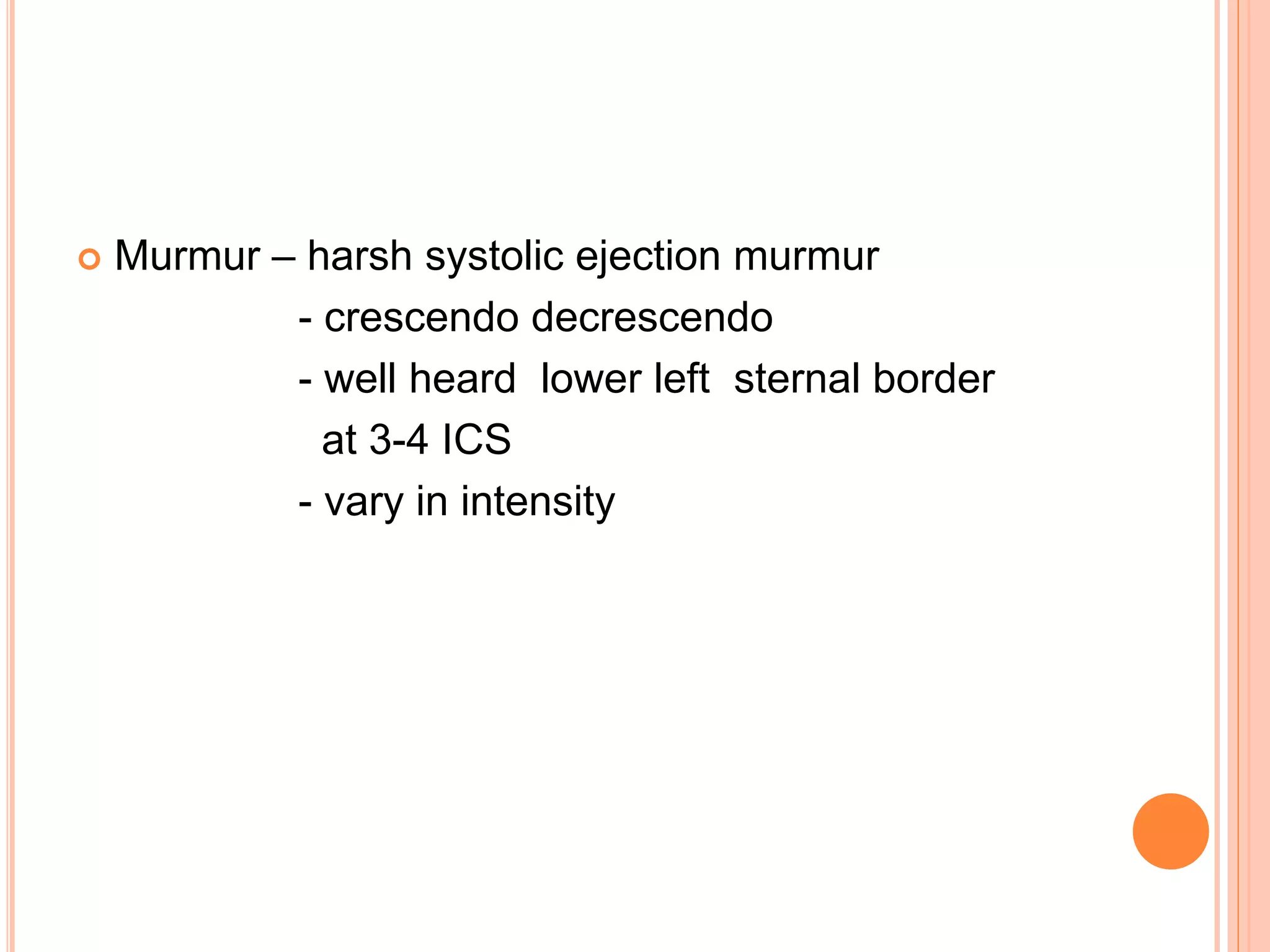
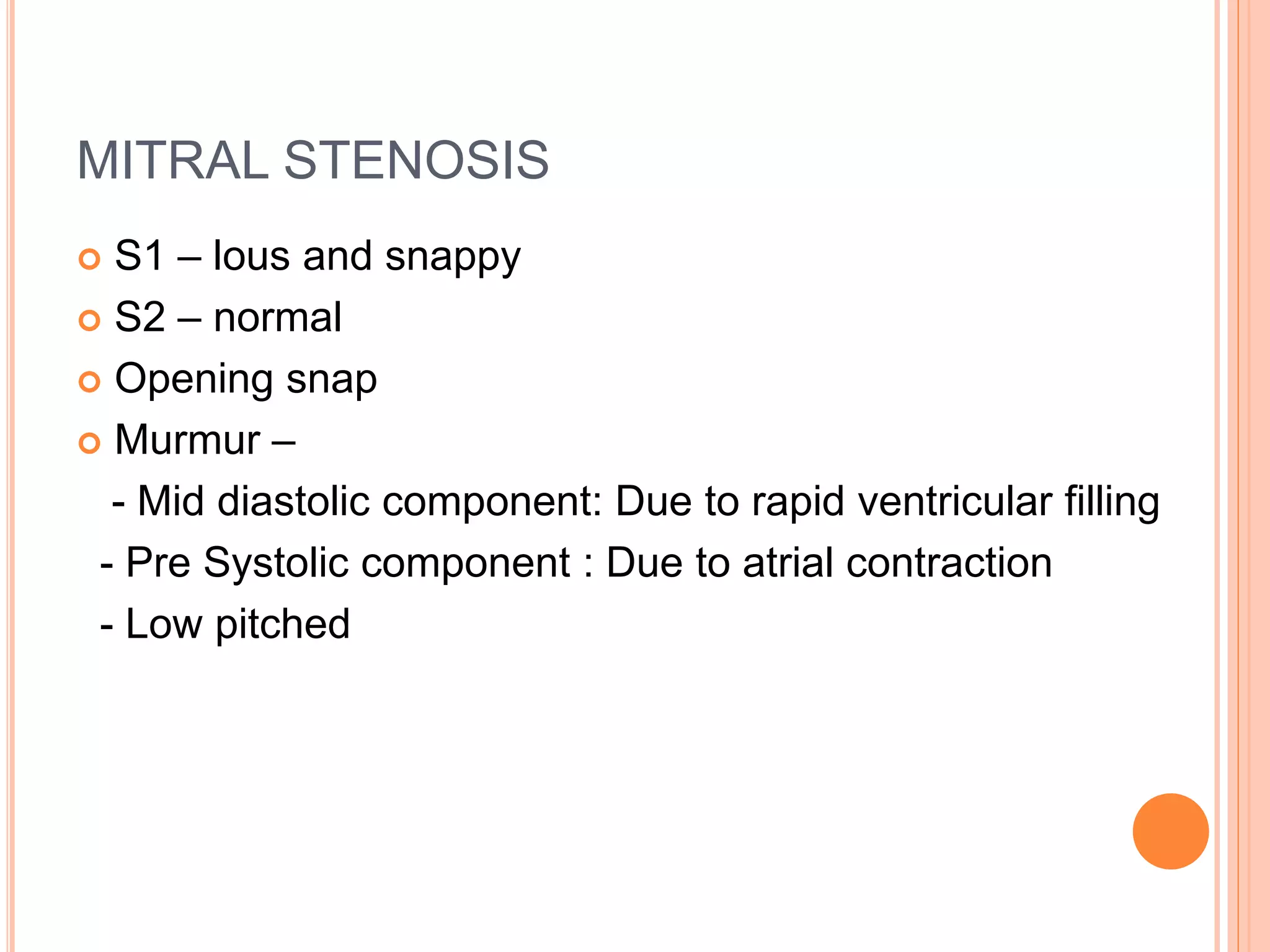
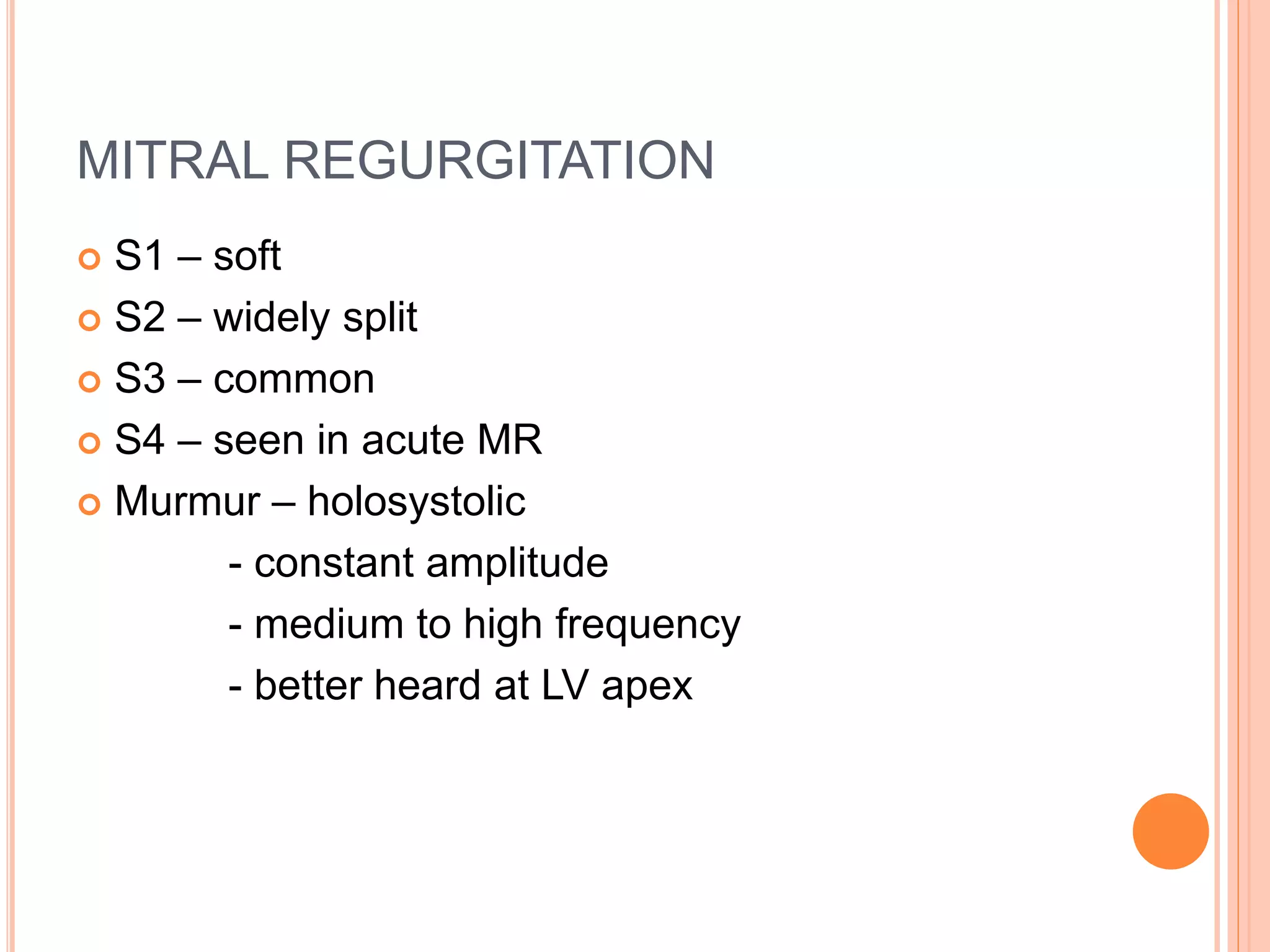
This document describes various types of cardiac murmurs and added heart sounds. It defines different types of murmurs such as systolic, diastolic, and continuous murmurs. It also describes how to characterize murmurs based on timing, location, intensity, and other factors. Specific heart conditions are discussed in relation to the murmurs and sounds they may cause, such as mid-systolic murmurs indicating aortic stenosis or holosystolic murmurs indicating mitral regurgitation. Grading scales for murmur intensity and examples of maneuvers that may modify murmurs are also provided.