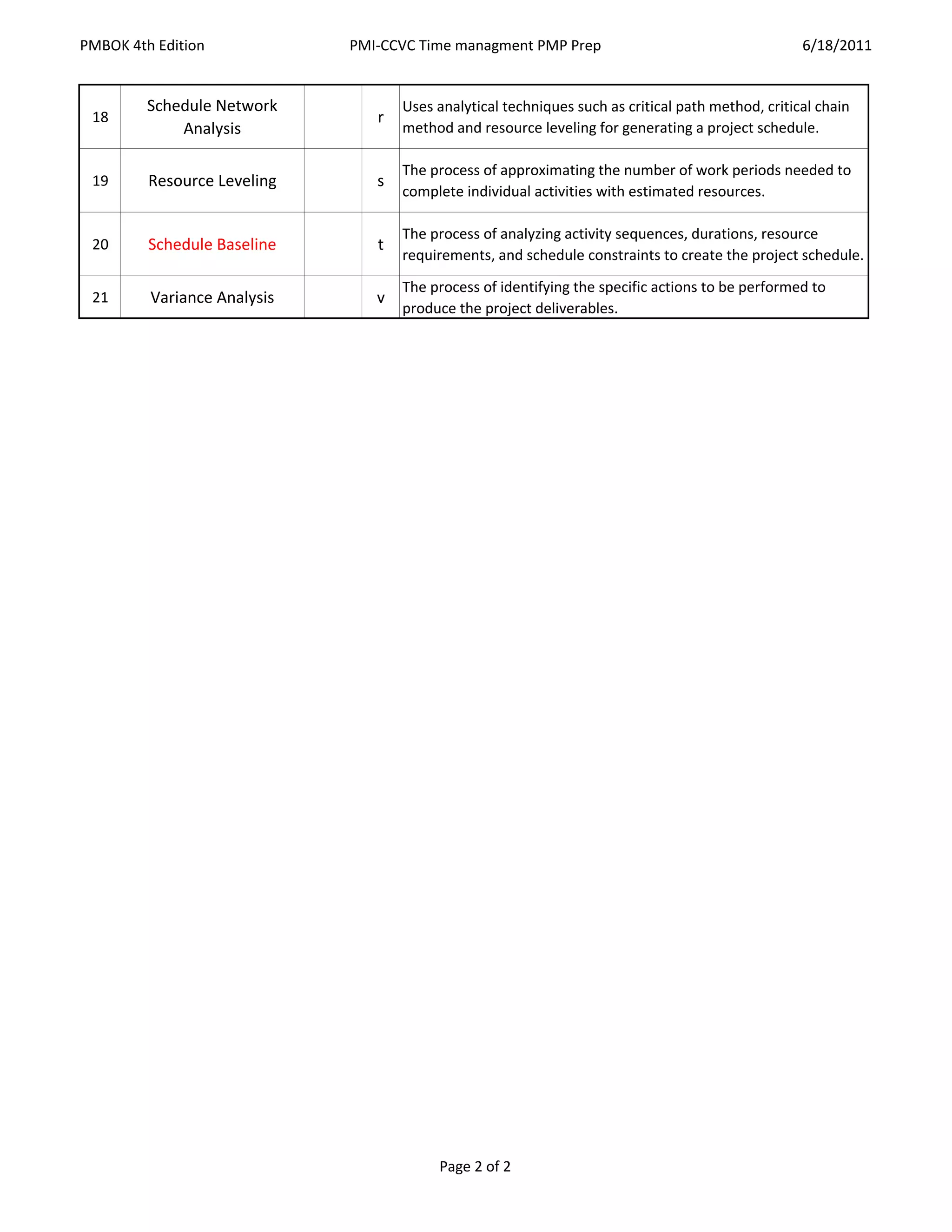
1. The document discusses various project scheduling techniques including defining activities, sequencing activities, estimating activity resources and durations, developing the schedule network, and controlling the schedule.
2. Key terms and techniques are defined, such as precedence diagramming (PDM), critical path method (CPM), resource leveling, bottom-up estimating, and earned value management.
3. The document provides an overview of 21 scheduling processes for planning, developing, and managing the project schedule.