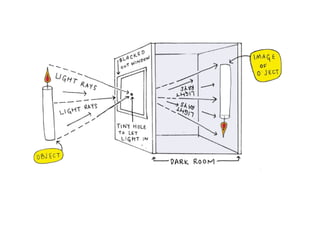
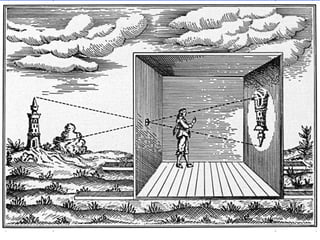
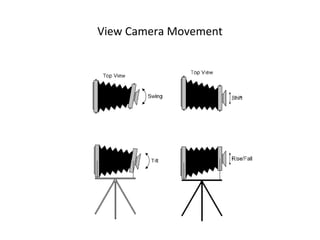
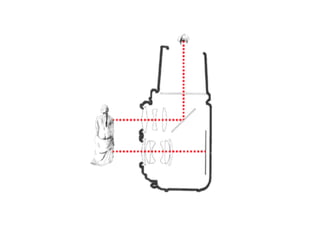
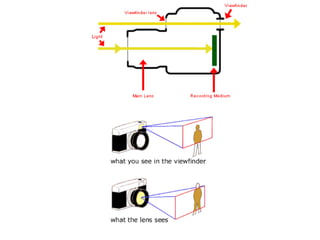
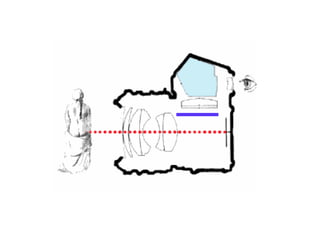
This document discusses different types of cameras. It describes five main types: pinhole cameras, view cameras, twin lens reflex cameras, rangefinder cameras, and single lens reflex cameras. Pinhole cameras have no lens and rely on a tiny hole, while view cameras consist of two boards linked by a bellows. TLRs have two identical lenses, one for viewing and one for capturing images. Rangefinder cameras use separate lenses for viewing and capturing with a focusing device. SLRs allow viewing through the capturing lens using mirrors and provide many adjustable options. Other camera types discussed include point and shoot, bridge, instant, stereo, and disposable cameras.