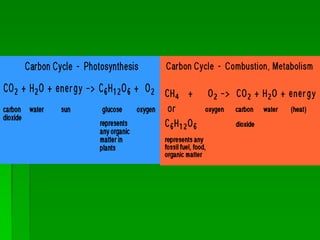
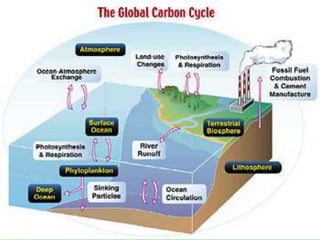
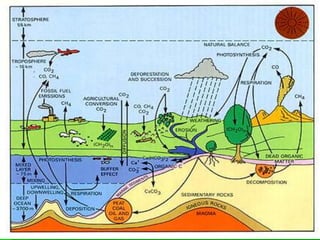
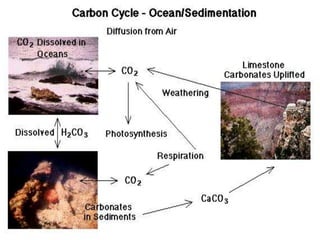
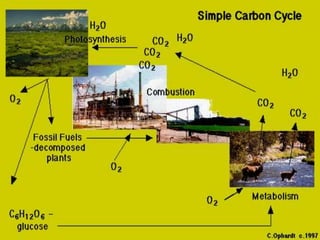
Photosynthesis is a key part of the carbon cycle. It involves producers converting inorganic carbon dioxide into organic compounds like glucose. Primary consumers obtain these organic compounds by eating producers, and secondary consumers obtain carbon by eating primary consumers. Cellular respiration by all organisms returns carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. Humans have disrupted this natural cycle by extracting and burning fossil fuels, releasing carbon that has been locked away for thousands of years back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide, contributing to increased global warming.