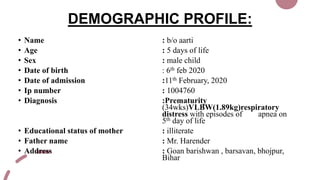
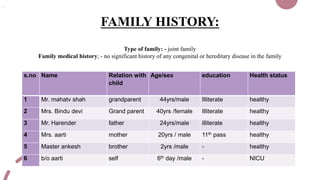
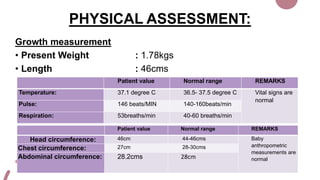
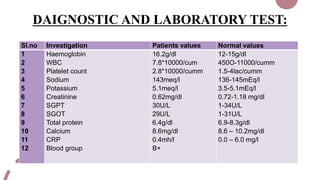
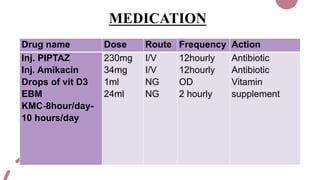
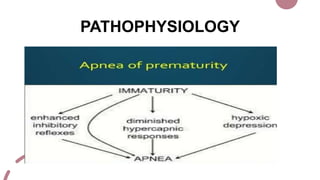
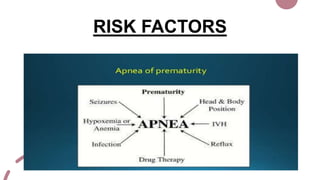
The case presentation is for a 5 day old male infant born prematurely at 34 weeks gestation with a very low birth weight of 1.89kg who was admitted to the NICU for respiratory distress and two episodes of apnea. Physical examination and laboratory tests were performed and showed the infant had normal vital signs and laboratory values. The infant was being treated with antibiotics, vitamins, and receiving breastmilk and KMC for episodes of apnea due to prematurity.