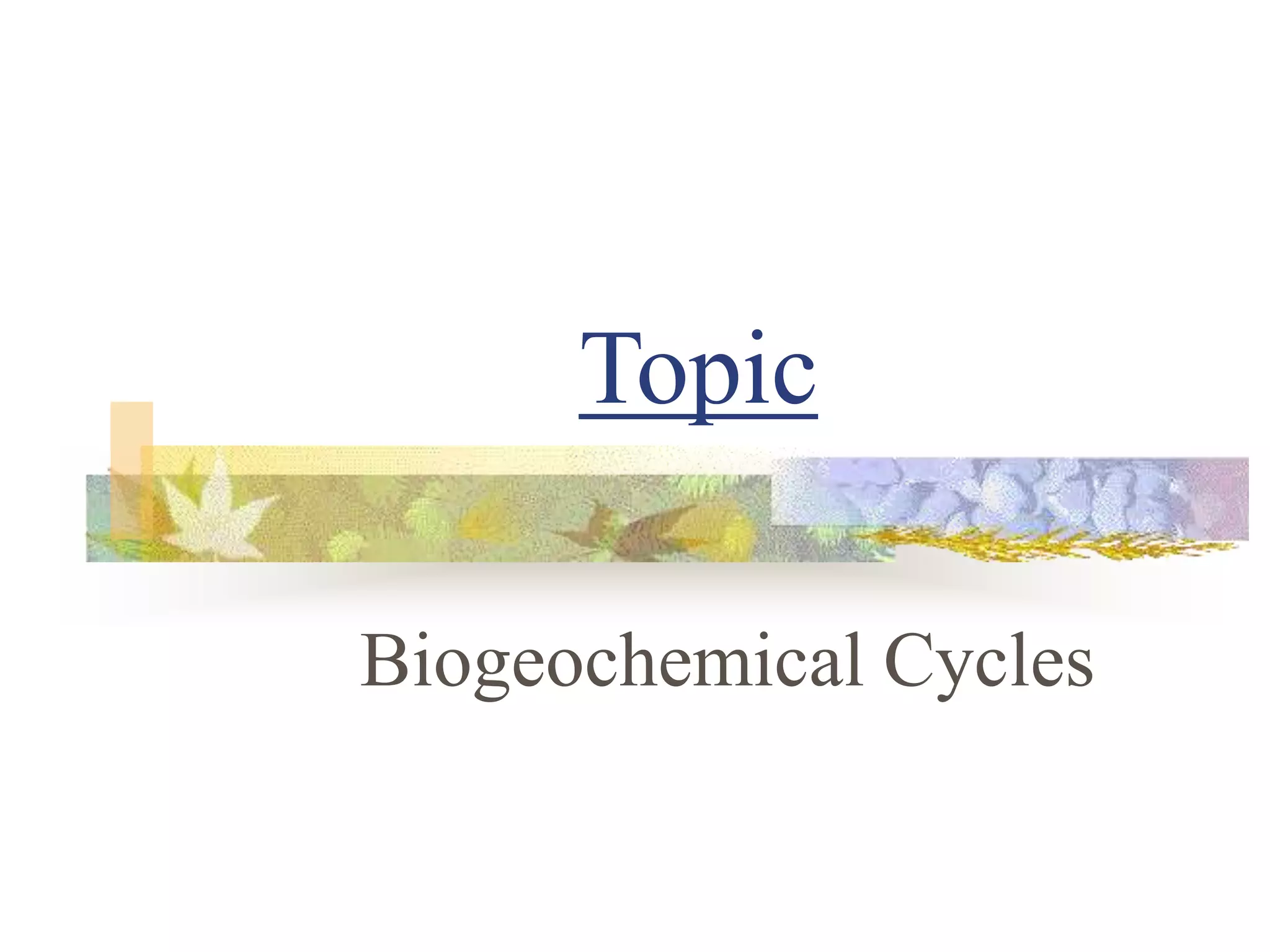
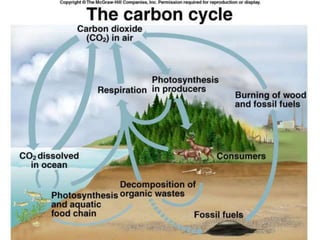
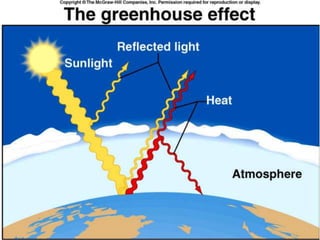
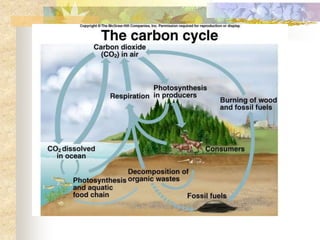
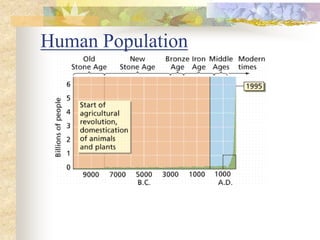
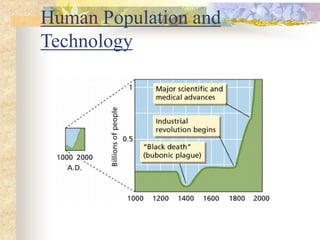
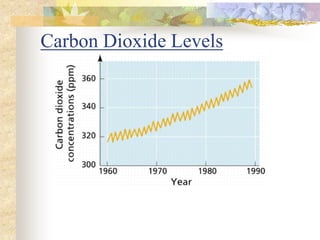
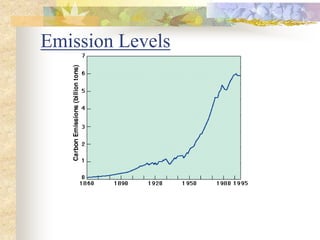
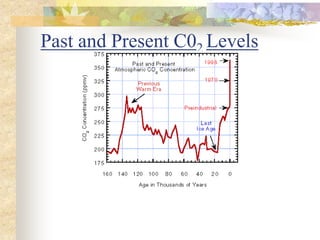
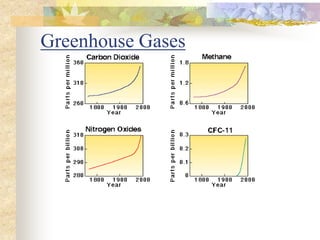
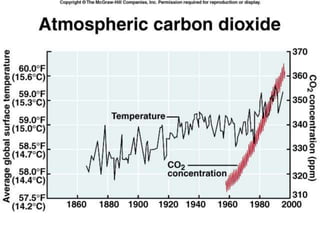
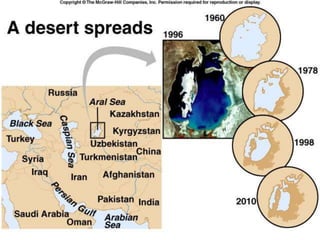
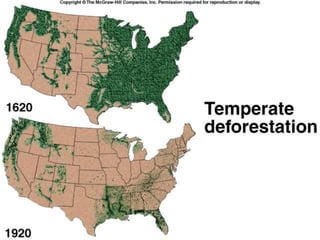
The carbon and oxygen cycles describe the movement of carbon and oxygen between the biosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere. Carbon dioxide is absorbed by plants through photosynthesis and released through respiration, while oxygen is a byproduct of photosynthesis and used in respiration. Human activities like burning fossil fuels have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, contributing to the greenhouse effect and global warming. This disrupts global climate patterns and ecosystems.