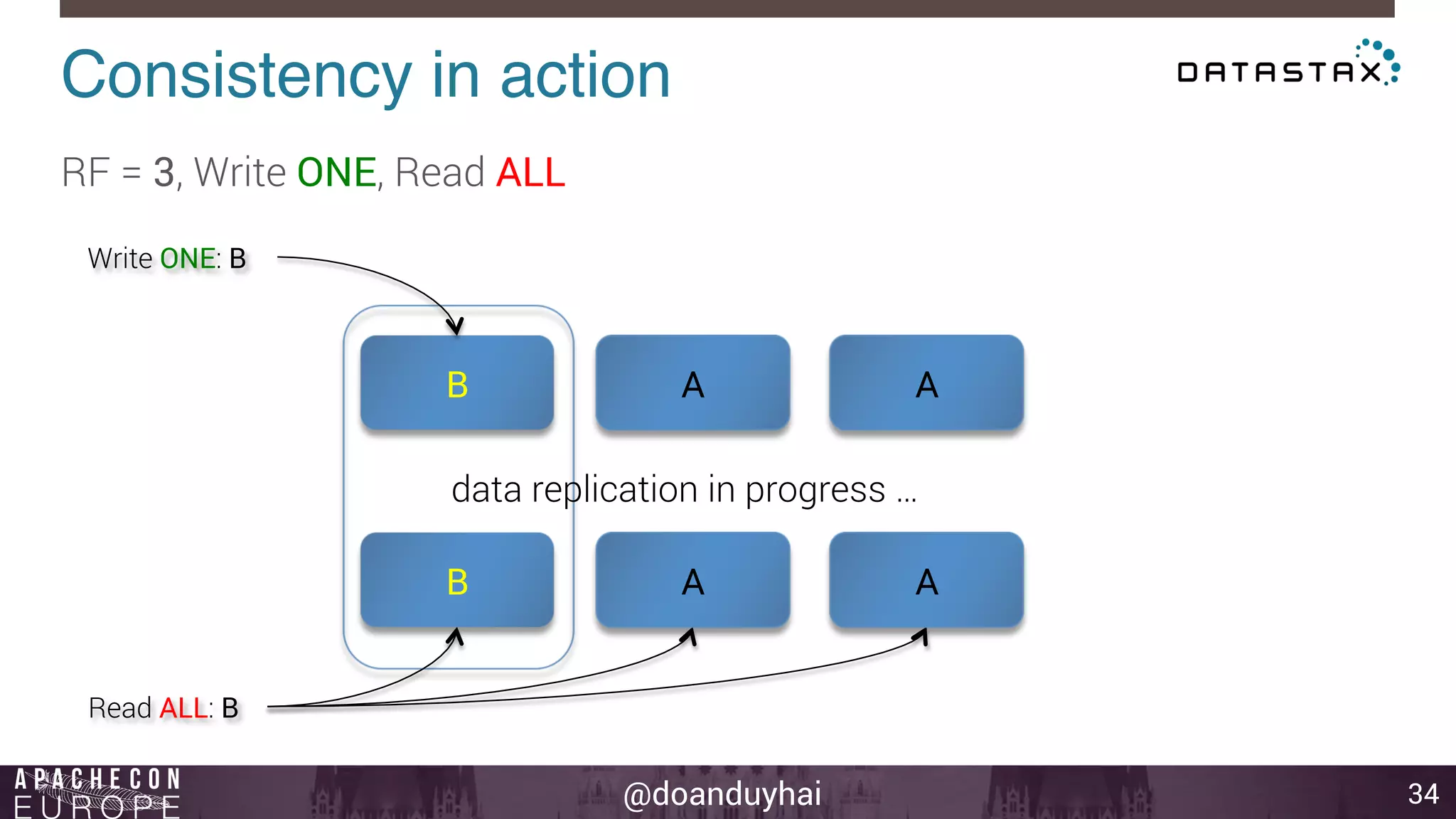
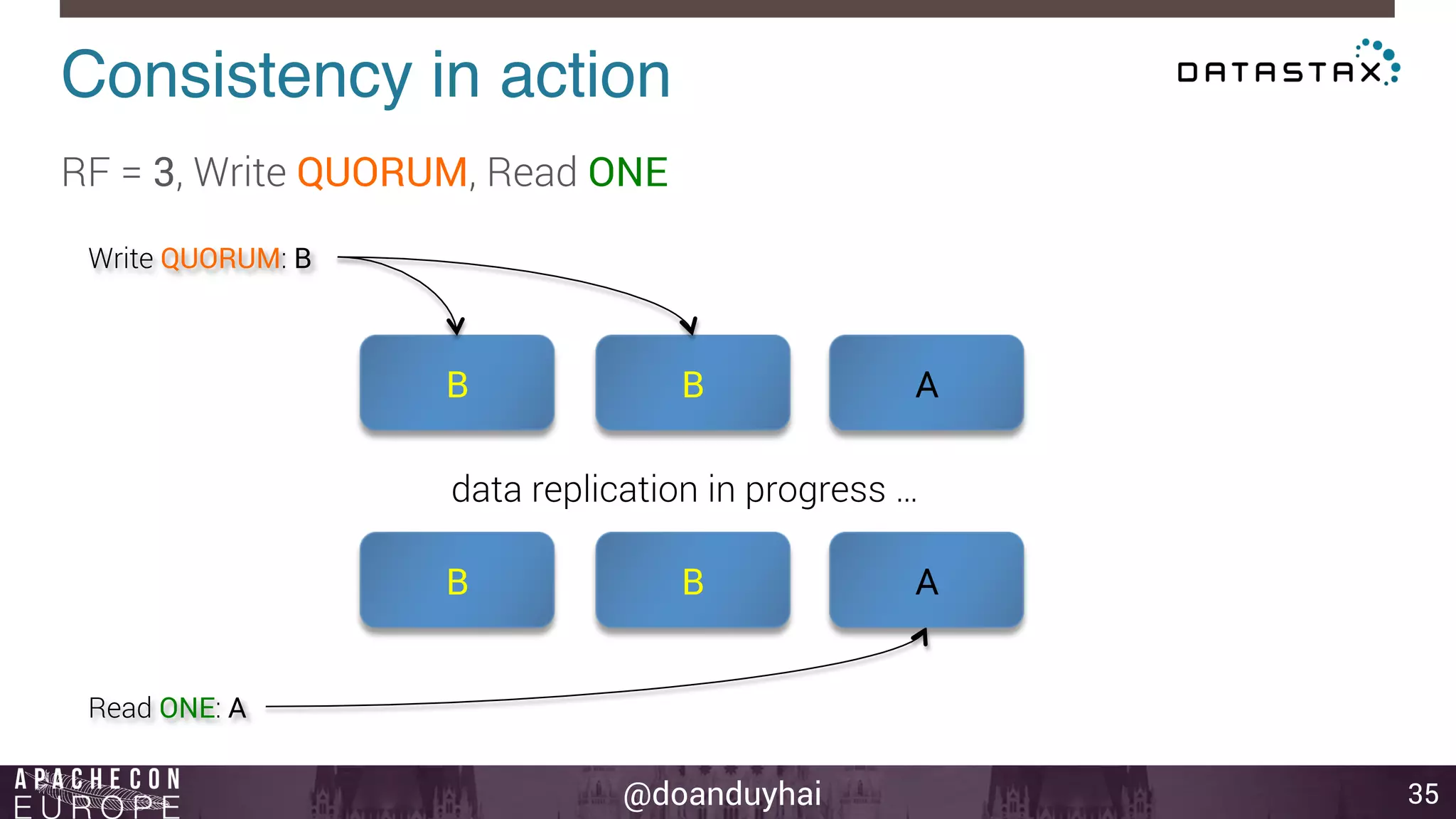
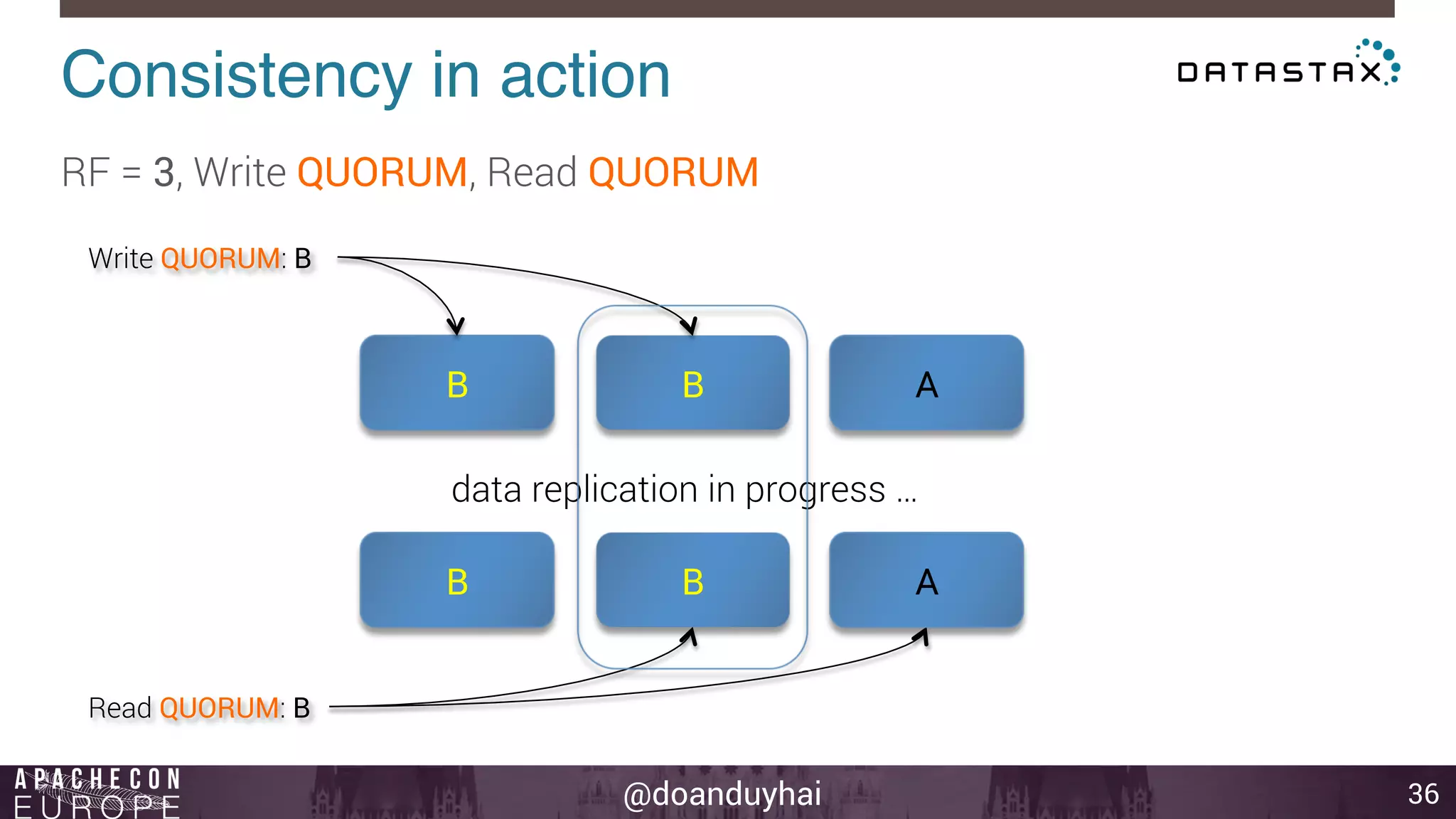
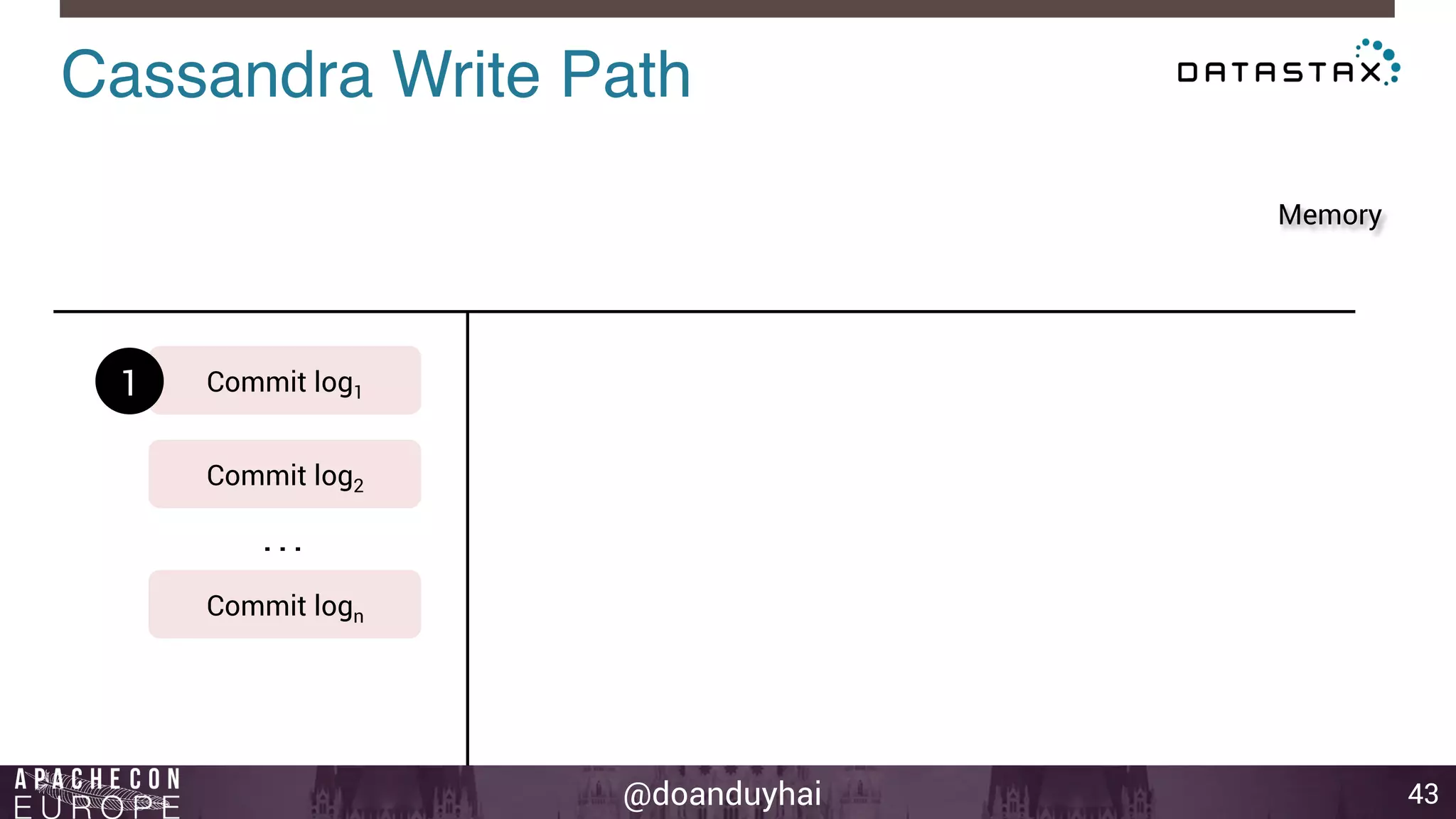
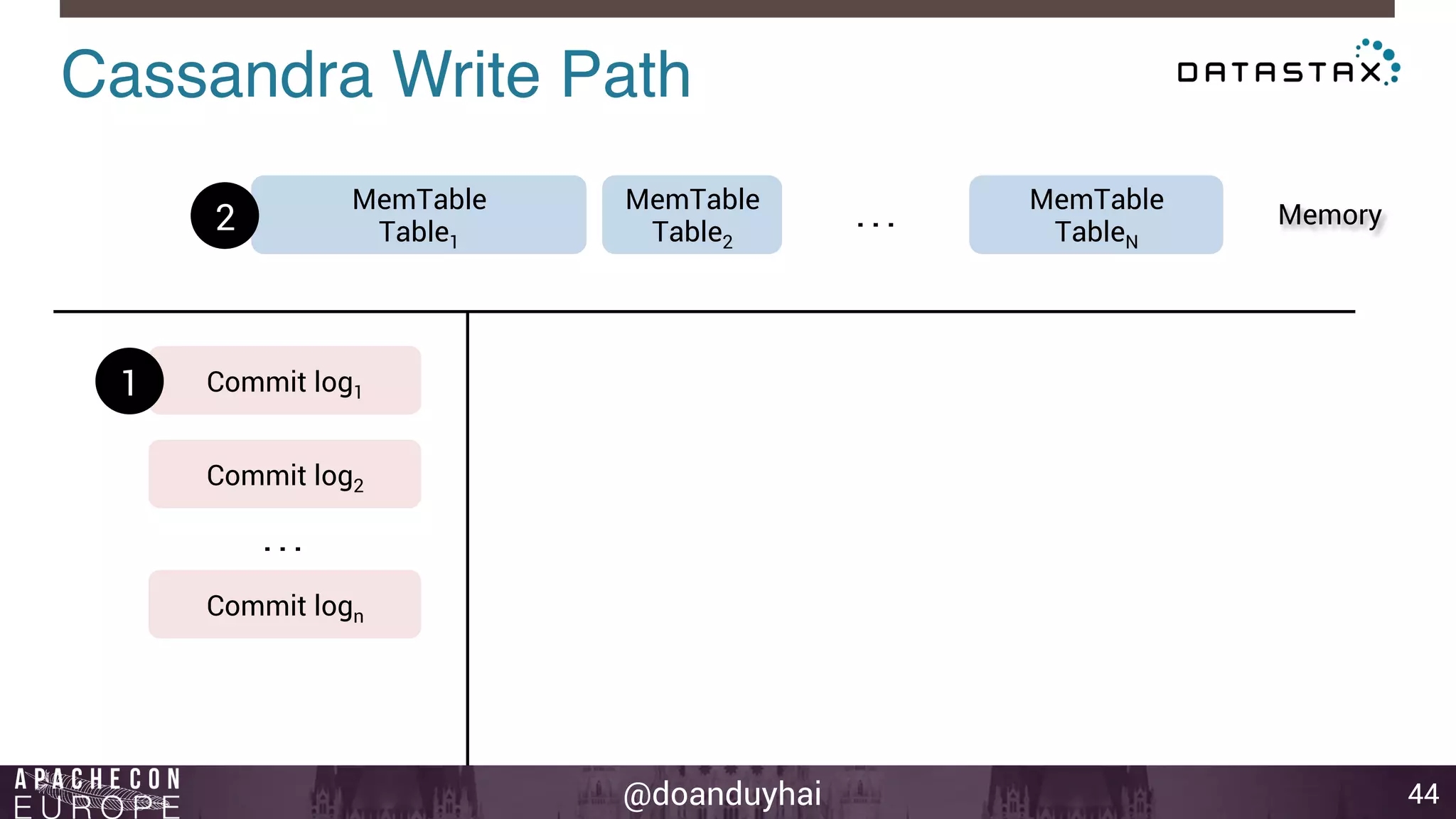
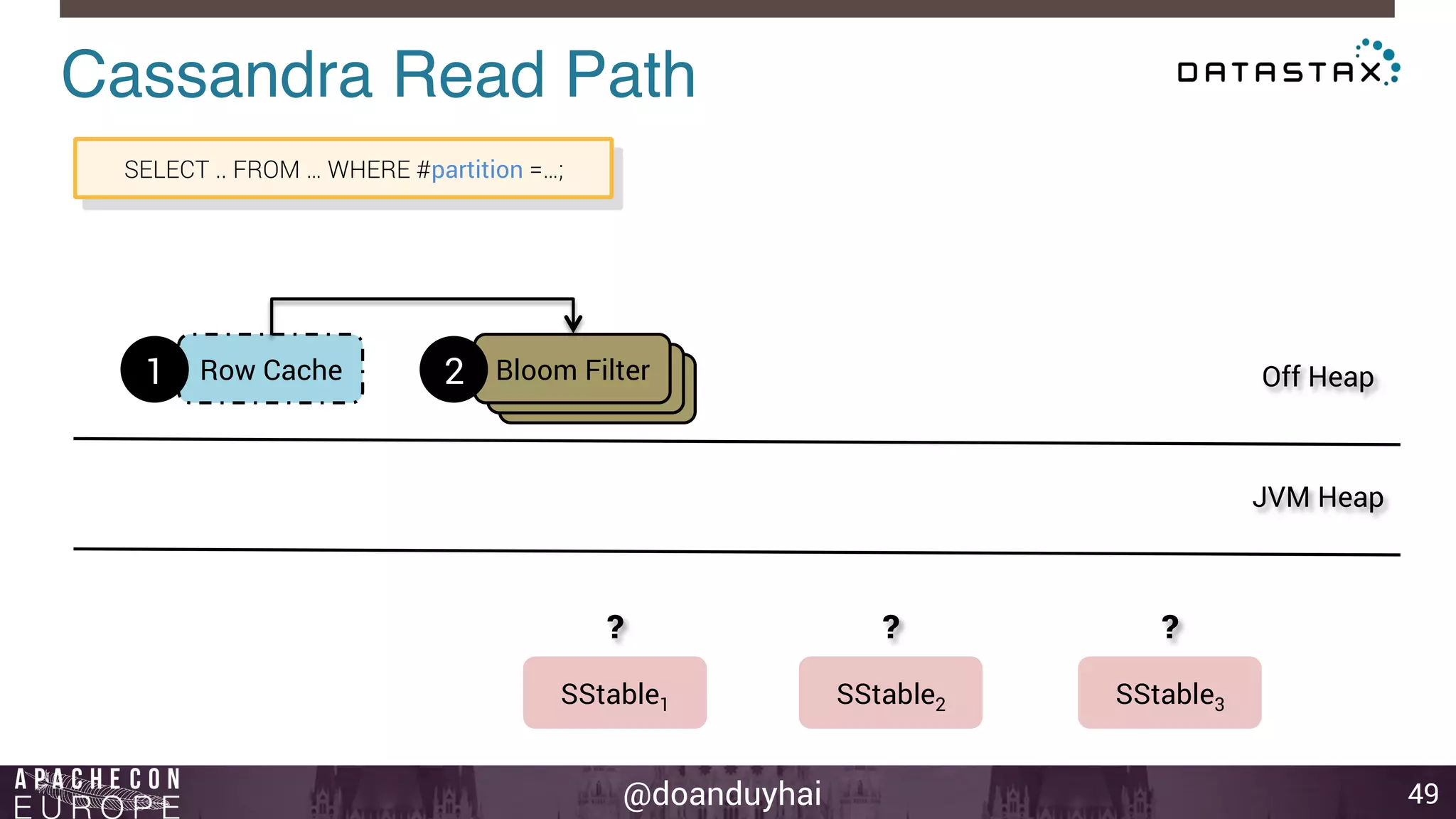
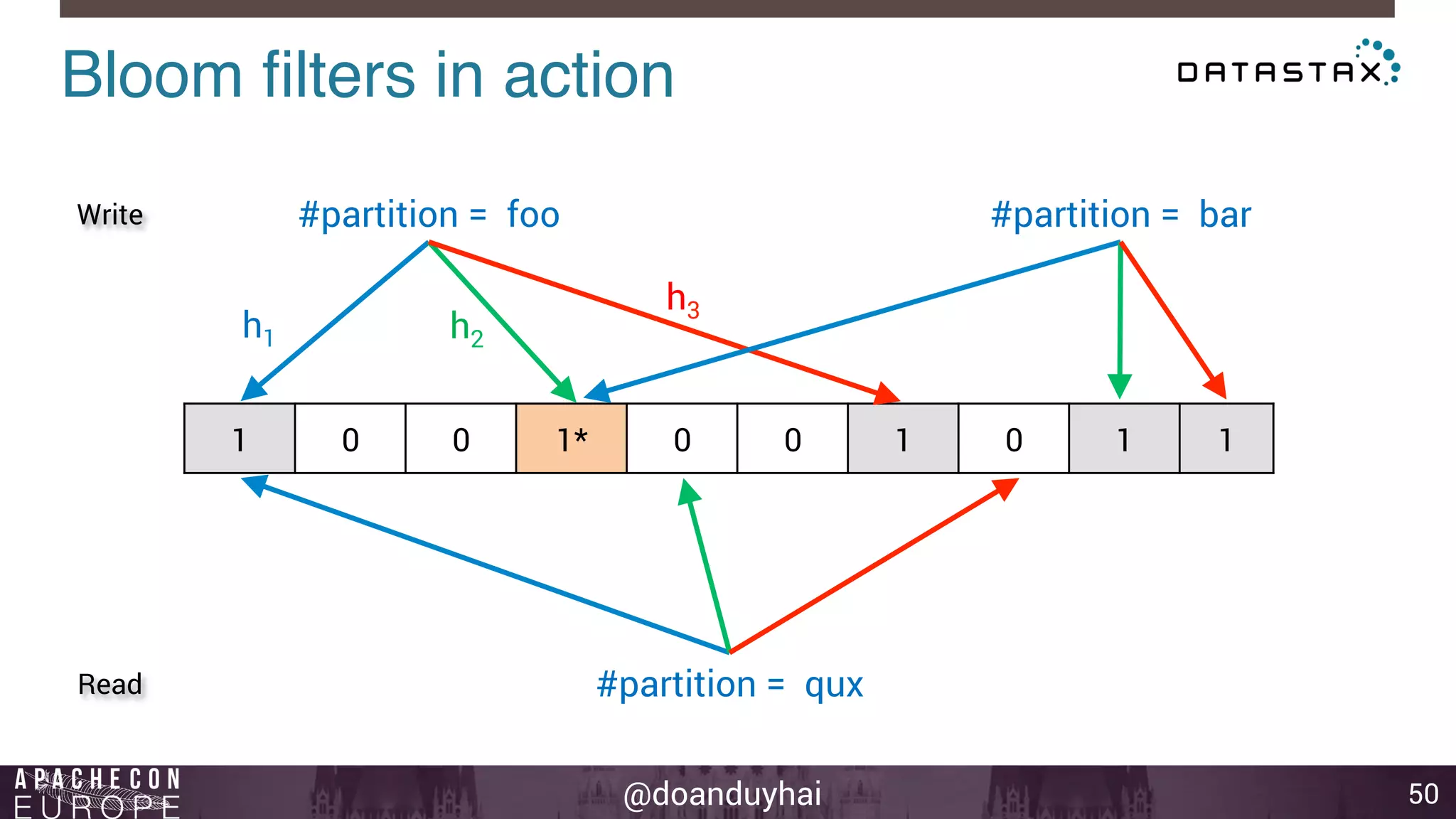
