Embed presentation
Downloaded 38 times

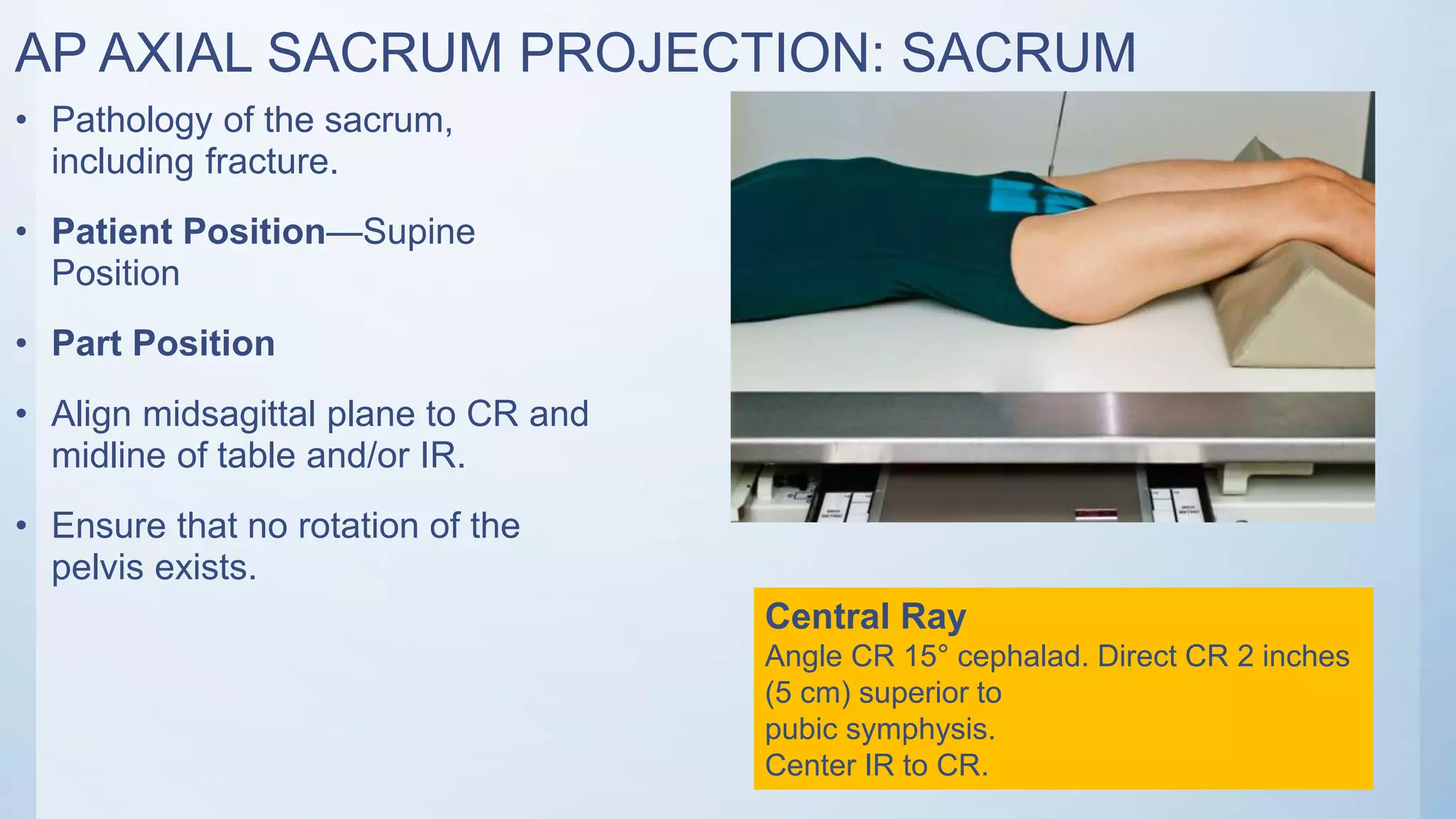
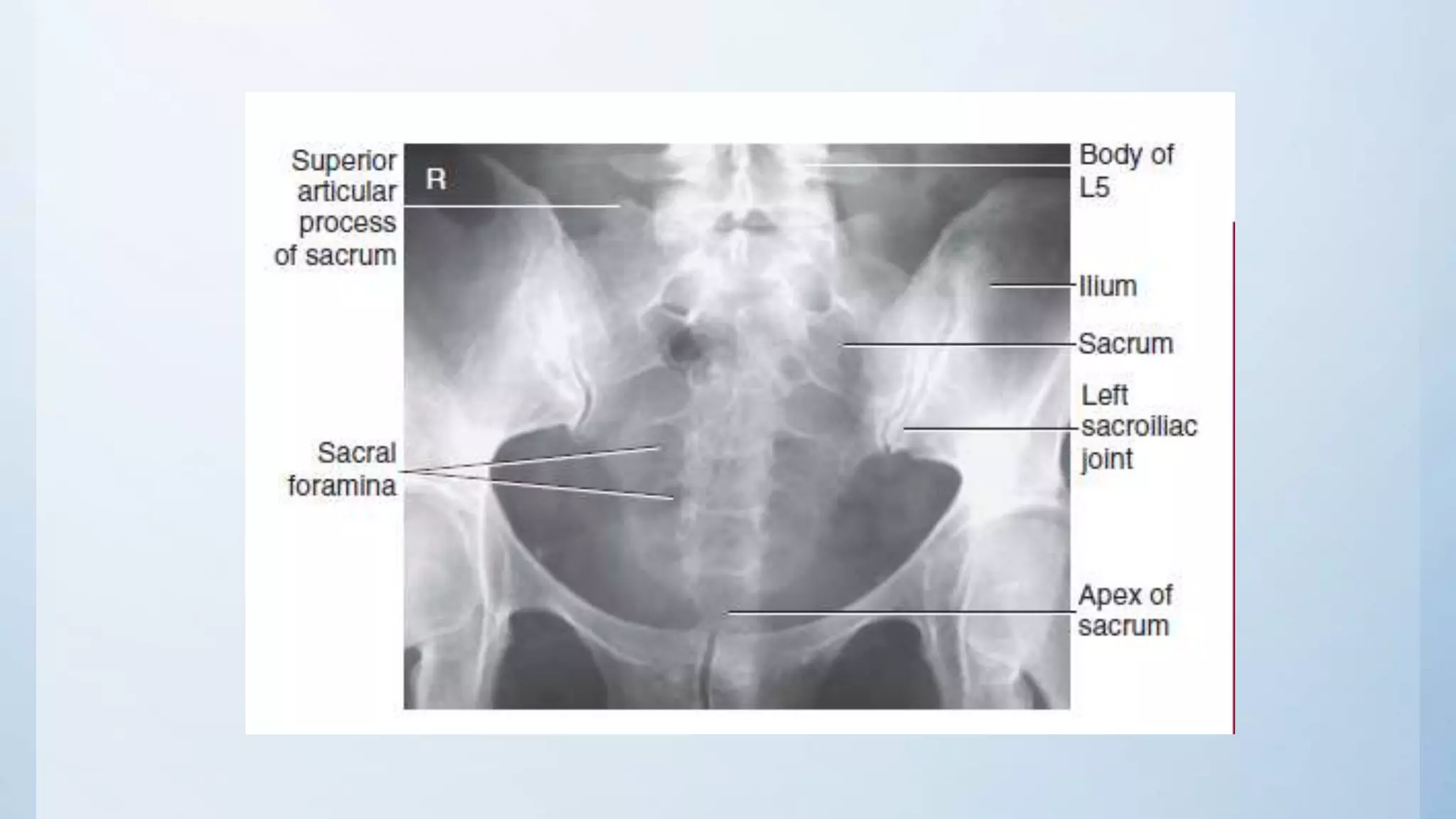
