Embed presentation
Download to read offline


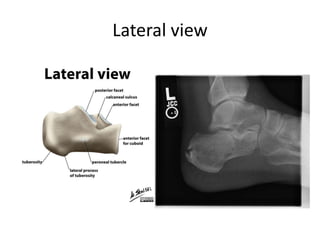


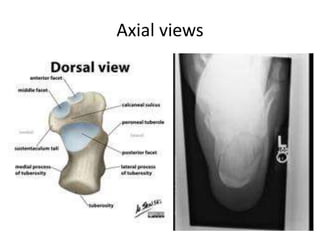
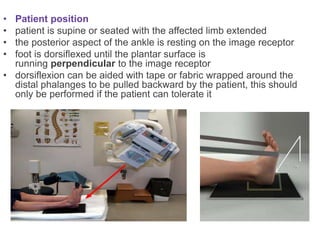

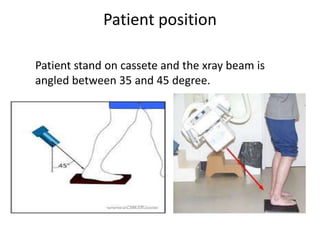
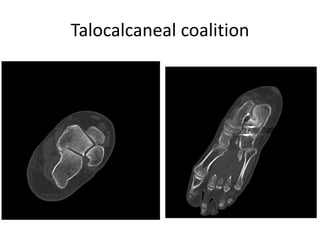
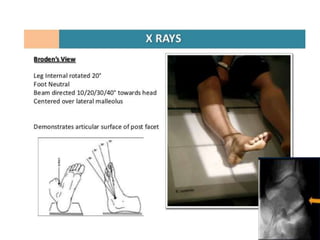


This document provides instructions for three radiographic views of the calcaneum: the lateral view, which assesses the calcaneum and surrounding joints from the side; the axial view, which images the talocalcaneal joint and plantar calcaneum from above; and the Harris view, a specialized projection used to detect talocalcaneal coalition. Patient positioning instructions are outlined for each view, including recumbent, supine, seated, or standing positions and manipulation of the foot and leg.