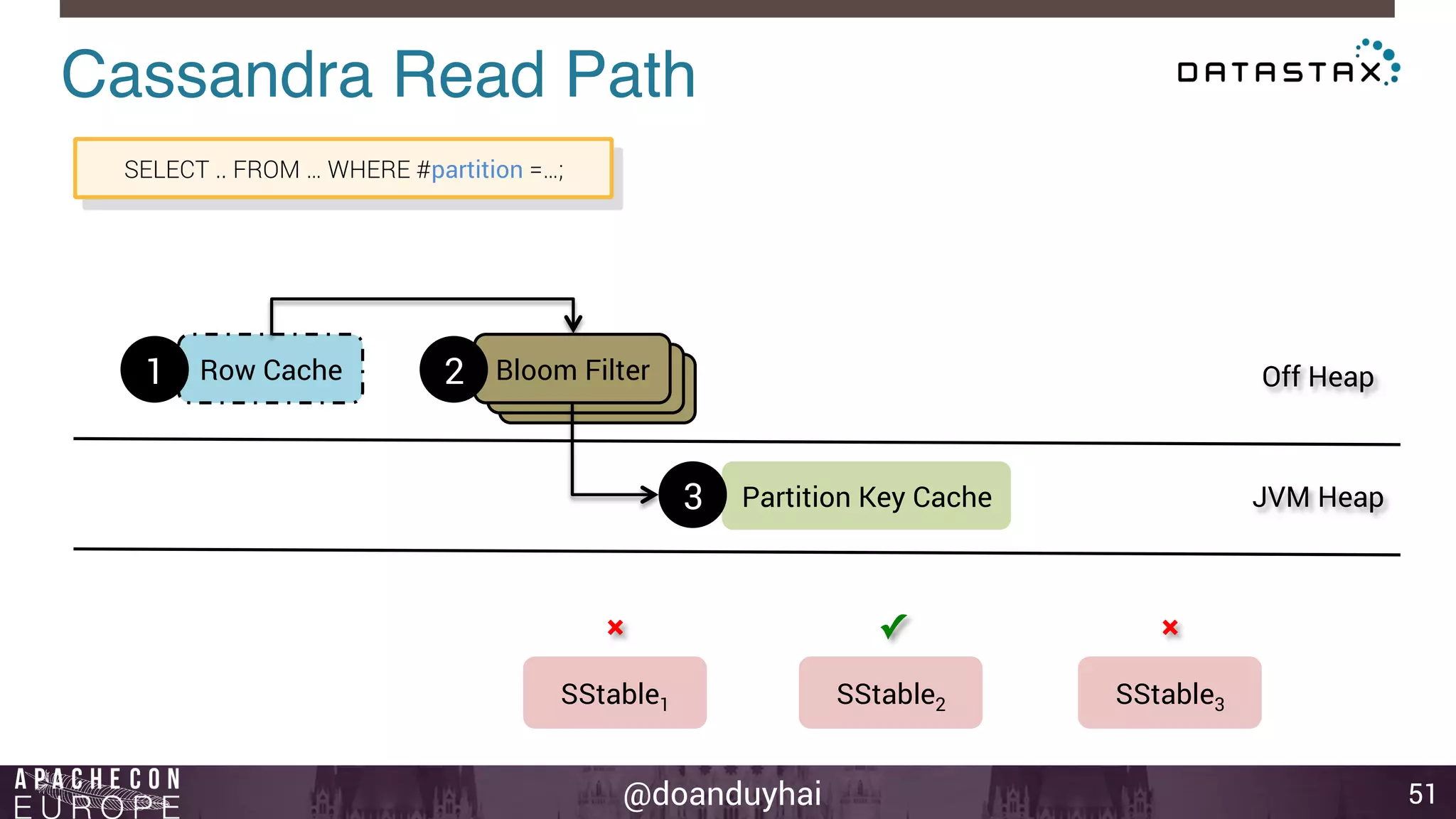
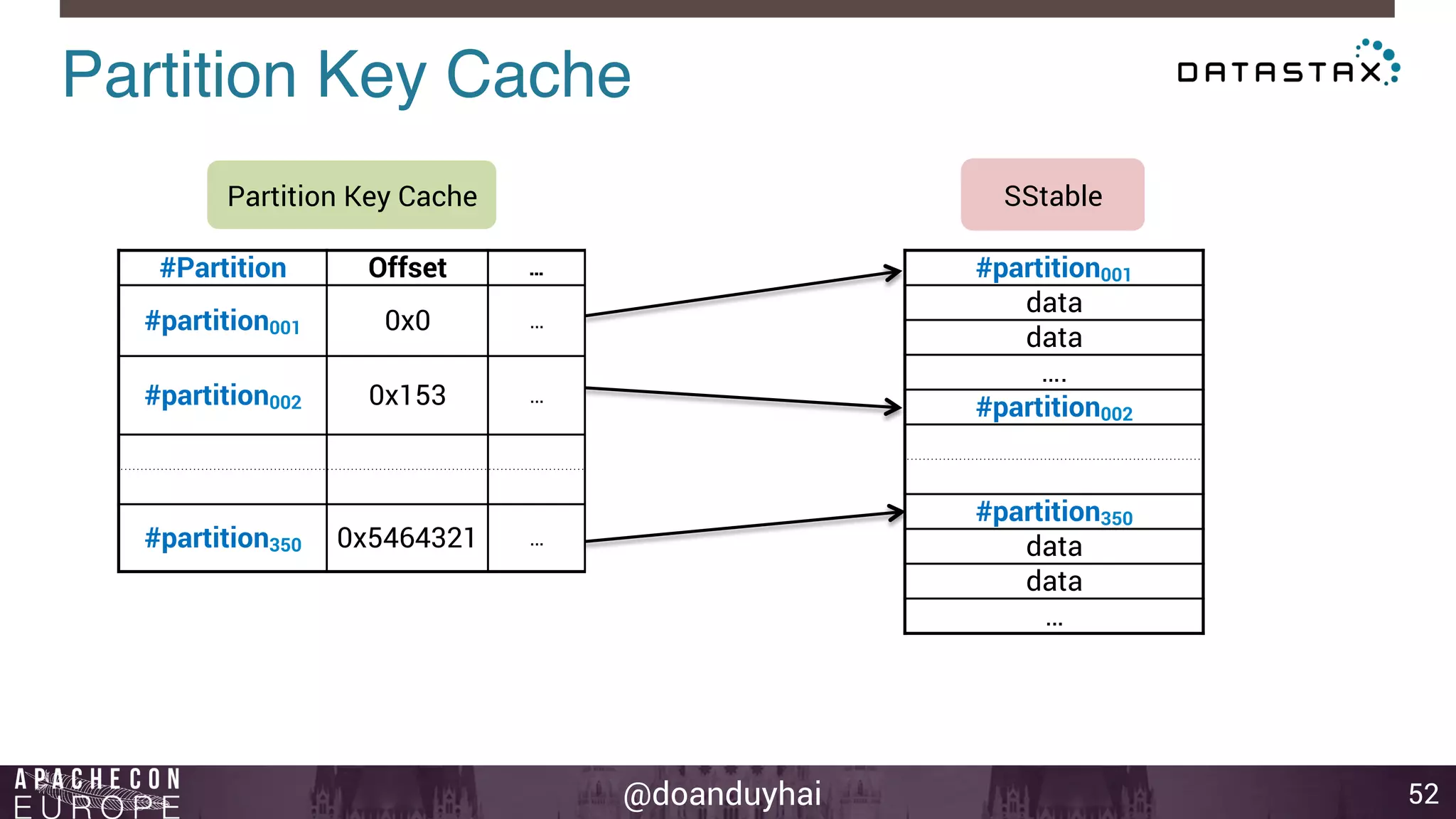
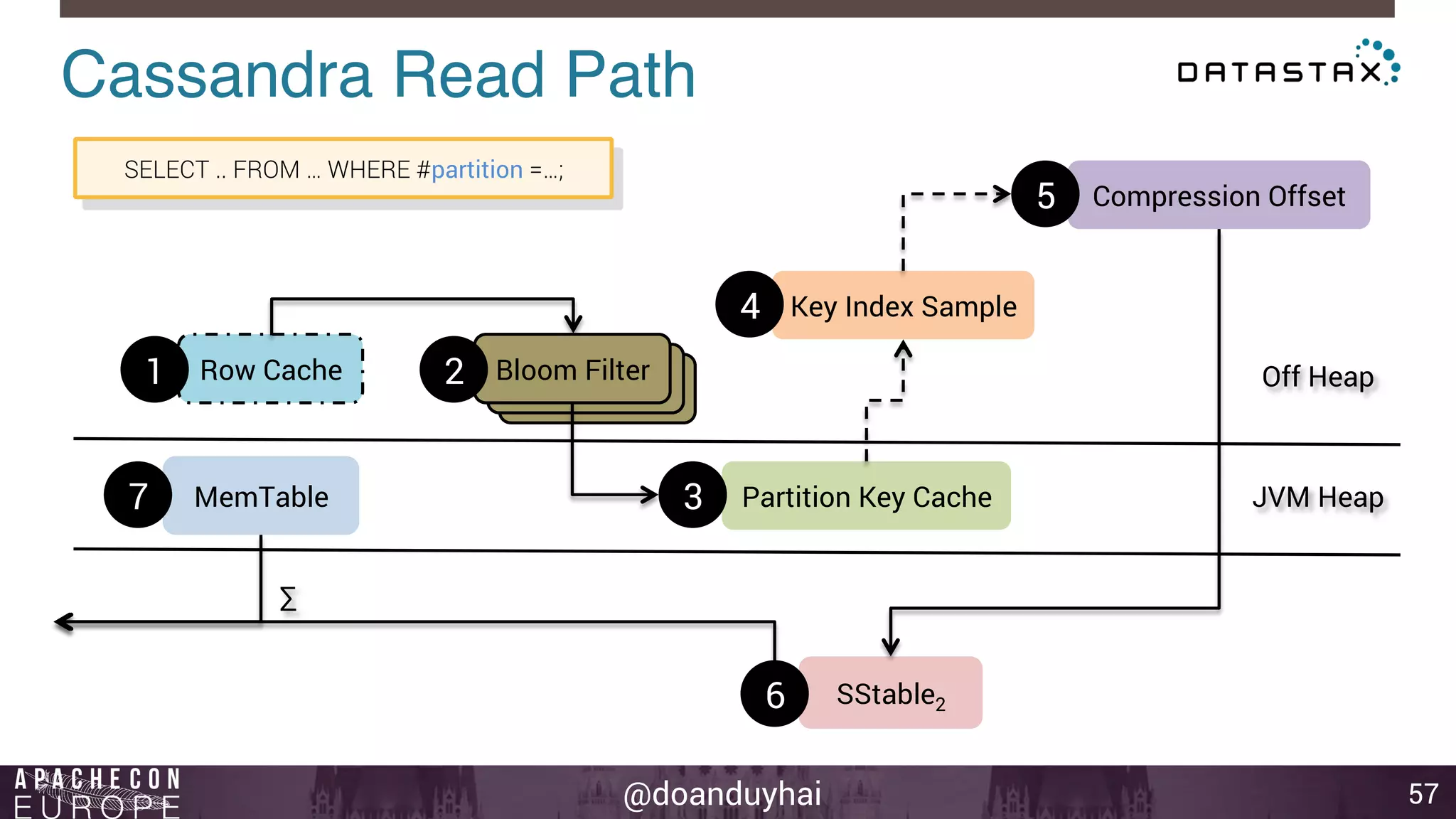
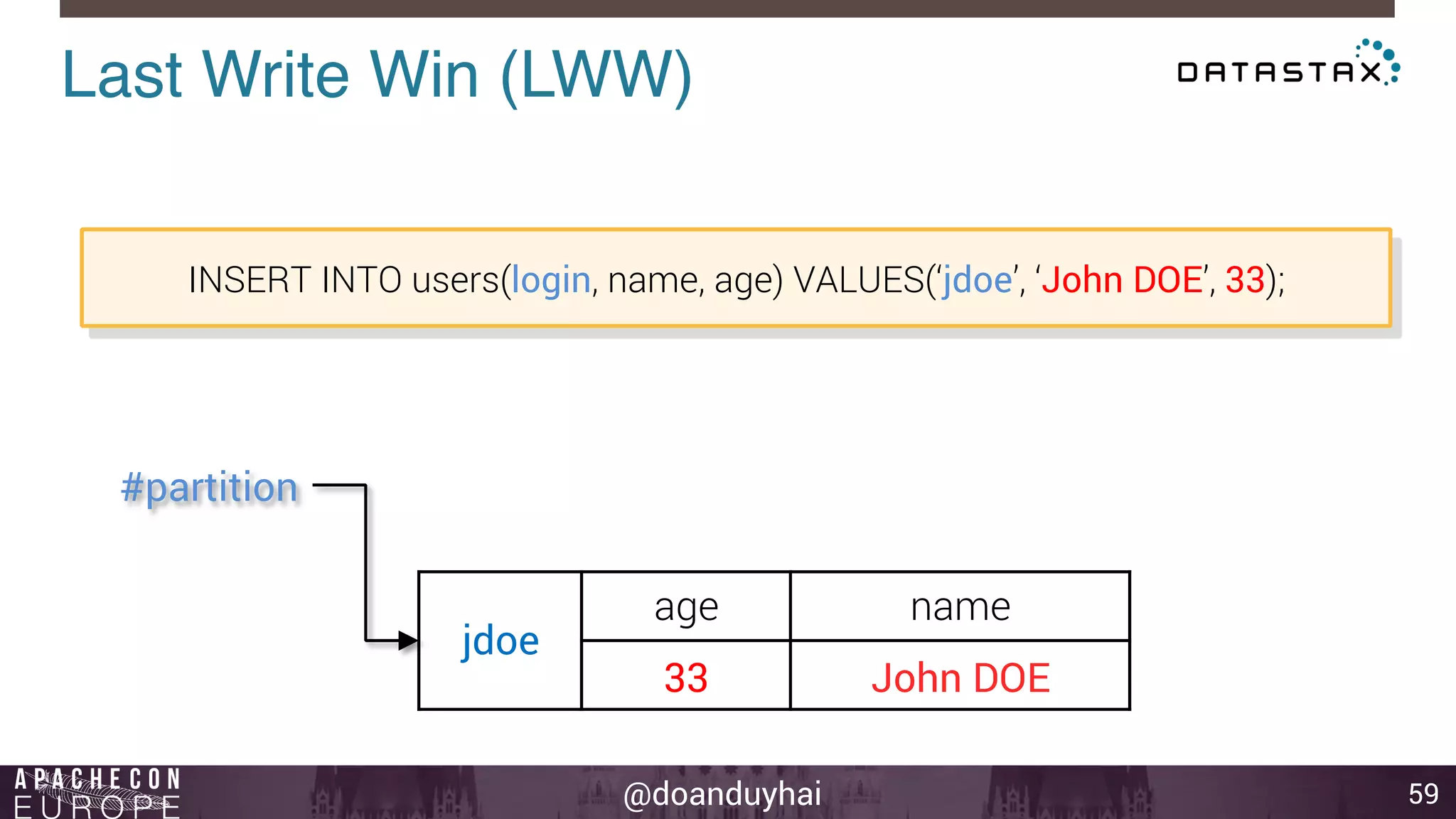
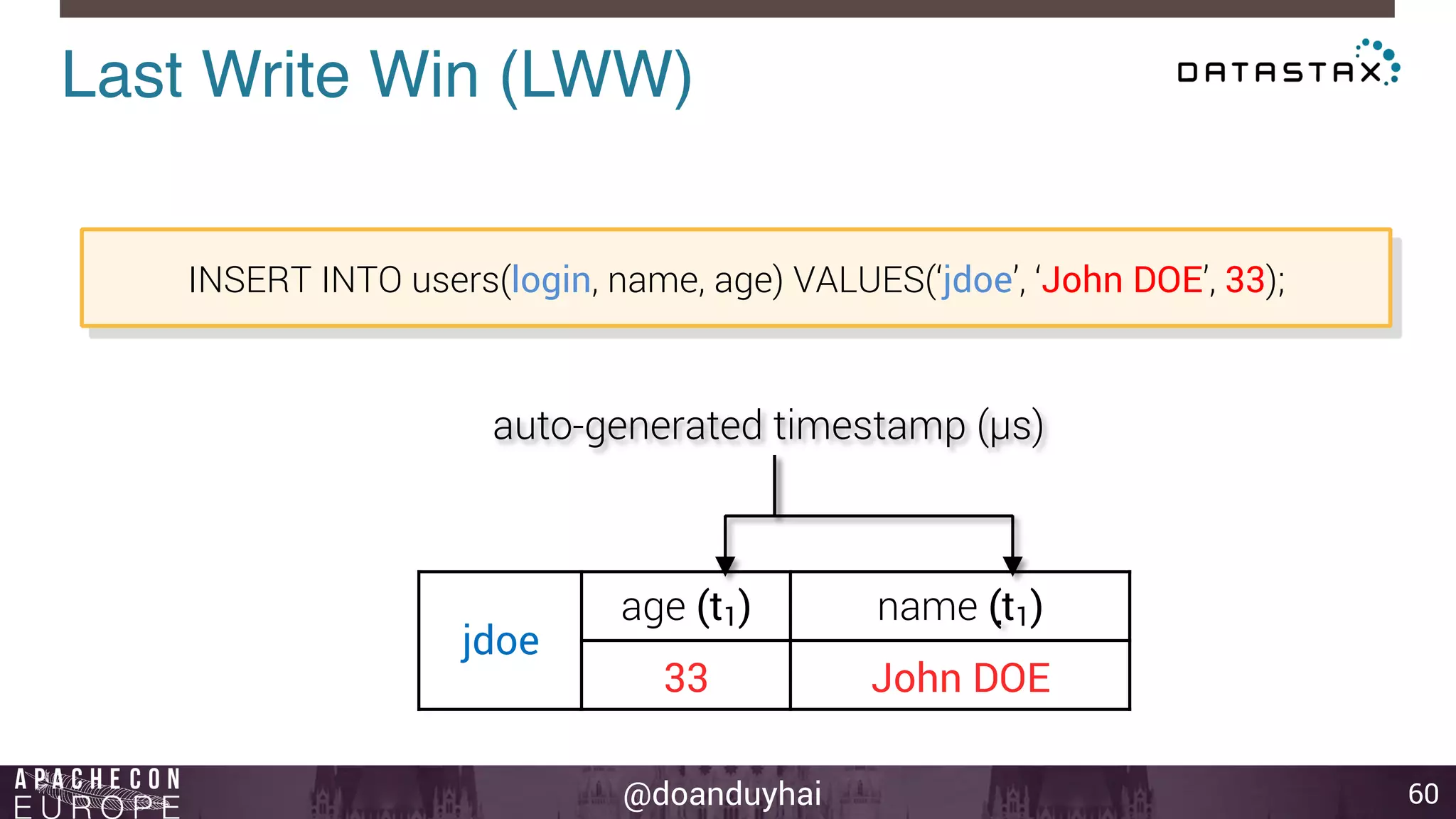
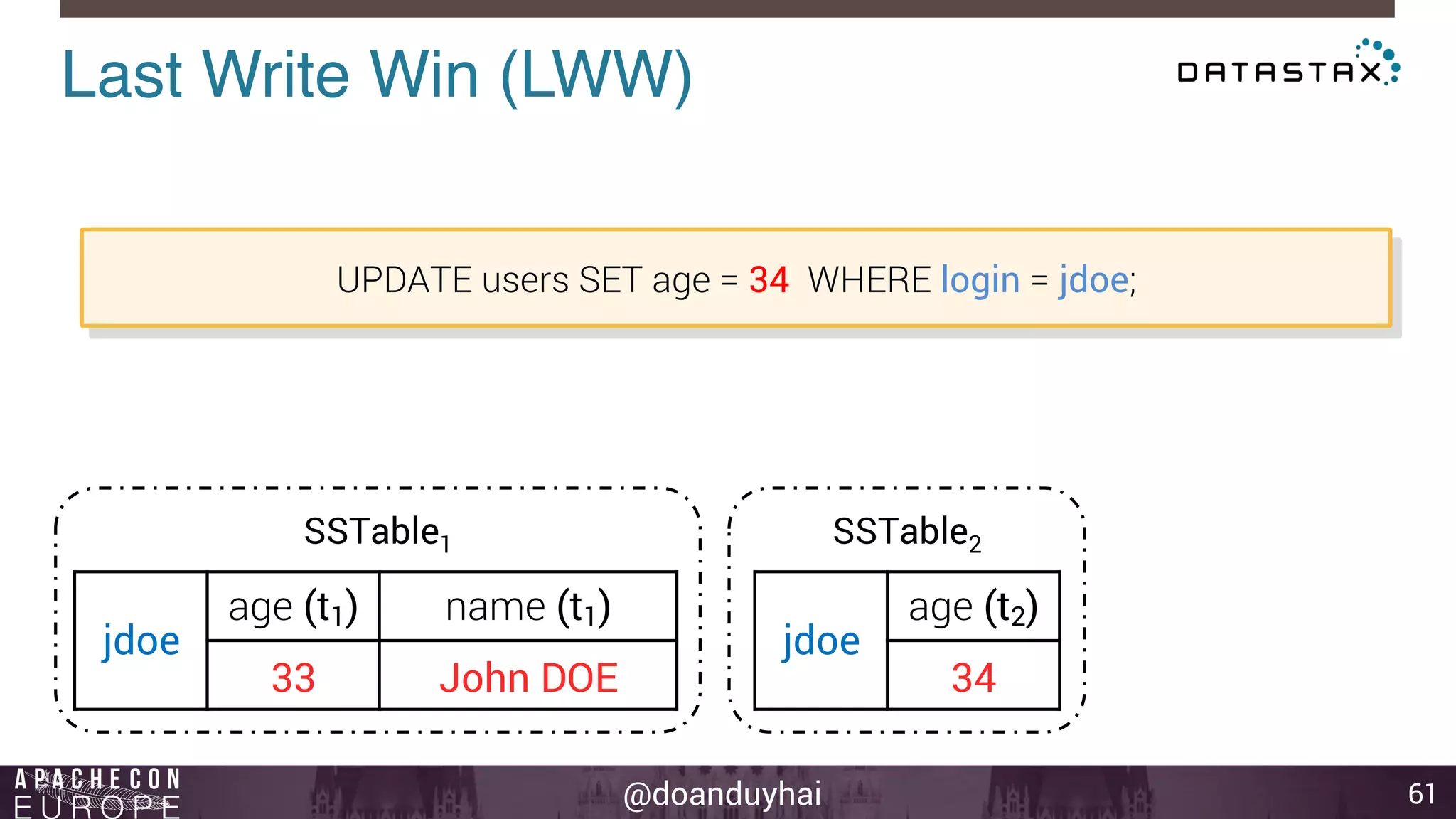
