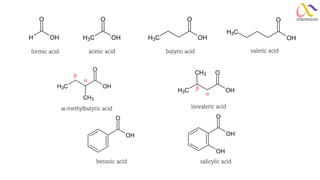
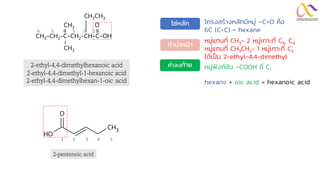
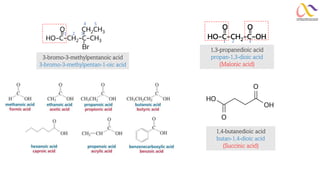
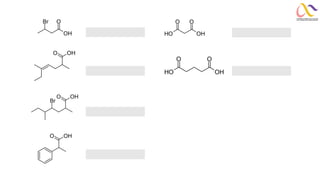
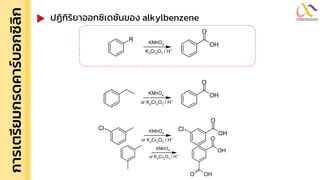
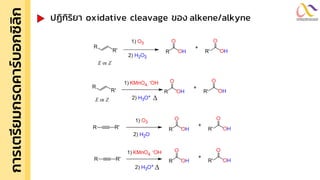
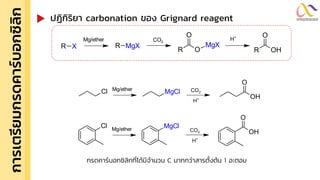
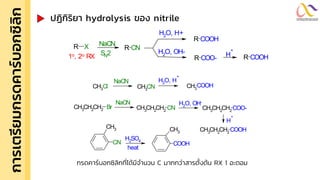
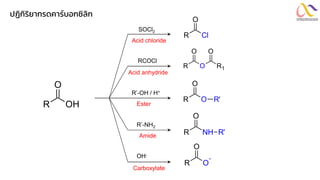
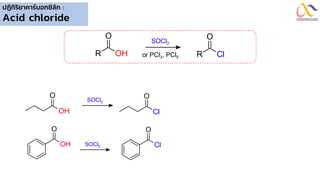
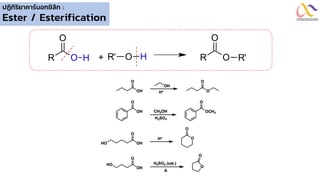
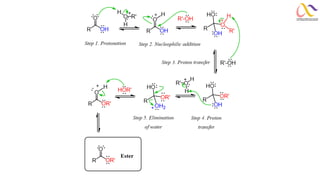
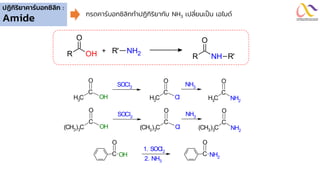
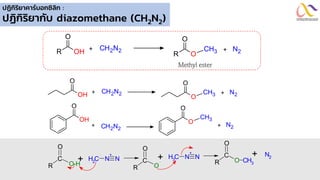
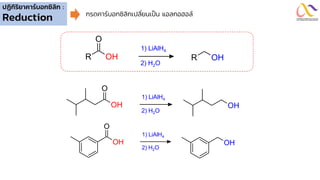
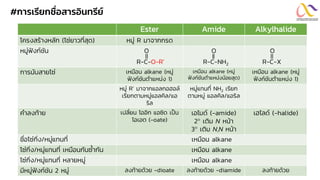
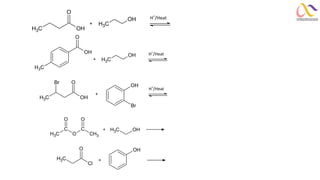
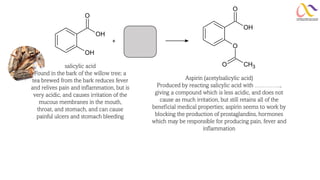
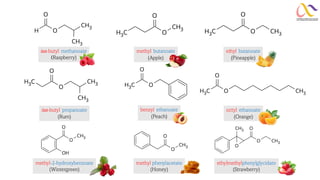
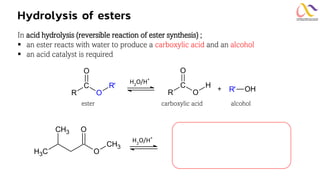
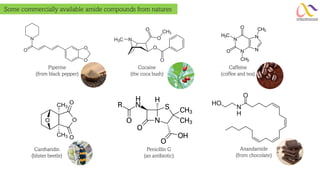
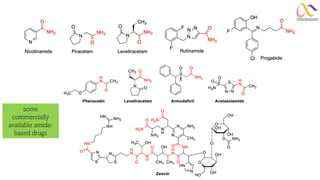
Chemistry: Carboxylic acid and Derivatives
Author: Asst.Prof.Woravith Chansuvarn, Ph.D.
Faculty of Science and Technology, RMUTP
Copyright @ 2023
Website: https://sci.rmutp.ac.th/woravith
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/woravith
Facebook Page: https://www.facebook.com/chemographics
Line: @woravith
https://www.tiktok.com/@woravithc
E-mail: woravith.c@rmutp.ac.th