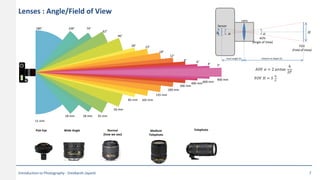
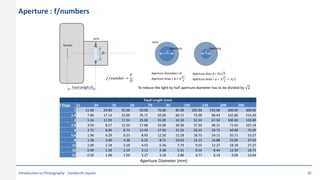
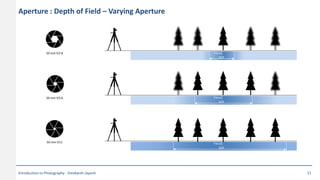
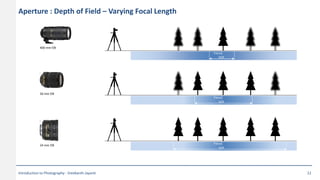
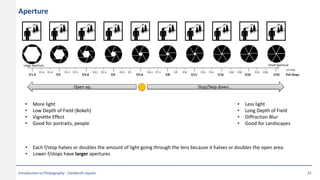
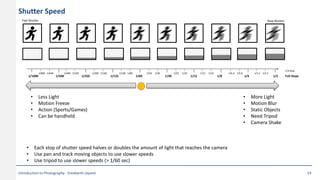
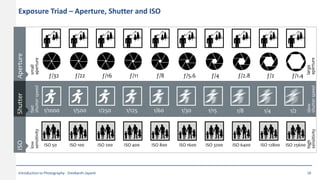
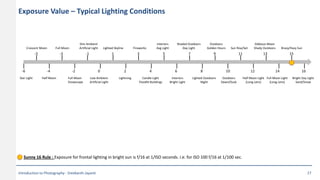
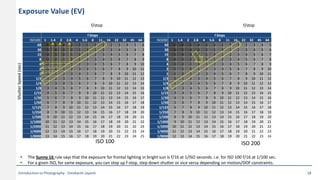
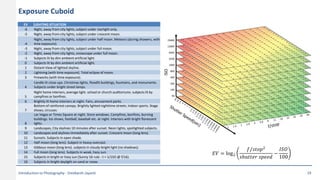
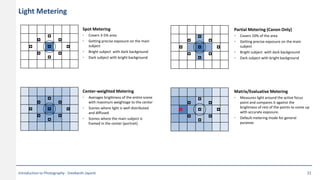
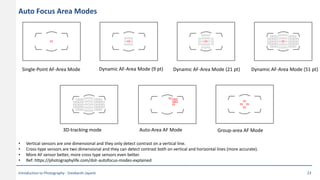
This document provides an introduction to photography concepts including camera parts, lenses, exposure fundamentals involving aperture, shutter speed, and ISO. It discusses different types of lenses and their uses. It explains aperture in terms of f-numbers and its effect on depth of field. It also covers shutter speed and how it can be used to freeze motion or blur it. Film/sensor speed and sensitivity are explained. The exposure value chart shows typical lighting conditions.