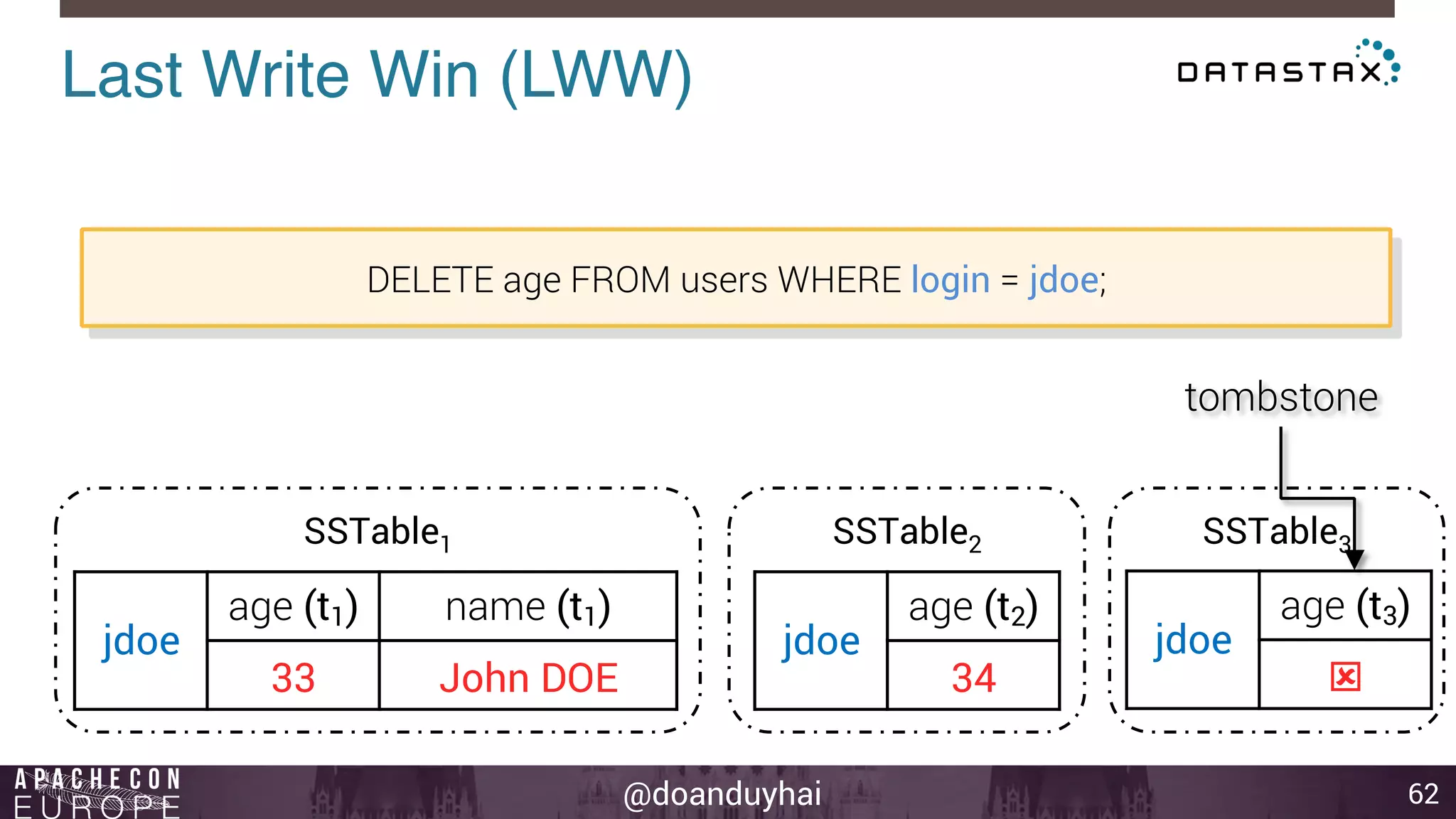
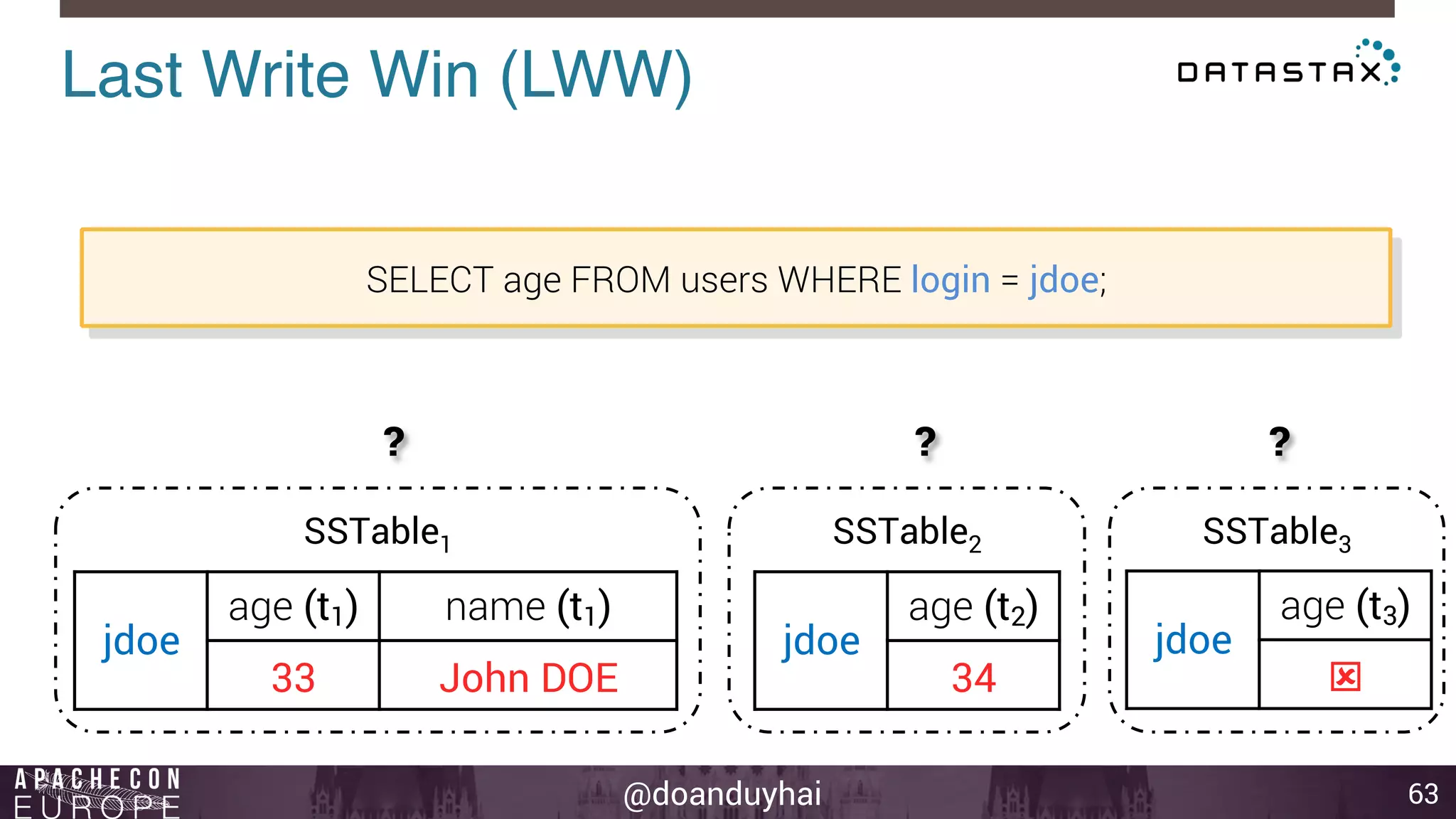
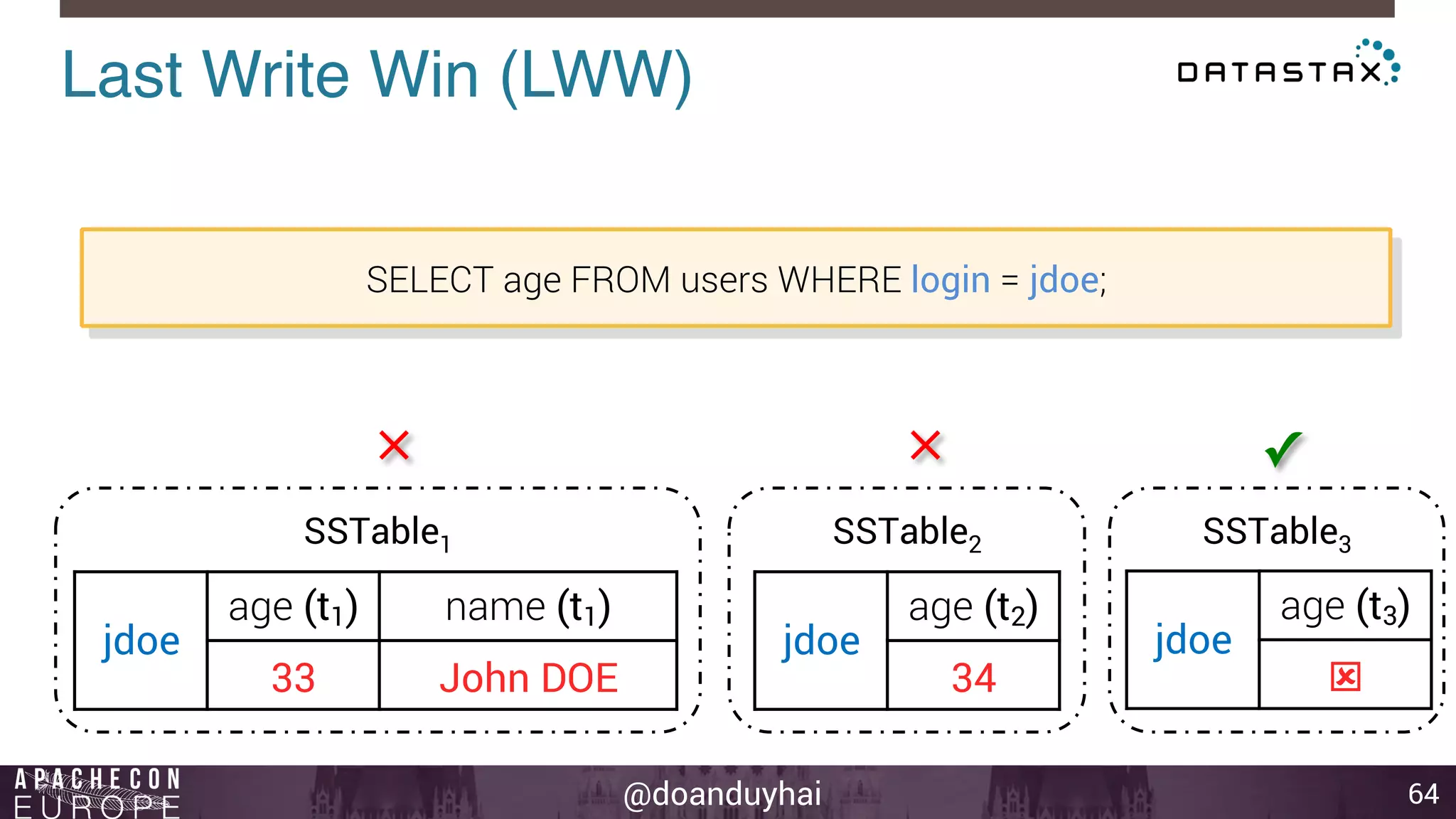
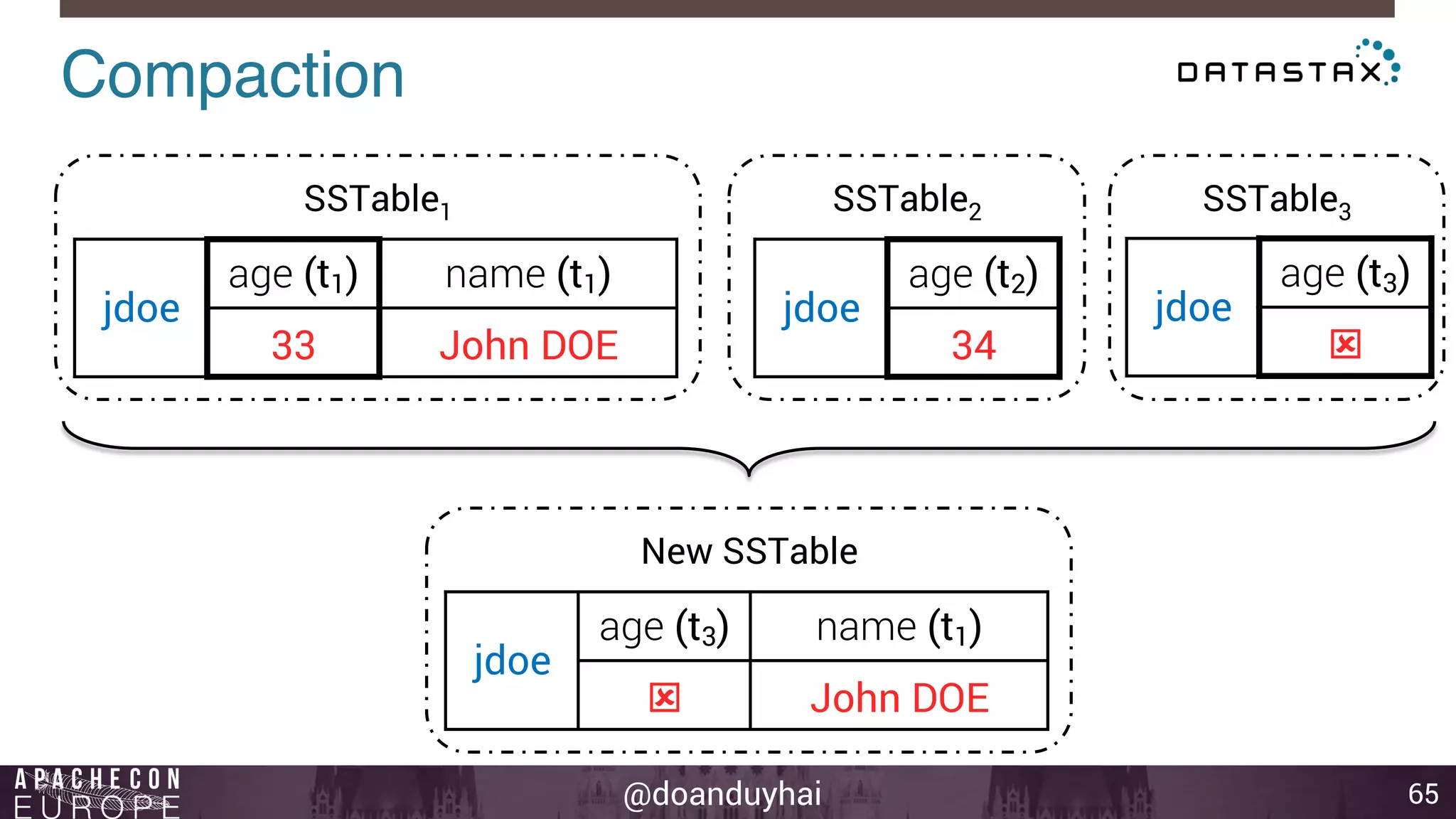
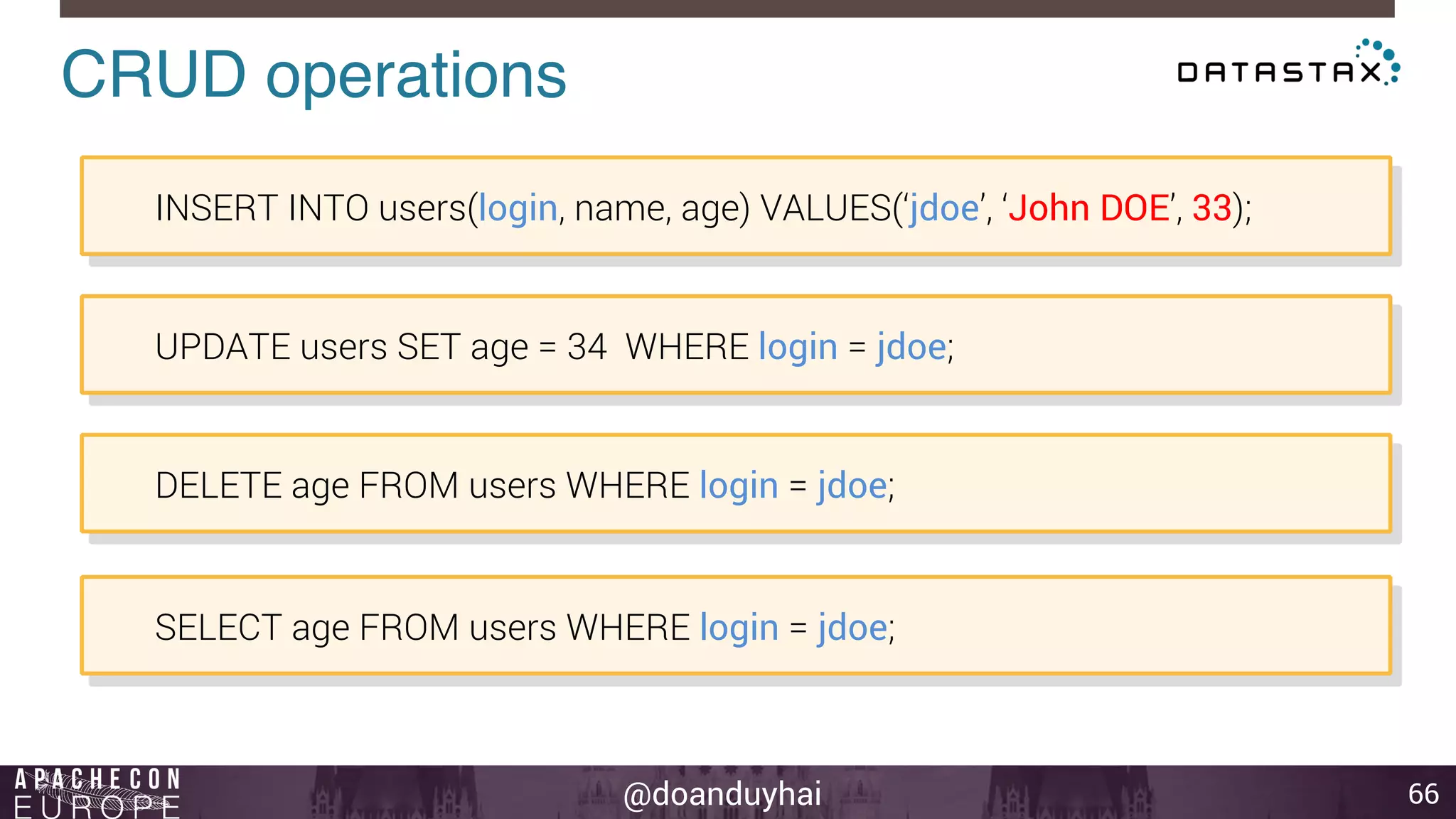
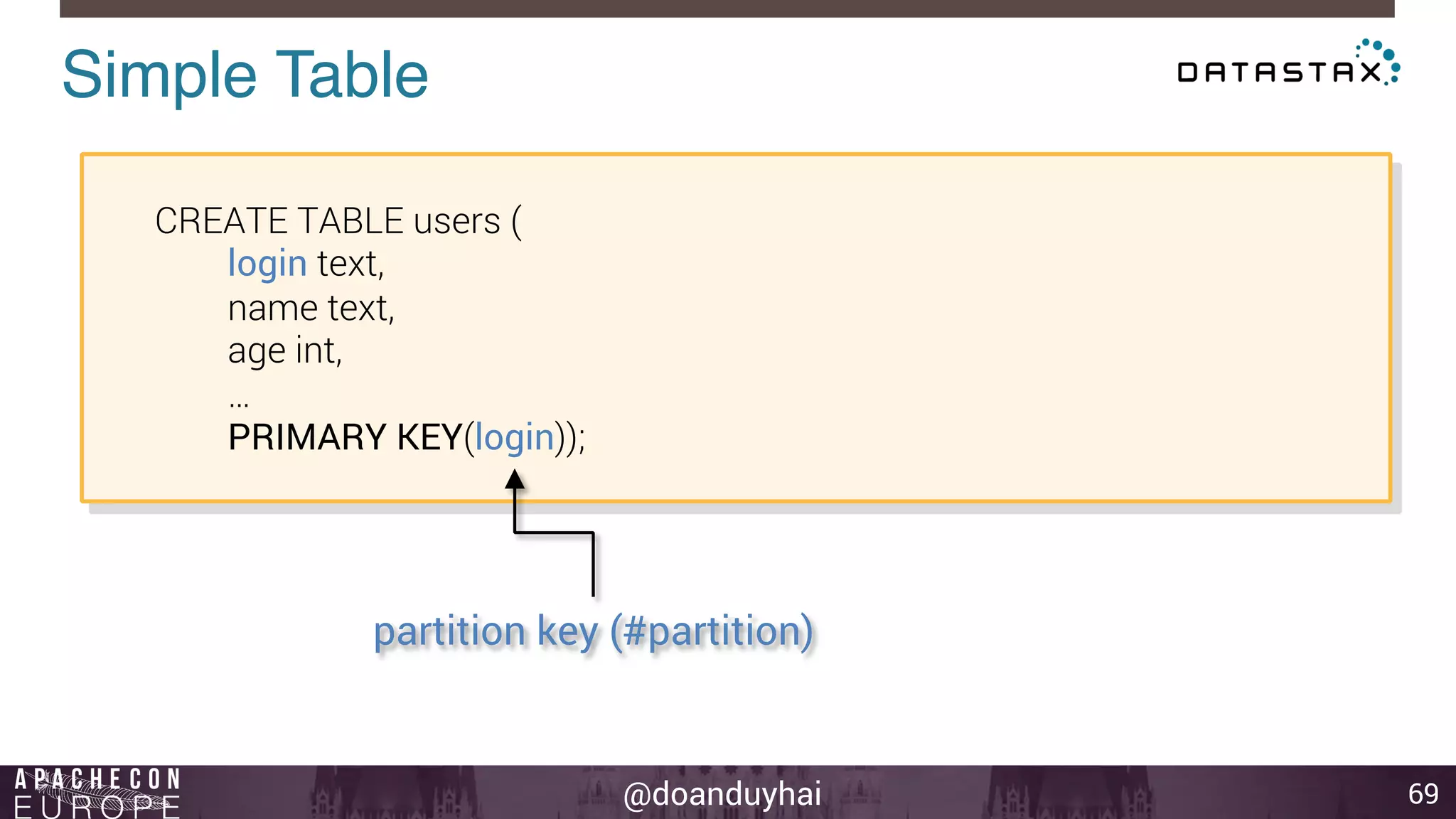
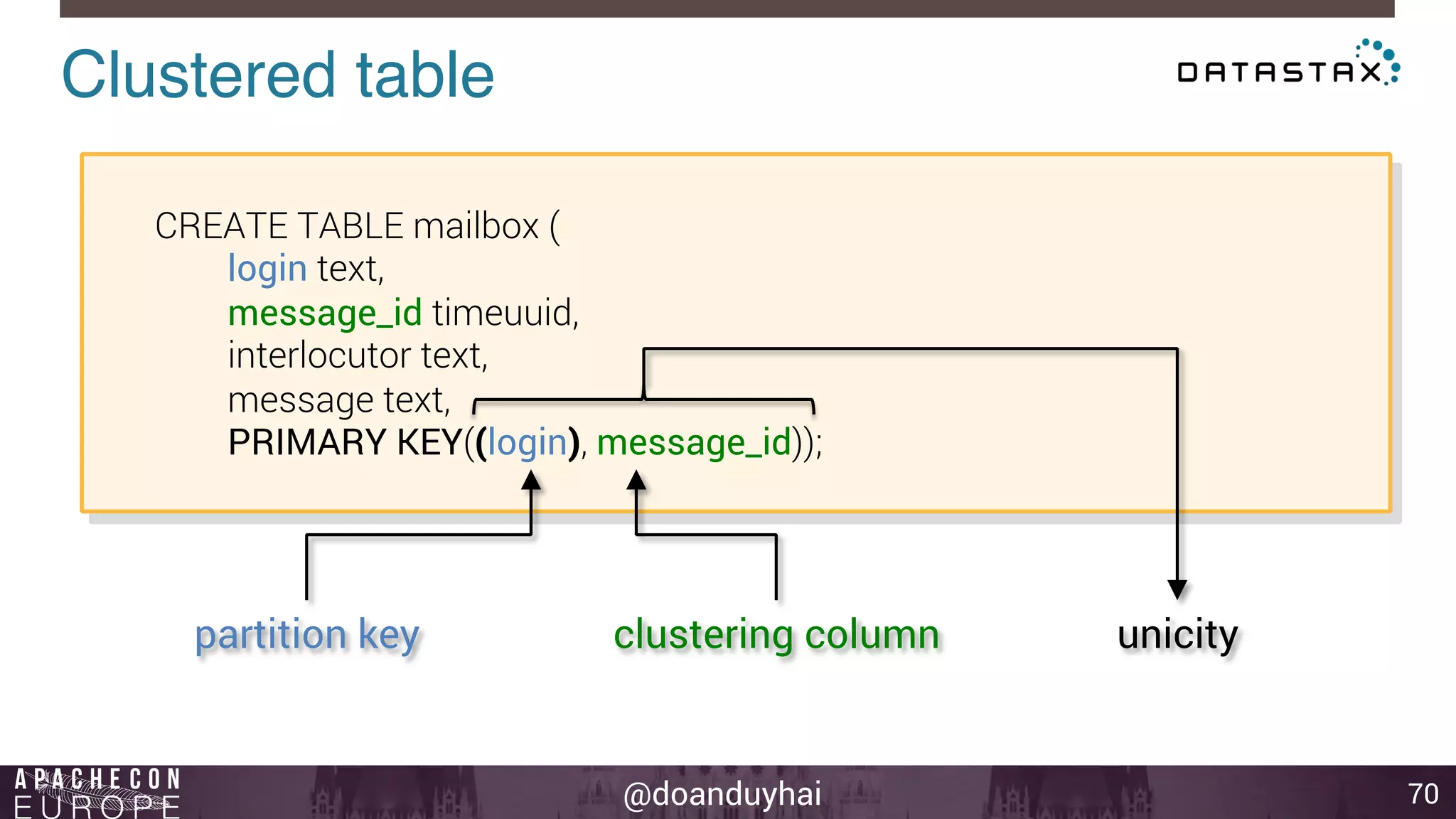
