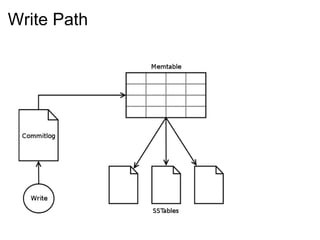
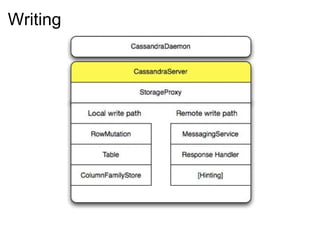
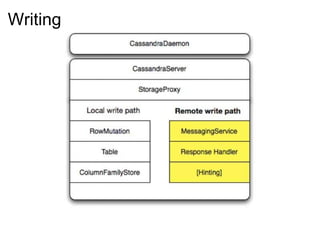
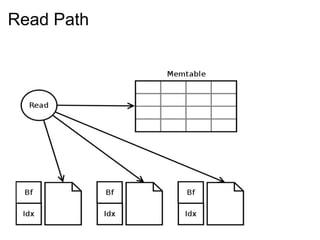
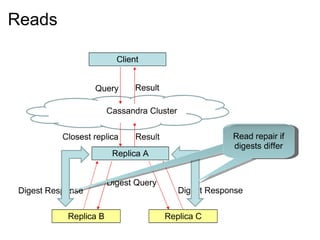
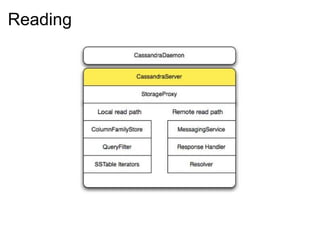
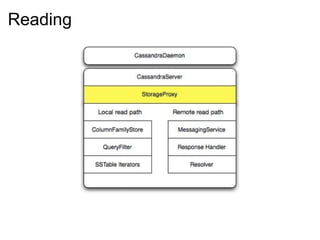
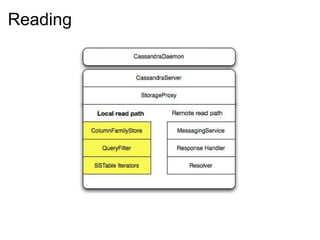
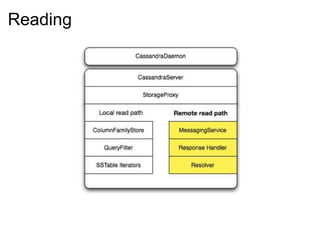
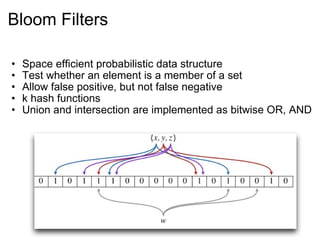
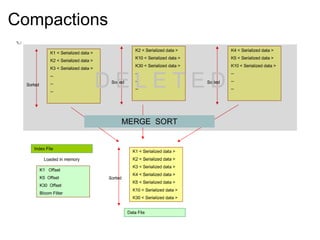
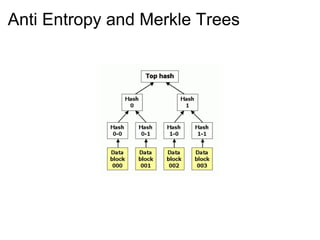
This document provides an introduction and overview of Cassandra and NoSQL databases. It discusses the challenges faced by modern web applications that led to the development of NoSQL databases. It then describes Cassandra's data model, API, consistency model, and architecture including write path, read path, compactions, and more. Key features of Cassandra like tunable consistency levels and high availability are also highlighted.