This document discusses updates in Redis v3.2, including new features like geospatial indices and a Lua debugger, as well as enhancements to its internal mechanisms for memory optimization and replication. Key topics covered at a meetup include geospatial functionality, security improvements, and performance optimizations. The document also emphasizes best practices for using Redis securely and effectively.









![New! GEO API, part 1
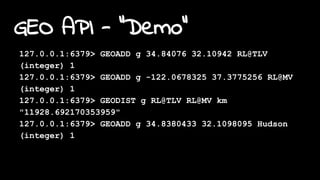
Add a point:
GEOADD key longitude latitude member [...]
Get longitude & latitude / geohash:
GEOPOS|GEOHASH key member [...]
Get the distance between two points:
GEODIST key member1 member2 [unit]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20160121redistlv-newinv3-160121210628/85/What-s-new-in-Redis-v3-2-15-320.jpg)

![New! GEO API, part 2
Search for members in a radial area:
GEORADIUS key longitude latitude radius unit ...
GEORADIUSBYMEMBER key member radius unit ...
Overthrows ZREVRANGEBYSCORE!!! #RedisTrivia
Delete a point - no GEOREM for you:
ZREM key member [...]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20160121redistlv-newinv3-160121210628/85/What-s-new-in-Redis-v3-2-18-320.jpg)









![Redimension "Demo"
~/src/lua-redimension$ redis-cli SCRIPT LOAD
"$(cat redimension.lua)"
"4abdad23c459145cbd658c991c0c8ad93d984d91"
~/src/lua-redimension$ redis-cli EVALSHA
4abdad23c459145cbd658c991c0c8ad93d984d91 0
1) "KEYS[1] - index sorted set key"
2) "KEYS[2] - index hash key"
3) "ARGV[1] - command. Can be:"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20160121redistlv-newinv3-160121210628/85/What-s-new-in-Redis-v3-2-28-320.jpg)
![Redimension "Demo", 2
4) " create - create an index with ARGV
[2] as dimension and ARGV[3] as precision"
5) " drop - drops an index"
6) " index - index an element ARGV[2]
with ARGV[3]..ARGV[3+dimension] values"
7) " unindex - unindex an element ARGV
[2] with ARGV[3]..ARGV[3+dimension] values"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20160121redistlv-newinv3-160121210628/85/What-s-new-in-Redis-v3-2-29-320.jpg)
![Redimension "Demo", 3
9) " update - update an element ARGV[2]
with ARGV[3]..ARGV[3+dimension] values"
10) " query - query using ranges ARGV
[2], ARGV[3]..ARGV[2+dimension-1], ARGV
[2+dimension]"
11) " fuzzy_test - fuzzily tests the library
on ARGV[2] dimension with ARGV[3] items using
ARGV[4] queries"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20160121redistlv-newinv3-160121210628/85/What-s-new-in-Redis-v3-2-30-320.jpg)












![ABCDEFn
char*
used unusedfree
4 bytes 4 bytes
old sds header
● grows in place(sometimes no need for realloc)
○ although realloc may nop instead of give new pointer and do
memcpy
● no need for strlen (search for null terminator)
● can be used in normal string functions like printf
struct sdshdr {
unsigned int len;
unsigned int free;
char buf[];
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20160121redistlv-newinv3-160121210628/85/What-s-new-in-Redis-v3-2-43-320.jpg)
![new sds header
ABCDEFn
char*
used unusedfree
4 bytes 4 bytes
old sds header
ABCDEFnused unusable
5 bits 3 bits
type5bit
ABCDEFnused unusedallocated
1 byte 1 byte 1 byte
type8bit
ABCDEFnused unusedallocated
2 bytes 2 bytes 1 byte
type16bit
ABCDEFnused unusedallocated
4 bytes 4 bytes 1 byte
type32bit
ABCDEFnused unusedallocated
8 bytes 8 bytes 1 byte
type64bit
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len; /* used */
uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
uint16_t len; /* used */
uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {
uint32_t len; /* used */
uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {
uint64_t len; /* used */
uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20160121redistlv-newinv3-160121210628/85/What-s-new-in-Redis-v3-2-44-320.jpg)




![Script replication before v3.2
Lua scripts are pushed down to the slaves for
local execution. This reduces wire traffic in
cases such as:
for i = 1, 1000000 do
redis.call('LPUSH', KEYS[1], i)
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20160121redistlv-newinv3-160121210628/85/What-s-new-in-Redis-v3-2-49-320.jpg)

![Free will
vs.
> EVAL "redis.call('SET', KEYS[1], redis.call
('TIME')[1])" 1 foo
(error) ... Write commands
not allowed after non
deterministic commands](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20160121redistlv-newinv3-160121210628/85/What-s-new-in-Redis-v3-2-51-320.jpg)
![Script replication in v3.2
- Same defaults
- NEW! redis.replicate_commands()
causes the script's effects to be replicated
- NEW! redis.set_repl(...)
redis.REPL_[ALL|NONE|AOF|SLAVE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20160121redistlv-newinv3-160121210628/85/What-s-new-in-Redis-v3-2-52-320.jpg)