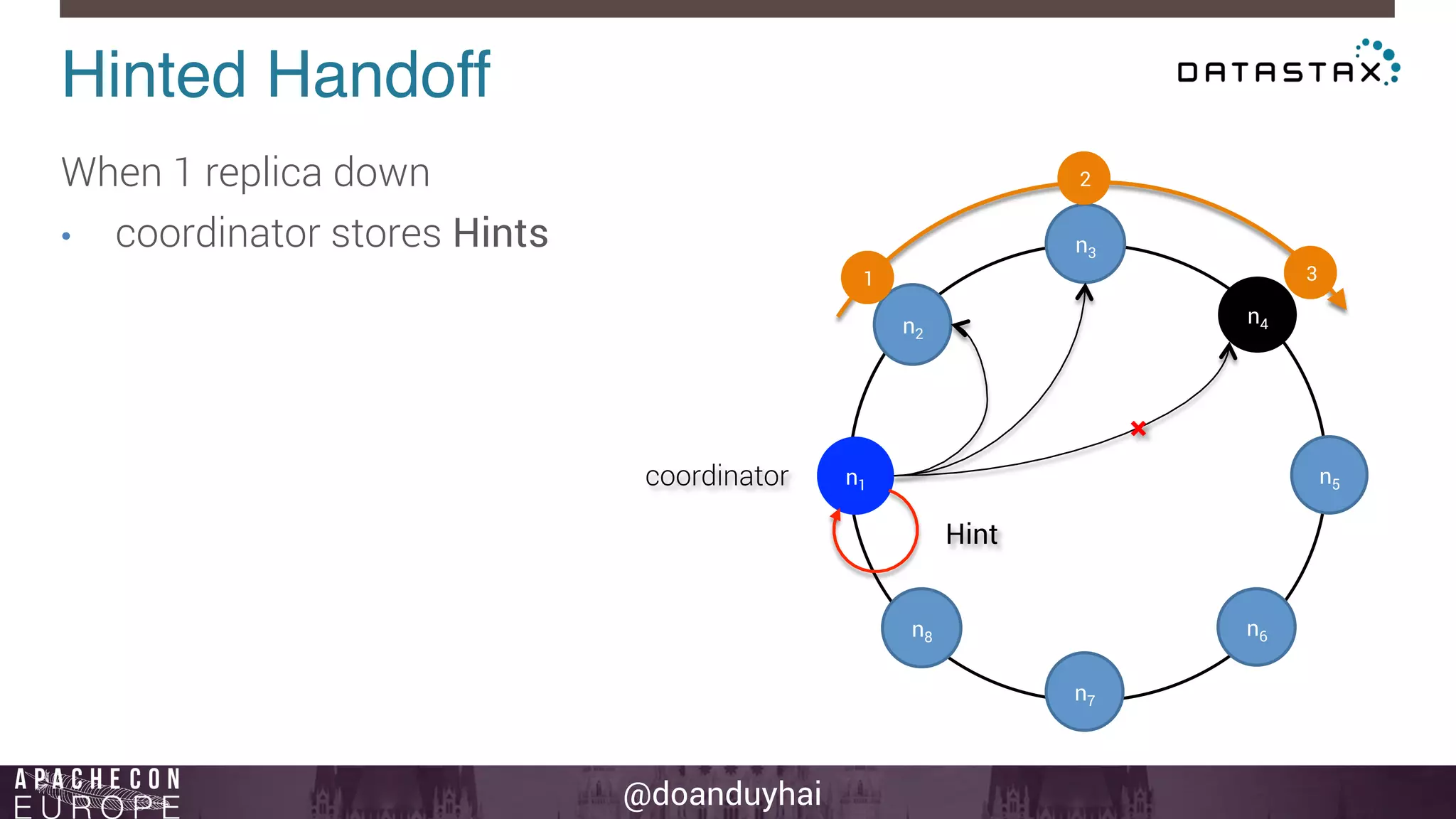
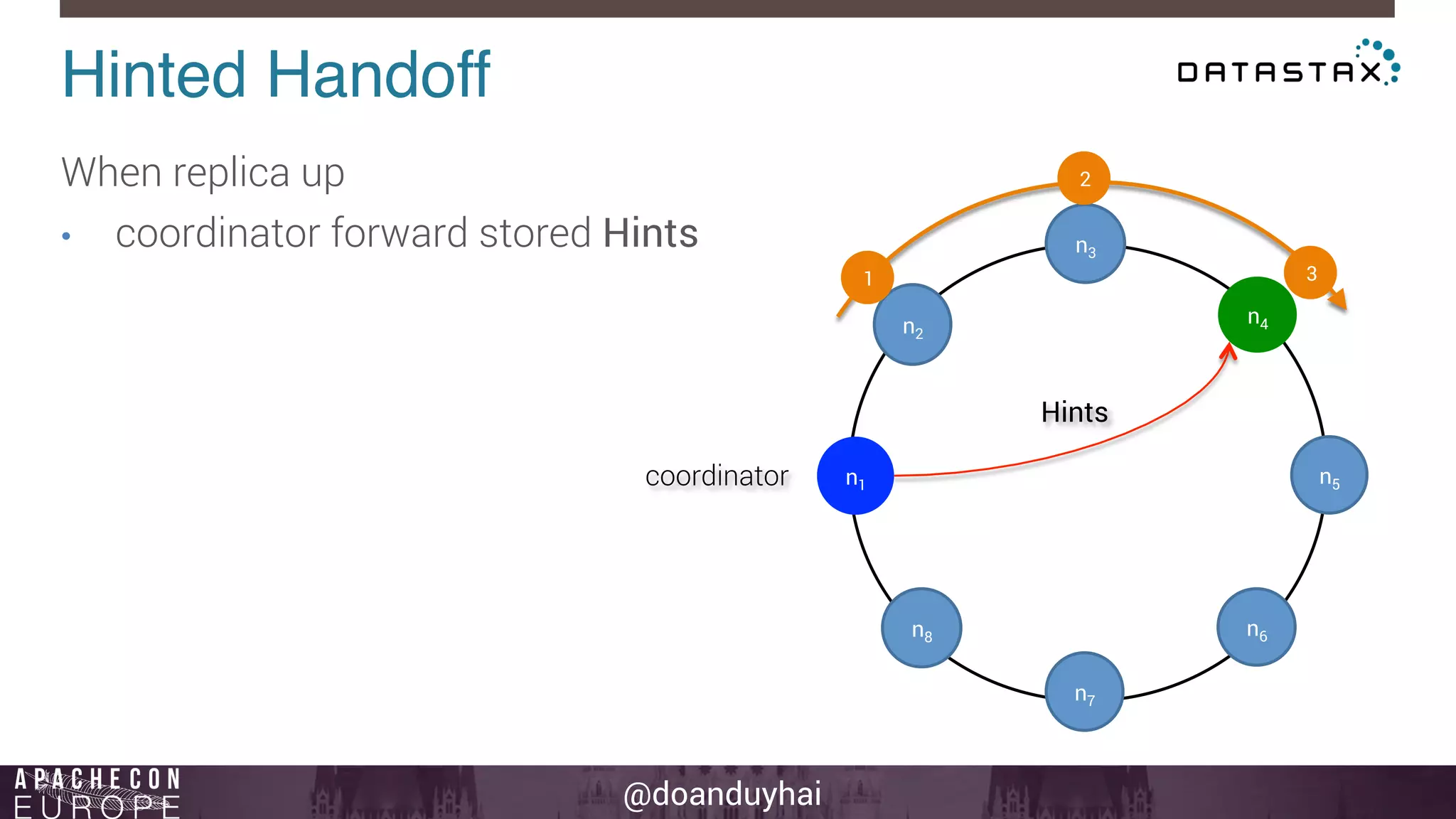
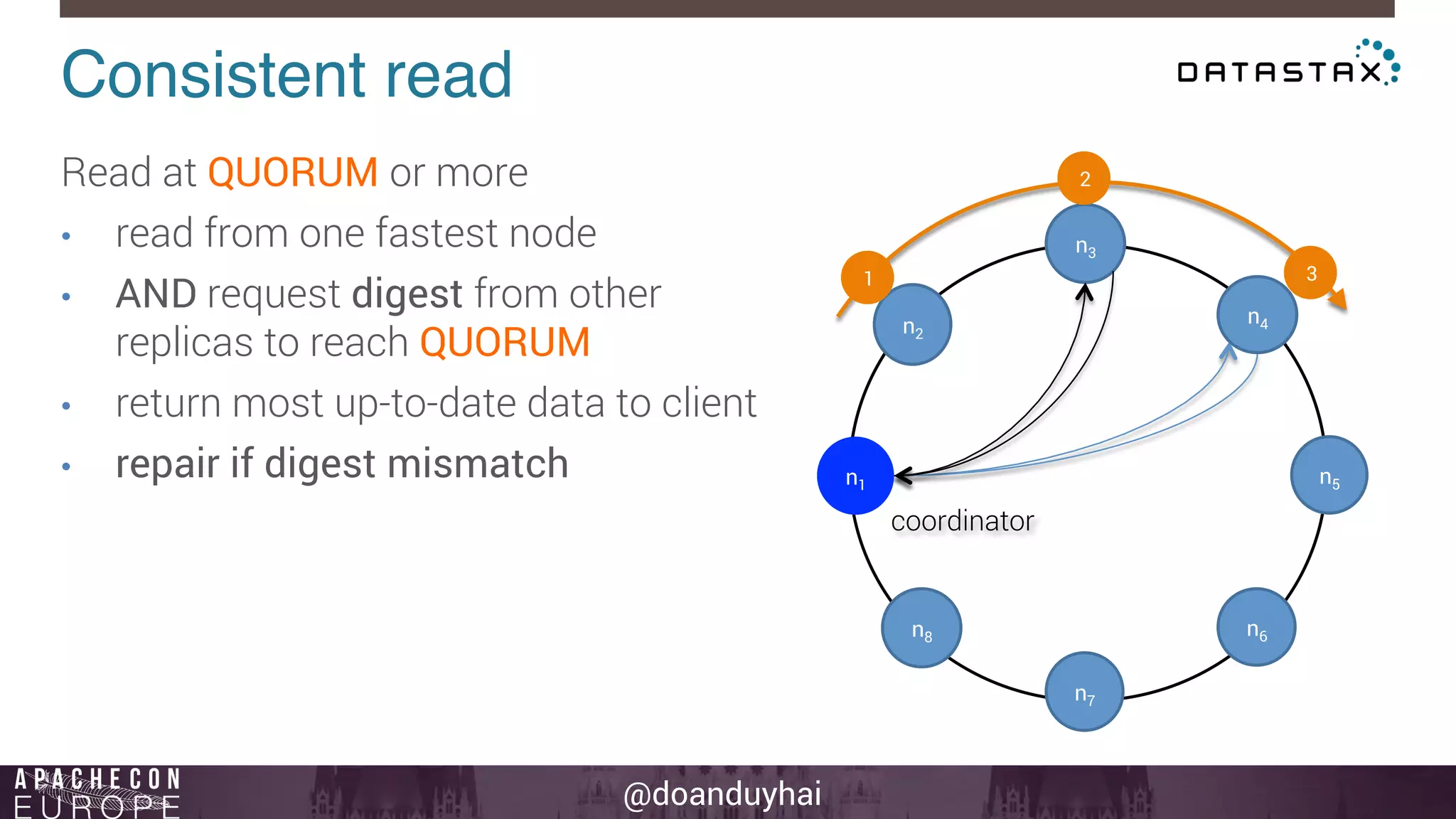
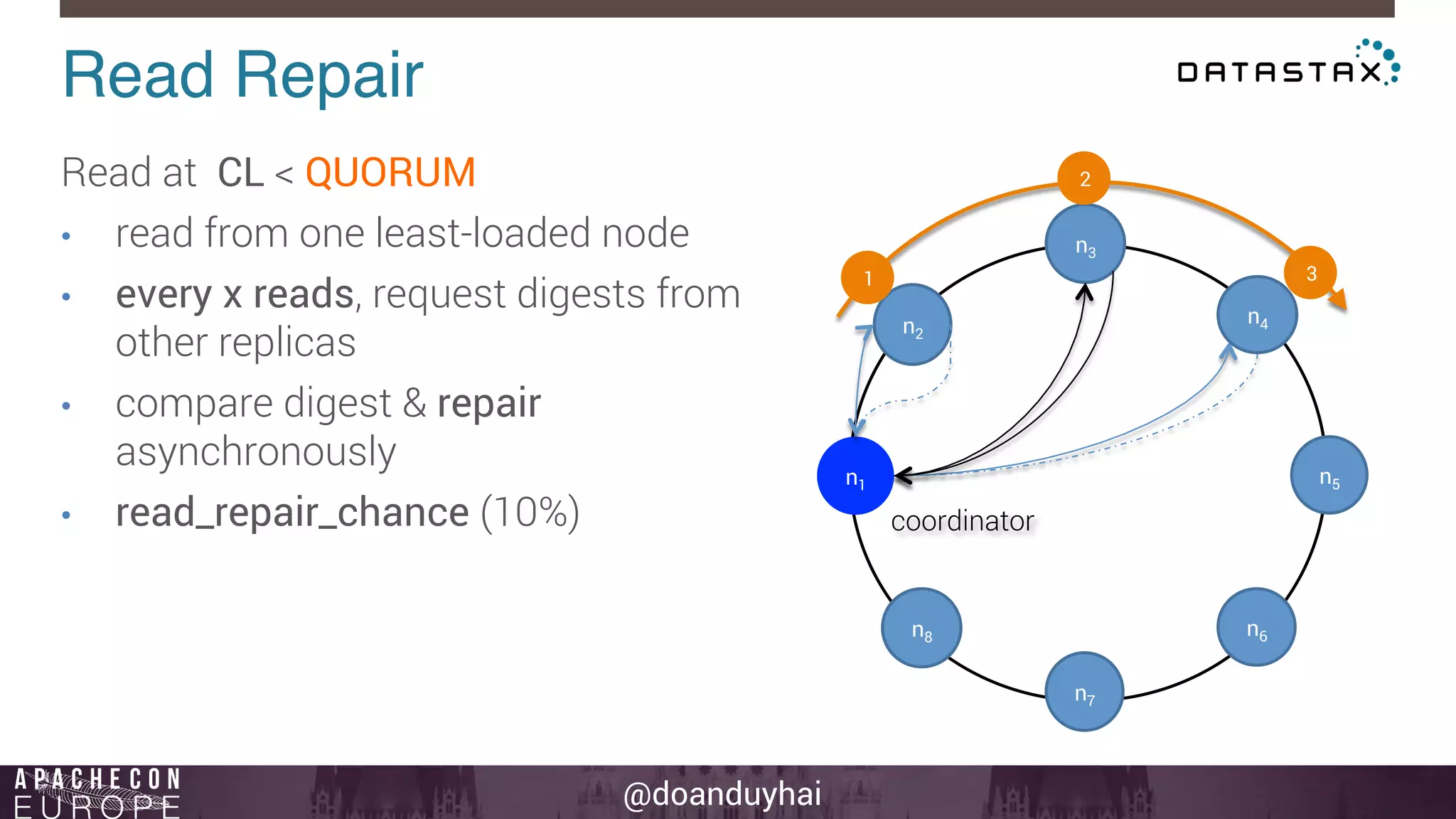
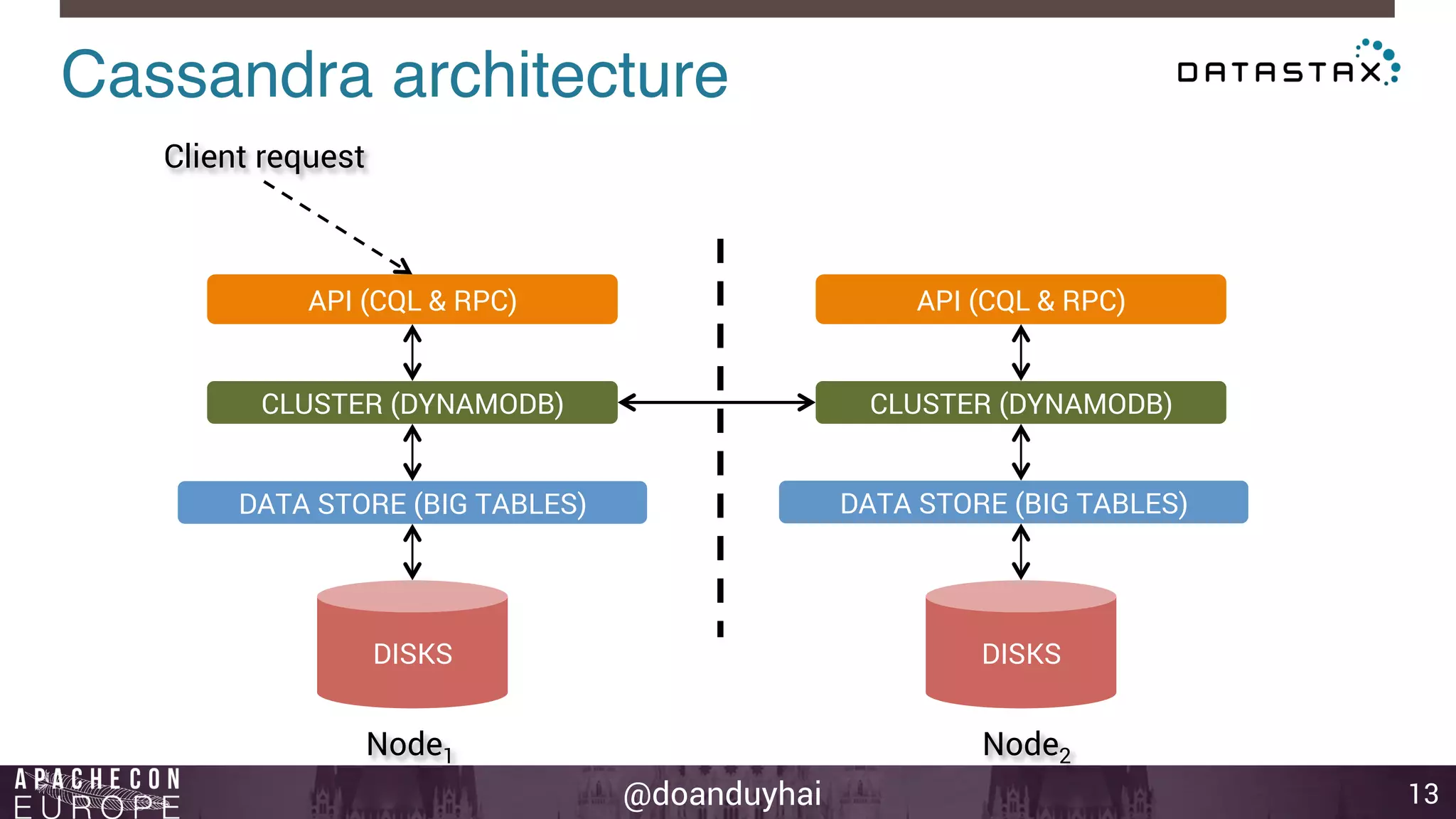
This document provides an introduction and summary of Cassandra