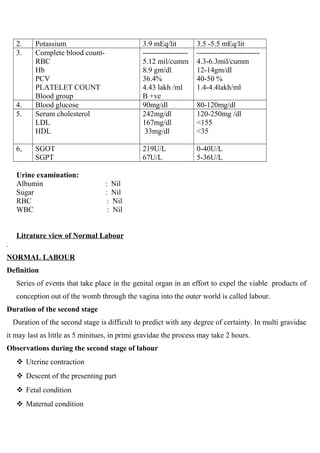
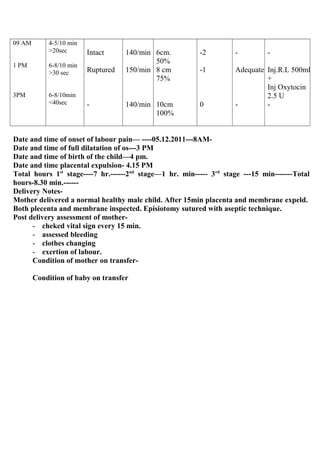
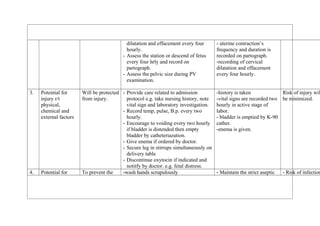
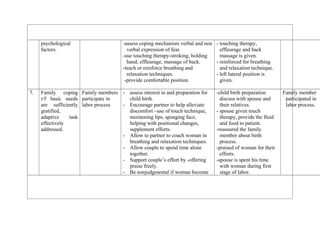
The patient profile document provides information about a 27 year old woman, Nisha, who was admitted to the labor ward on December 5, 2010 at 8am for labor. Her chief complaints were amenorrhea for 9 months and labor pains since 4am. On examination, her cervical dilation was 2cm and effacement was 30%. Her labor progressed normally over 7 hours with full dilation at 3pm and she delivered a healthy male child at 4pm.