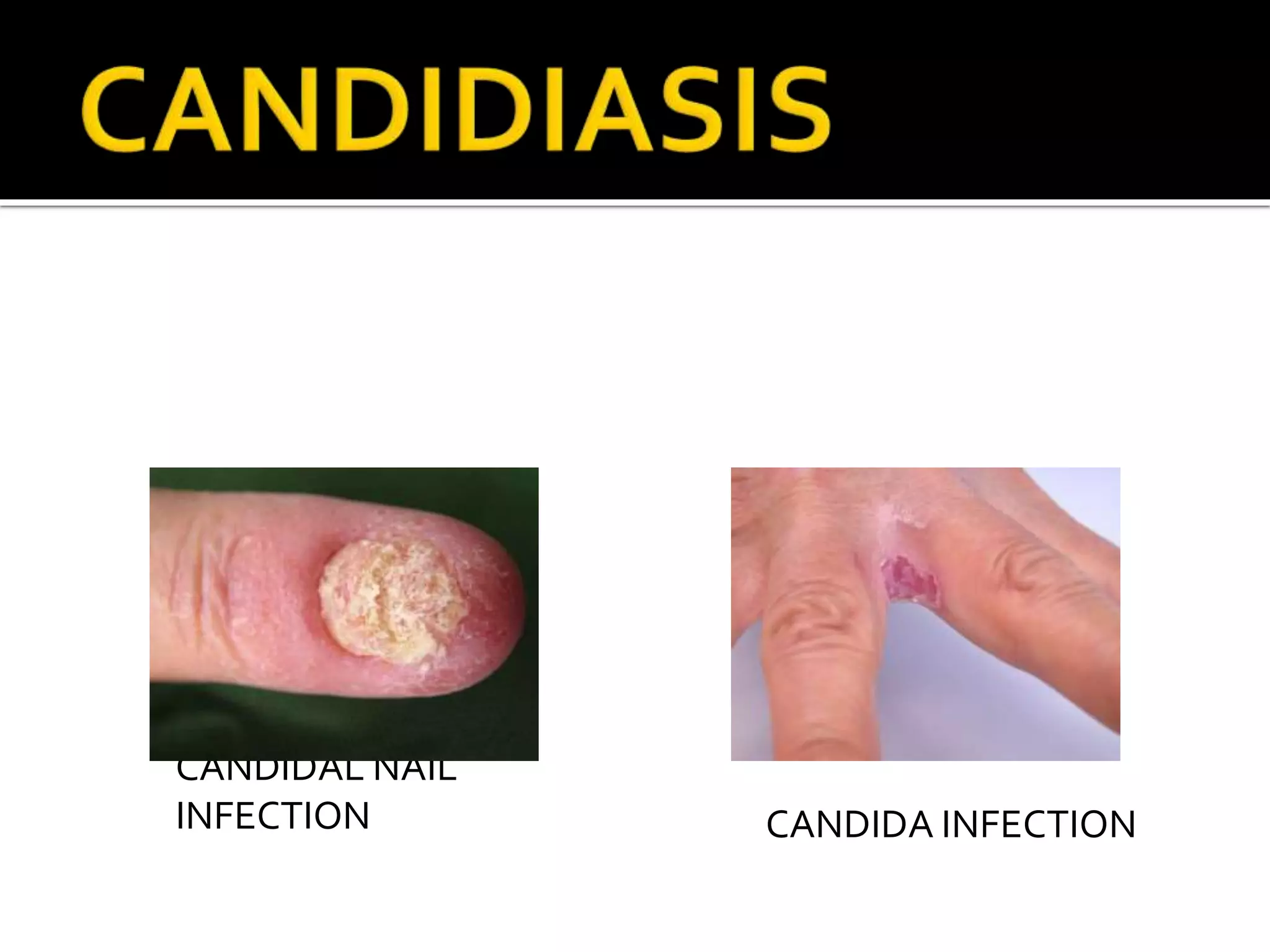
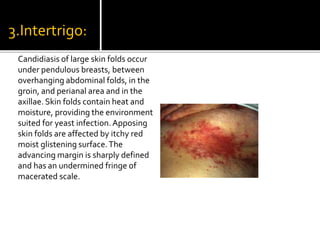
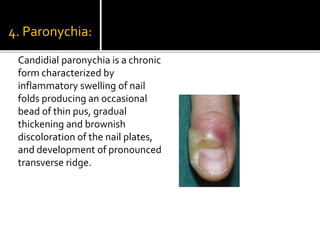
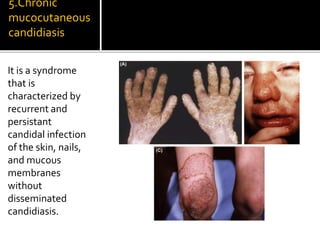
Candida is a common fungus that can cause infections in humans. It normally lives harmlessly in the digestive tract but can cause issues if the host's immune system is compromised. Common types of candidal infections include oral thrush, vaginal yeast infections, skin infections in moist areas like skin folds. Diagnosis involves microscopic examination of samples showing fungal structures. Treatment focuses on antifungal medications and reducing moisture and occlusion.