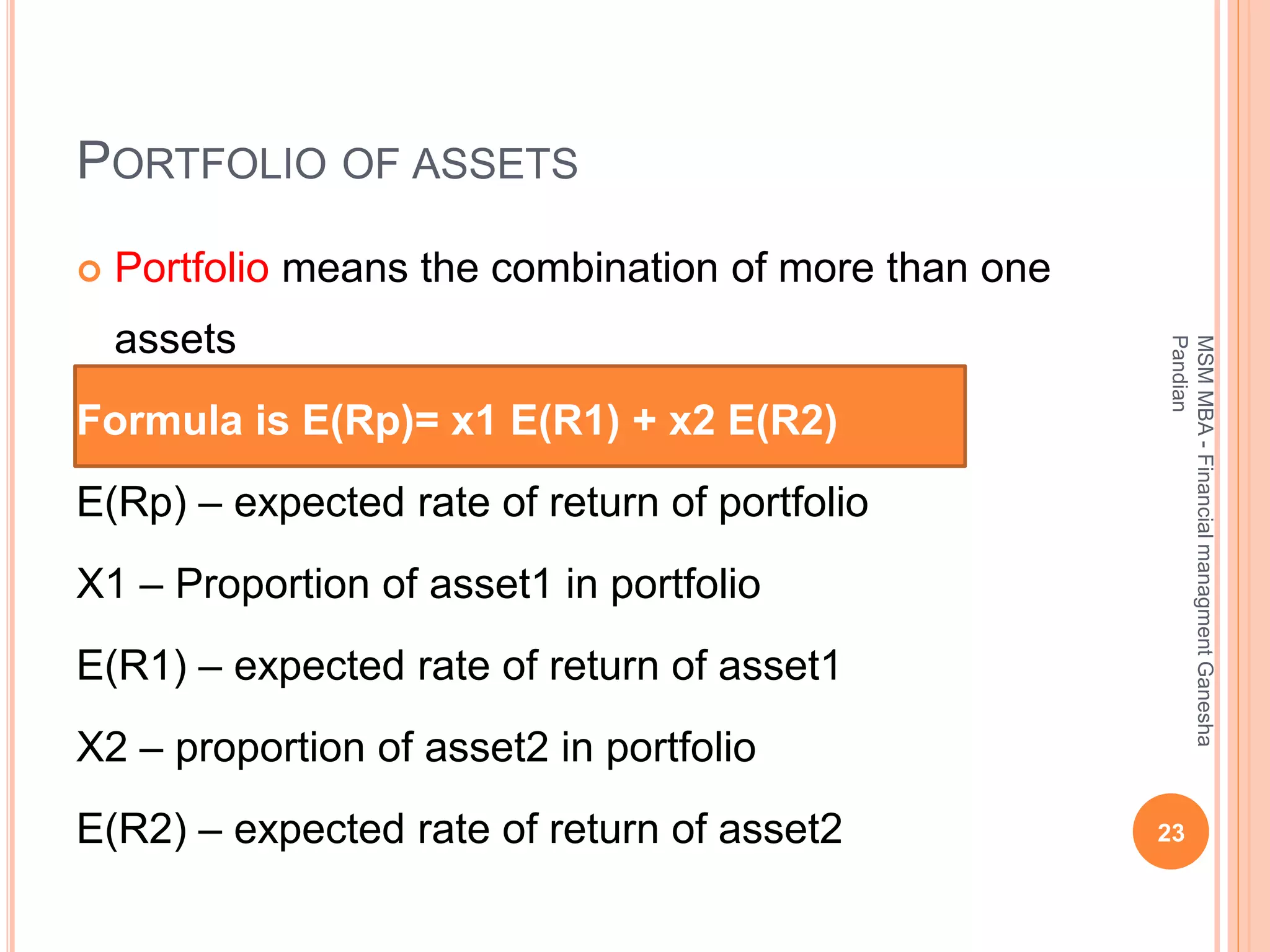
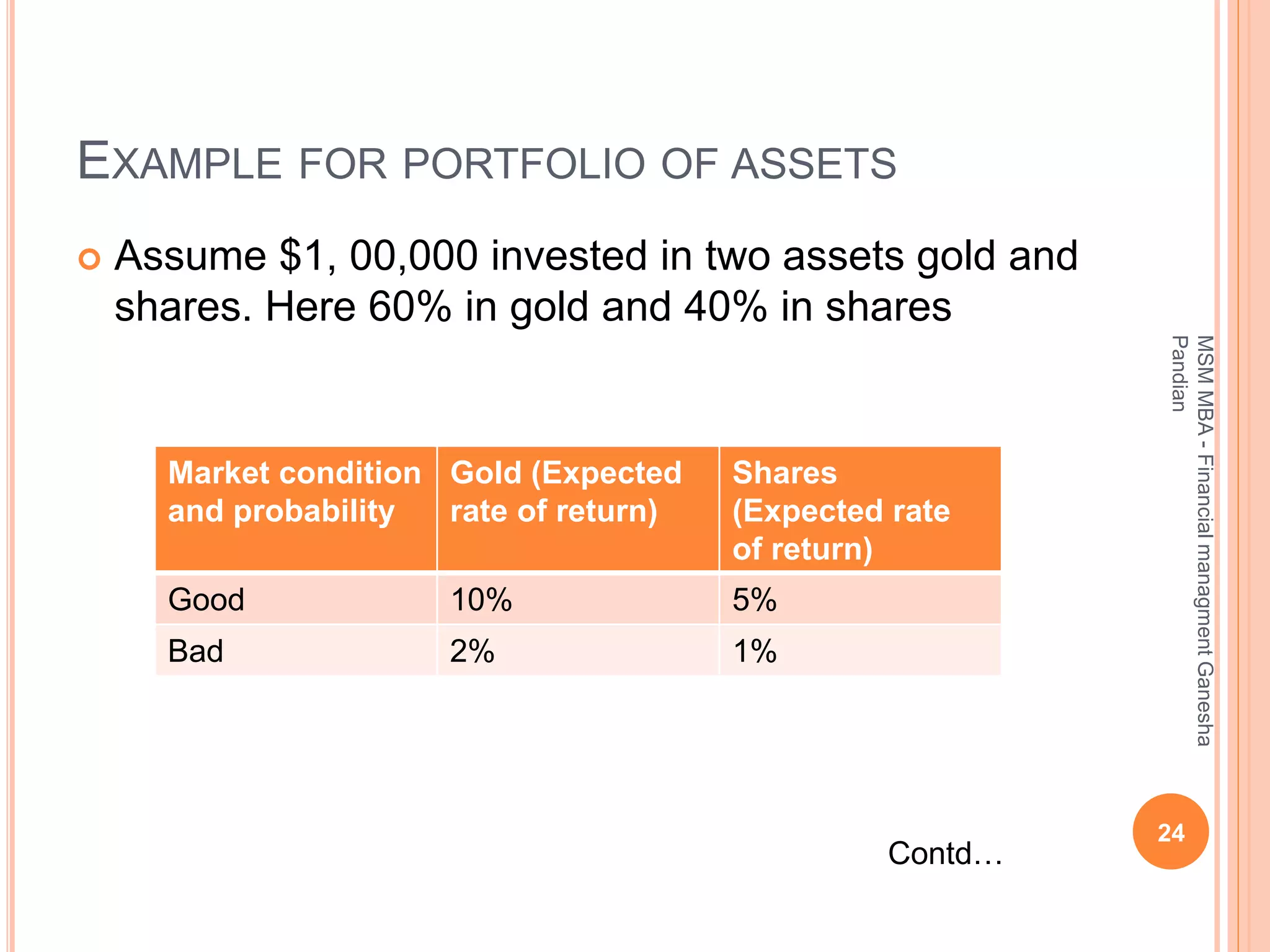
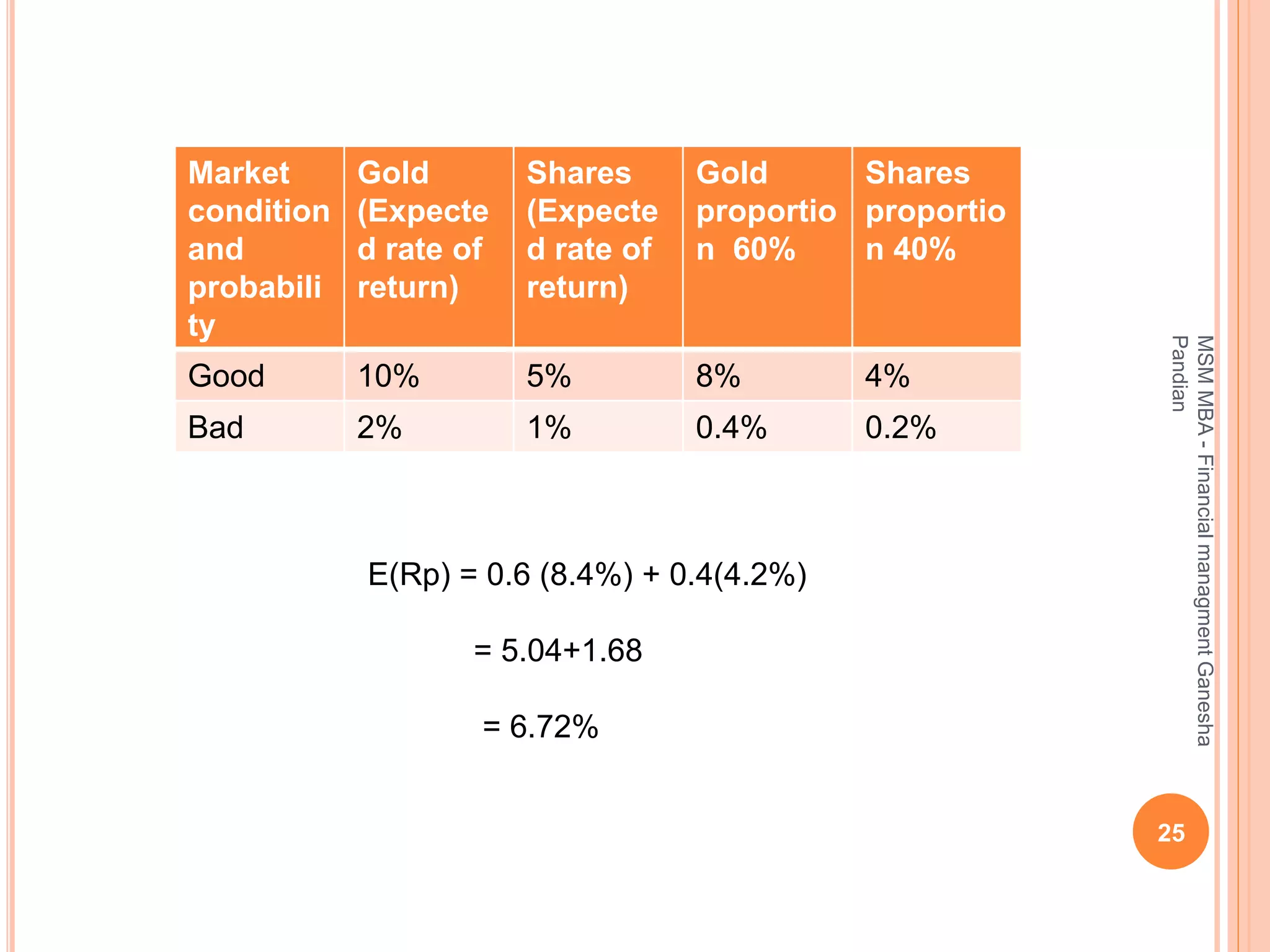
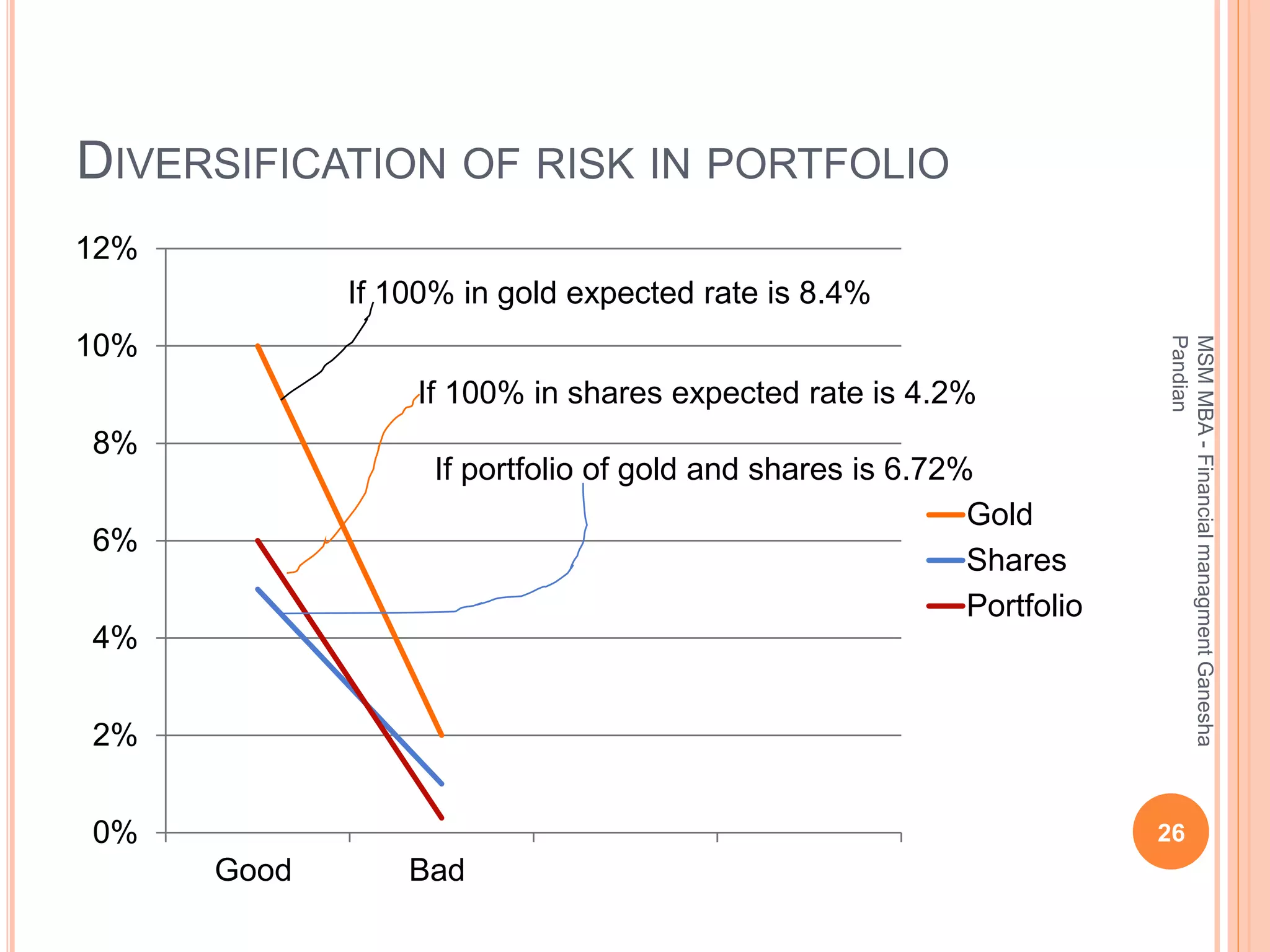
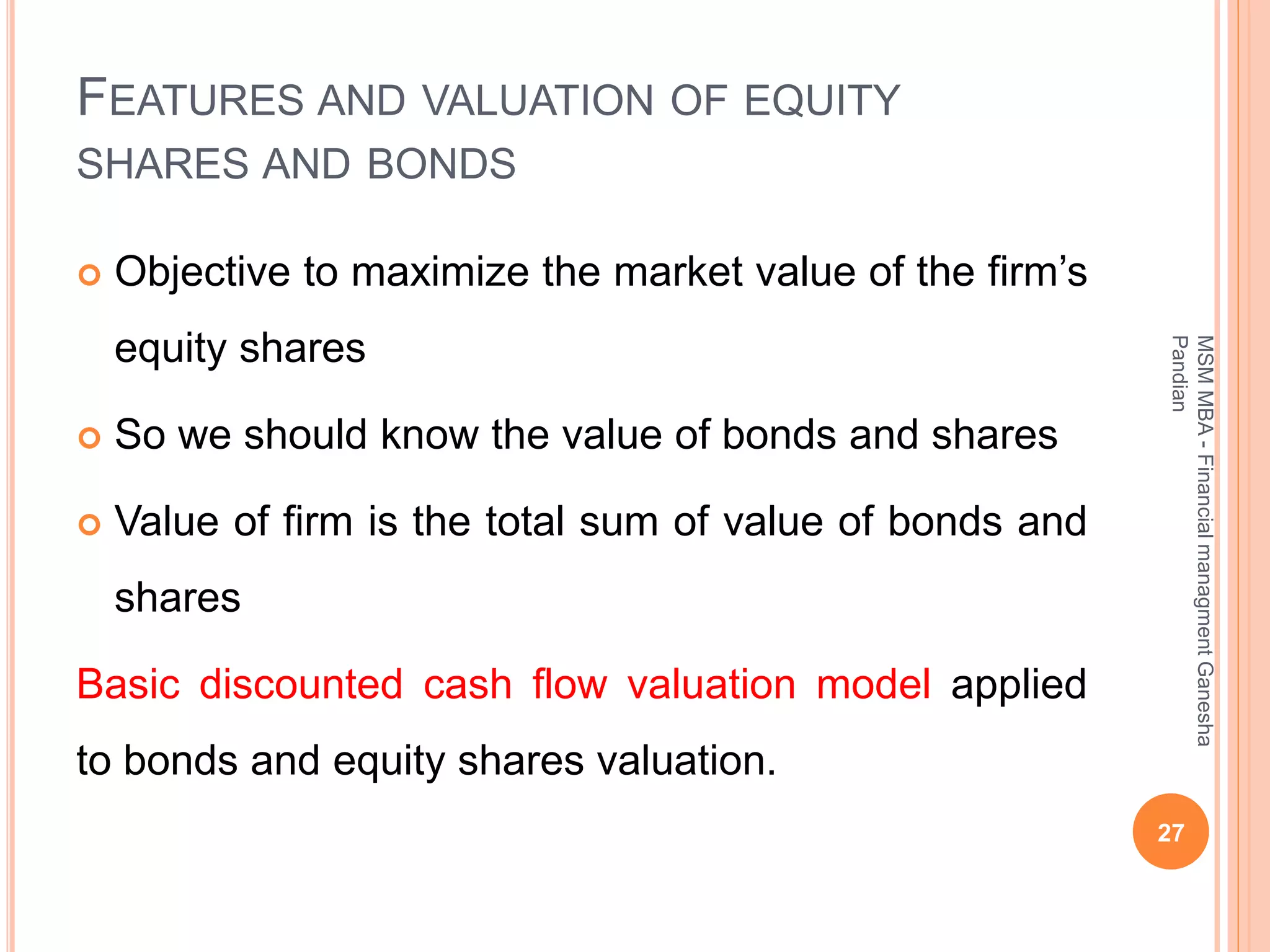
