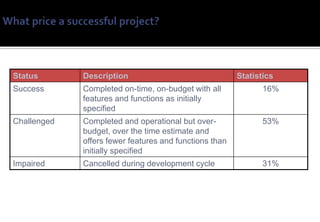
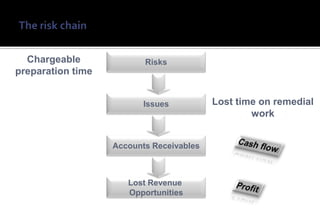
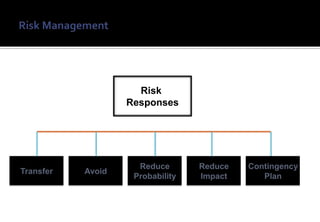
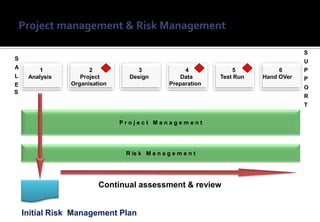
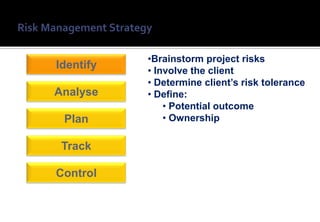
1) Risk management is an important practice for any ERP implementation project to help manage risks and increase the chances of success.
2) When estimating projects, risks are assumed but rarely communicated or managed during the project.
3) Implementing a structured risk management process provides visibility of project risks, defines risk ownership, and provides action plans to avoid or mitigate risks.