presented by Duy Hai Doan. It discusses Cassandra's history as a NoSQL database created at Facebook and open sourced in 2008. The key architecture of Cassandra including its data distribution across nodes, replication for failure tolerance, and consistency models for reads and writes is summarized.








![@doanduyhai
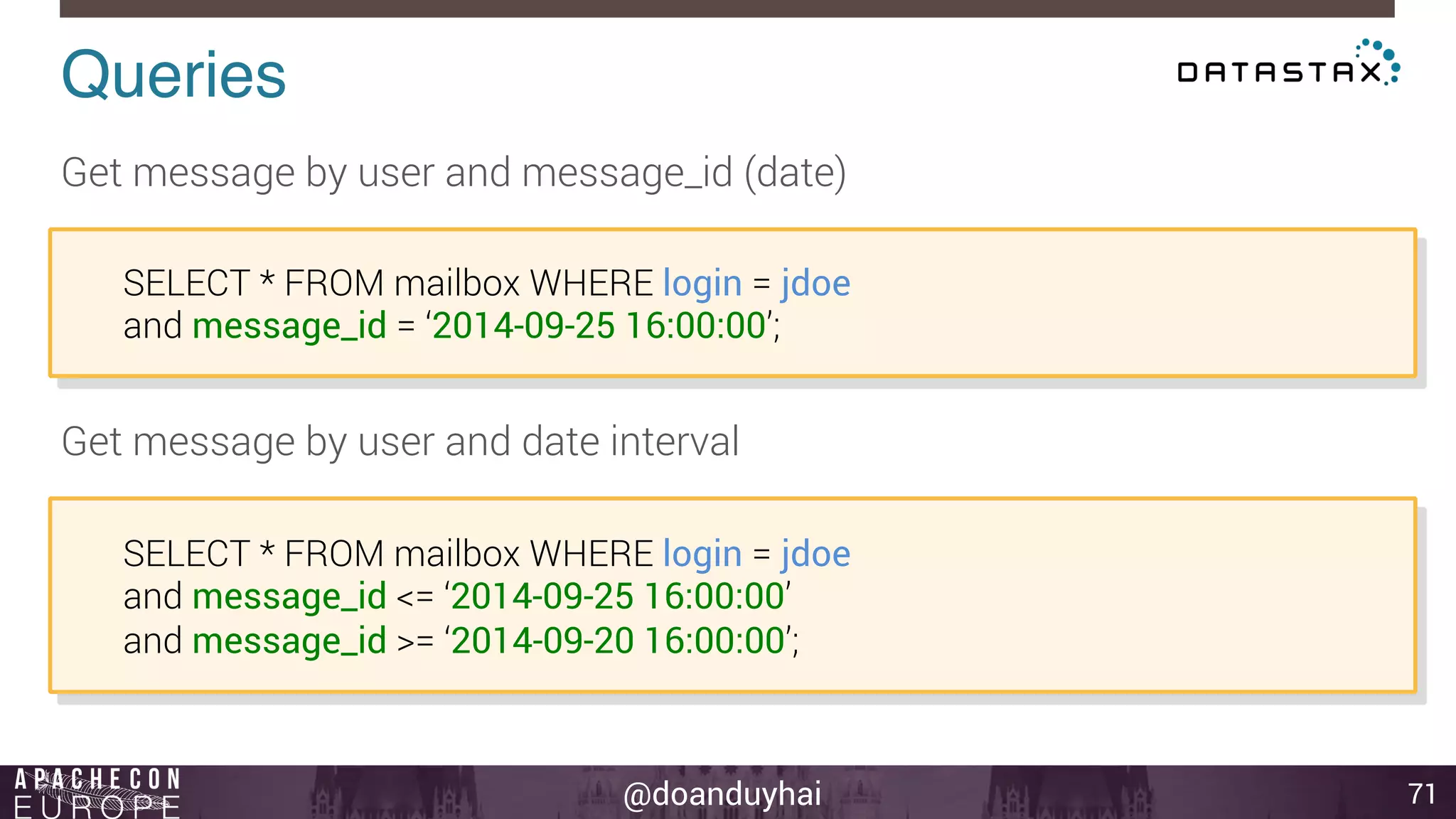
Data distribution!
14
Random: hash of #partition → token = hash(#p)
Hash: ]-X, X]
X = huge number (264/2)
n1
n2
n3
n4
n5
n6
n7
n8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cassandraintroductionapachecon2014budapest-141118083914-conversion-gate01/75/Cassandra-introduction-apache-con-2014-budapest-14-2048.jpg)
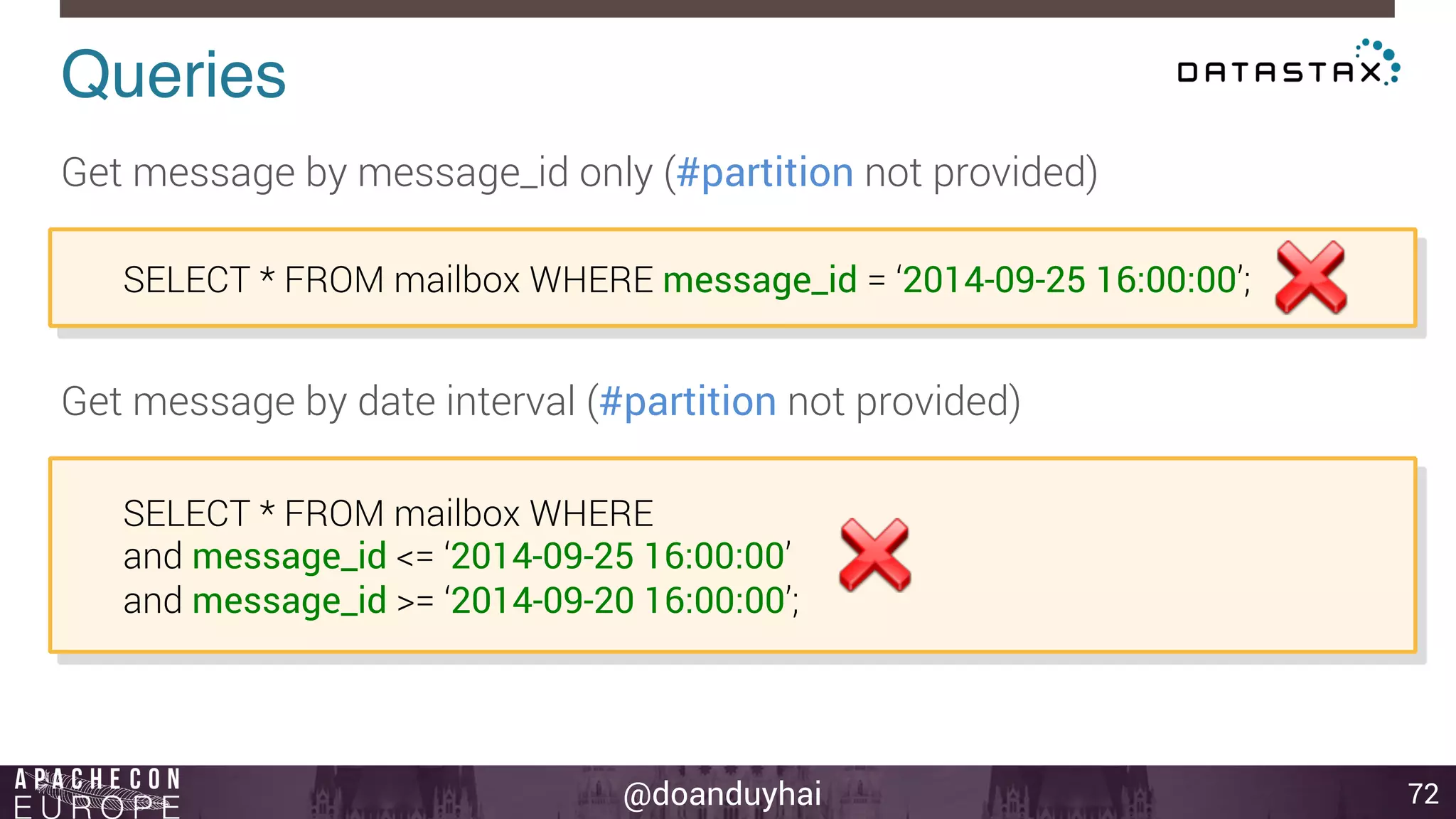
![@doanduyhai
Token Ranges!
15
A: ]0, X/8]
B: ] X/8, 2X/8]
C: ] 2X/8, 3X/8]
D: ] 3X/8, 4X/8]
E: ] 4X/8, 5X/8]
F: ] 5X/8, 6X/8]
G: ] 6X/8, 7X/8]
H: ] 7X/8, X]
n1
n2
n3
n4
n5
n6
n7
n8
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cassandraintroductionapachecon2014budapest-141118083914-conversion-gate01/75/Cassandra-introduction-apache-con-2014-budapest-15-2048.jpg)