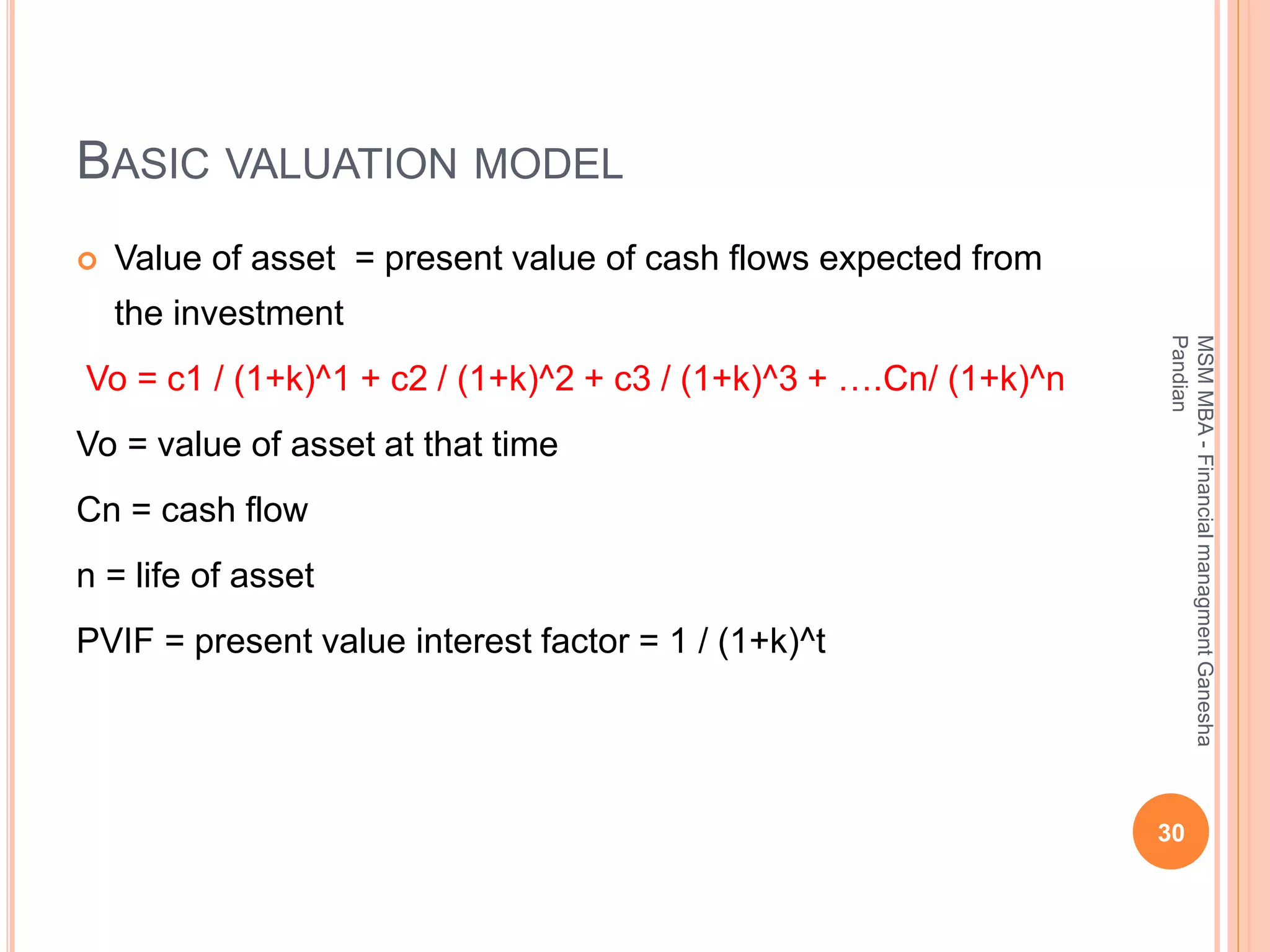
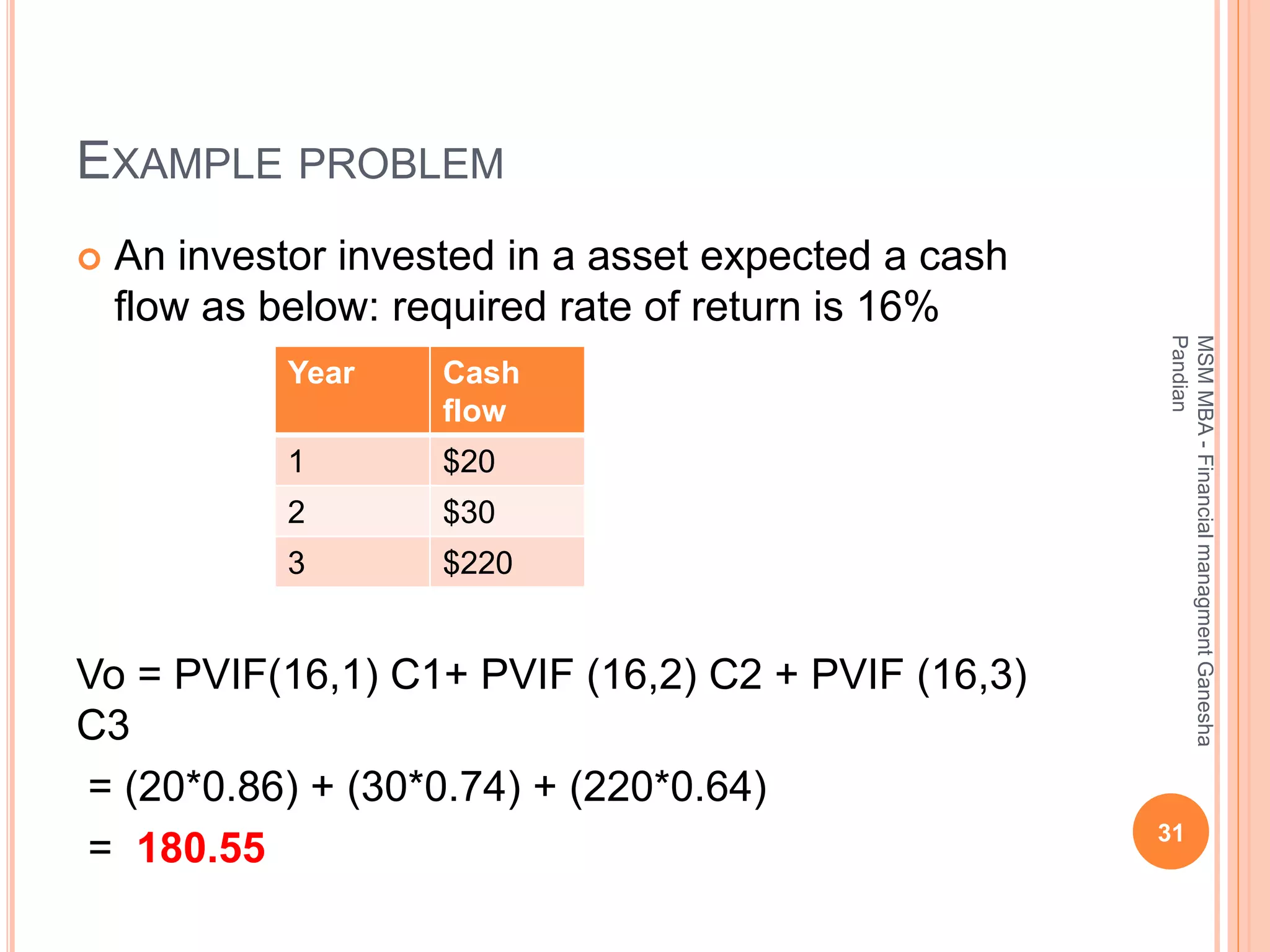
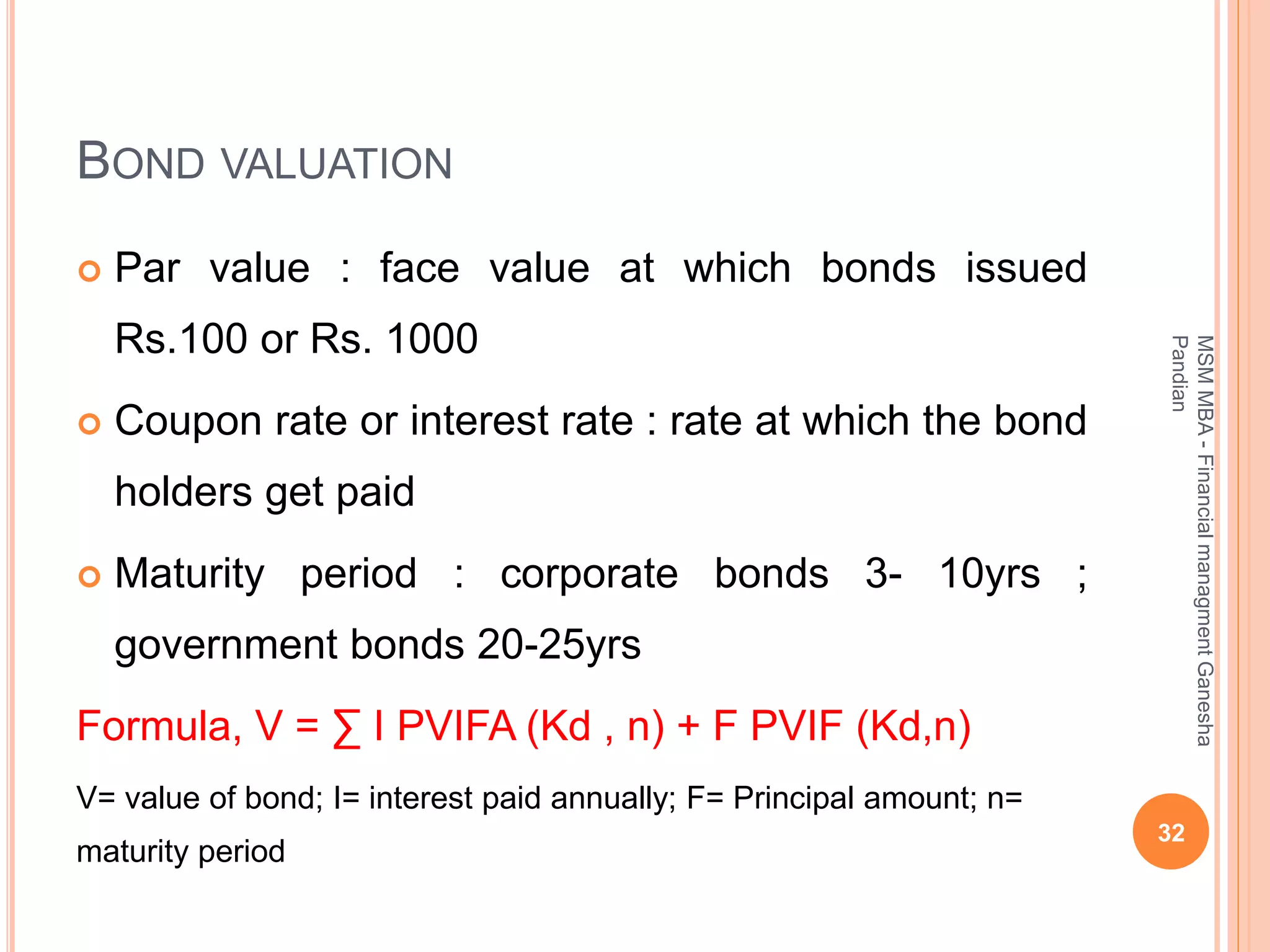
This document provides an overview of the key topics covered in the BA 5203 Financial Management unit on the