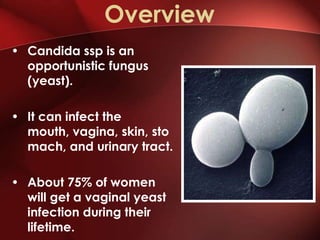
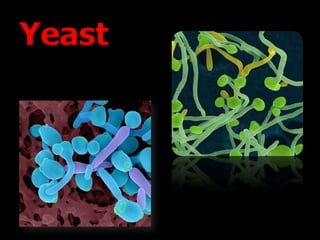
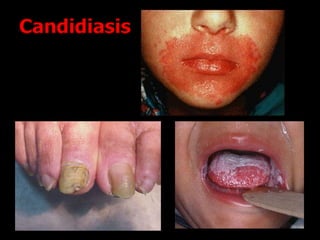
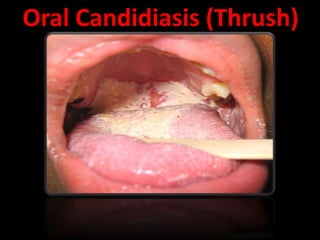
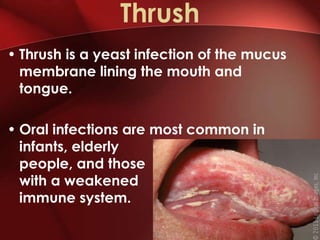
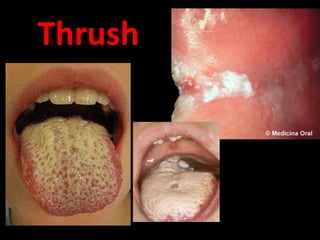
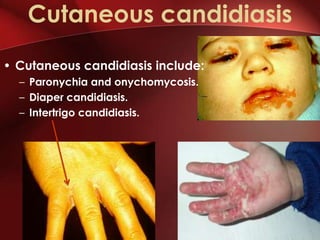
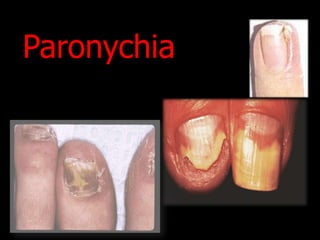
Candida is a common fungus that can cause infections in humans. It normally lives on the skin and mucosal surfaces without causing problems, but under certain conditions it can overgrow and lead to candidiasis. Candidiasis includes infections of the mouth (thrush), skin, esophagus, and vagina. Risk factors include diabetes, pregnancy, HIV/AIDS, and broad-spectrum antibiotic use. Symptoms vary by location but may include redness, cracks, sores, white patches or lesions, itching, and pain. Treatment involves topical or oral antifungal medications.