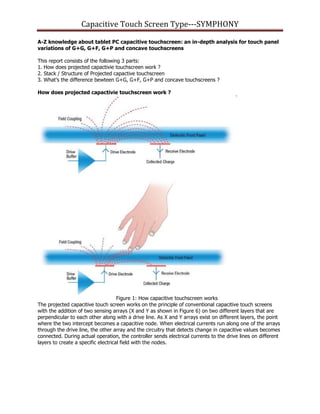
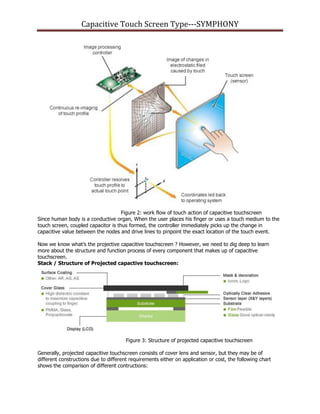
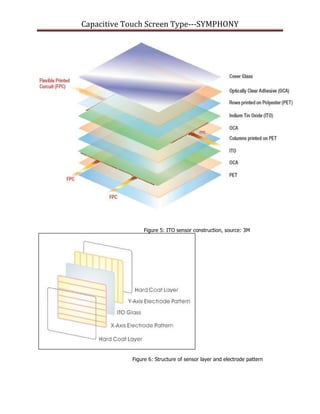
This document provides an in-depth analysis of projected capacitive touch screens, including how they work, their structure, and differences in types. It discusses how projected capacitive touch screens use two perpendicular sensing arrays to detect touch locations. The structure generally involves a cover lens and sensor, which can be constructed in different ways, such as G/G (glass/glass), G/F (glass/film), or G/P (glass/PET). The main difference between types is whether the lens is glass or film. Concave touch screens are most common due to their low-cost single ITO layer glass sensor with a printed film.

![Capacitive Touch Screen Type---SYMPHONY
Figure 7: Mutual Capacitance Rows and Columns
Figure 8: capacitive sensing
Sensor grid in diamond patterns are printed on the ITO sensor. As shown above.
Mutual capacitance is the intentional or unintentional capacitance between two "charge holding objects."
Projected capacitance touchscreens intentionally create mutual capacitance between ele¬ments of
columns and rows [see figure 8] in the vicinity where each intersect the other. This allows the system
electronics to measure each node (intersection) individually to detect multiple touches on the screen
during one screen scan.
When a finger touches near an intersection, some of the mutual capacitance between the row and
column is coupled to the finger which reduce the capacitance at the intersection as measured by the
consystem electronics. This reduced capacitance crosses the "touch threshold" set by the electronics
indicating a touch has occurred.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capacitivetouchtechnology-140824060951-phpapp01/85/Capacitive-touch-technology-5-320.jpg)
