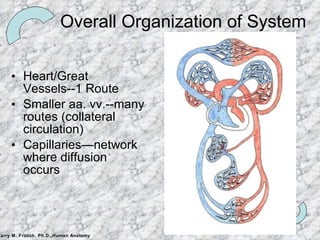
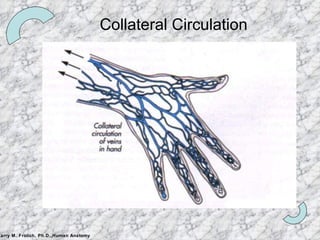
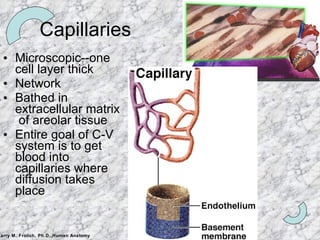
The document summarizes the key components and functioning of the cardiovascular system. It describes the heart structures and chambers, circulation paths through arteries, veins and capillaries, and the roles of valves and vessels in pumping blood throughout the body for gas and nutrient exchange as well as immune system functions. Fetal circulation and remnants in adults are also briefly outlined.