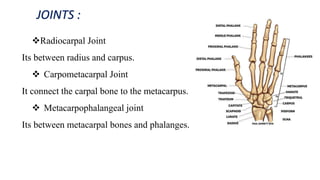
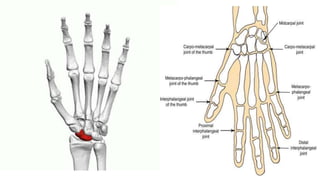
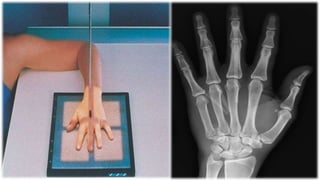
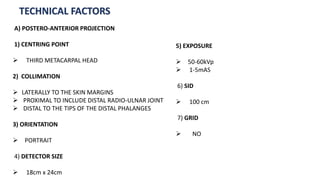
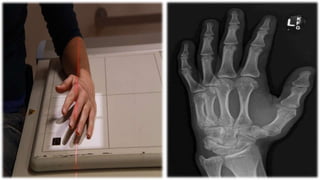
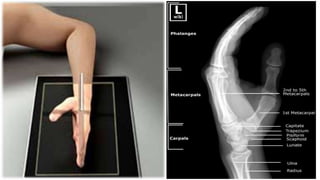
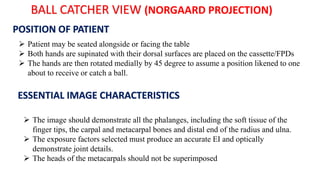
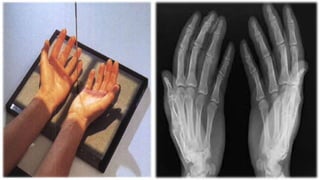
The document details the anatomy and projections of the hand, highlighting the three major types of bones: phalanges, metacarpals, and carpals. It covers various joints and outlines the indications and basic supplementary projections used in radiographic imaging of the hand. Essential imaging techniques and characteristics are specified to ensure accurate representation of the anatomical structures.