foundations of finance. It introduces concepts such as financial management objectives and functions, the time value of money, risk and return analysis of single assets and portfolios. Methods for calculating present and future values are presented. The differences between equity shares and bonds are outlined. Overall it serves as an introductory guide to fundamental principles of corporate finance.


















![Formula may be refined as,
Rate of return = Annual income + End price – begin price
begin price begin price
Now rate of return = [2.4/60]+[(69-60)/60] = 0.4+0.15
= 0.19 = 19 %
19
MSMMBA-FinancialmanagmentGanesha
Pandian](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/financialmanagementunit1-180108054830/75/Financial-management-unit-1-Foundations-of-finance-19-2048.jpg)

![ Expected rate of return E(R) = 11.5%
Calculation of standard deviation of return:
= root of [ ∑ Pi (Ri – E(R))^2 ]
21
MSMMBA-FinancialmanagmentGanesha
Pandian
Econo
mic
conditi
on
Proba
bility
Pi
Rate
of
return
Ri
Pi Ri Ri –
E(R)
Ri –
E(R)^2
Pi(Ri –
E(R)^2
)
Boom 0.3 16 4.8 4.5 20.25 6.075
Normal 0.5 11 5.5 -0.5 0.25 0.125
Reces
sion
0.2 6 1.2 -5.5 30.25 6.050
Contd…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/financialmanagementunit1-180108054830/75/Financial-management-unit-1-Foundations-of-finance-21-2048.jpg)