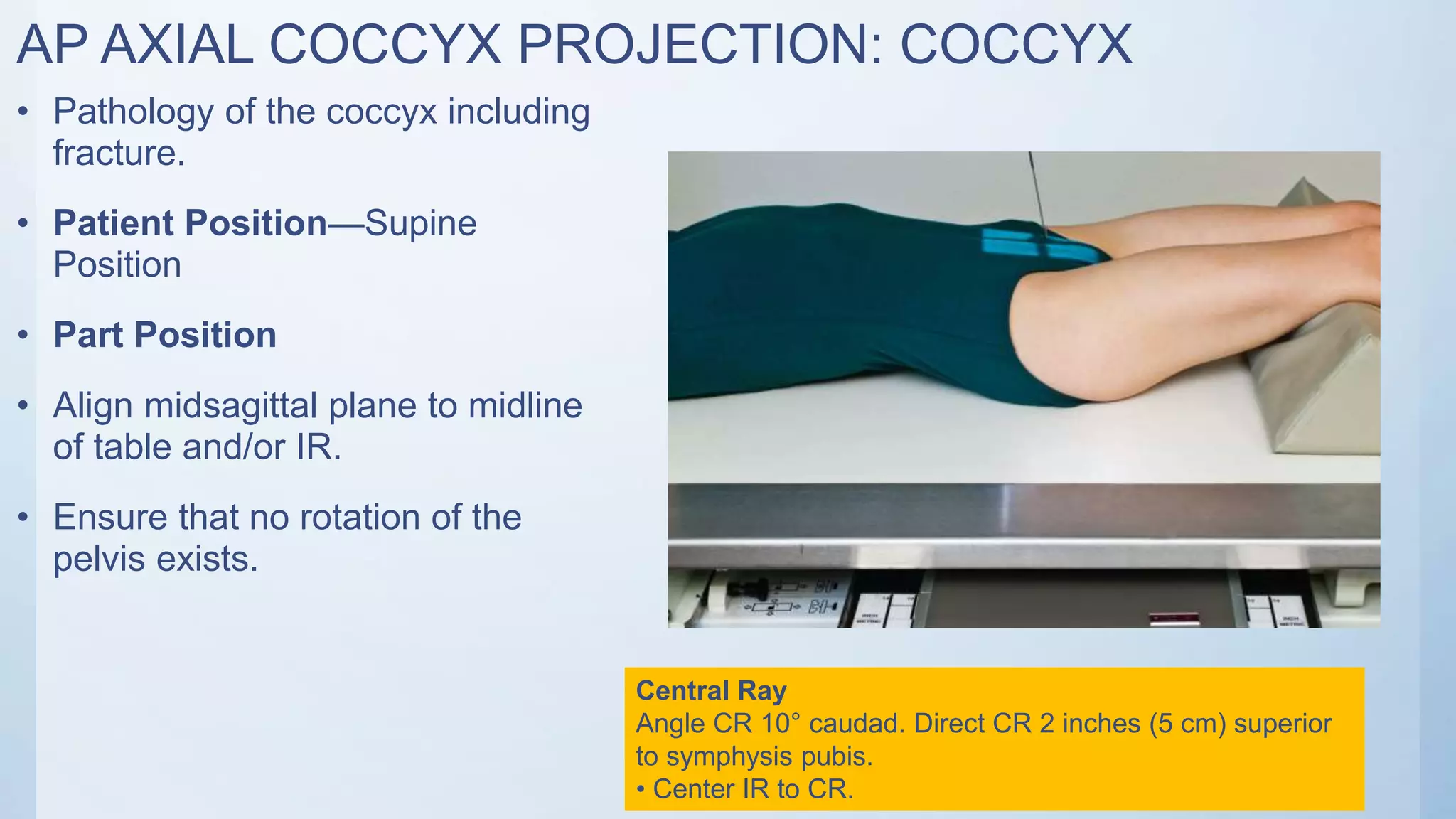


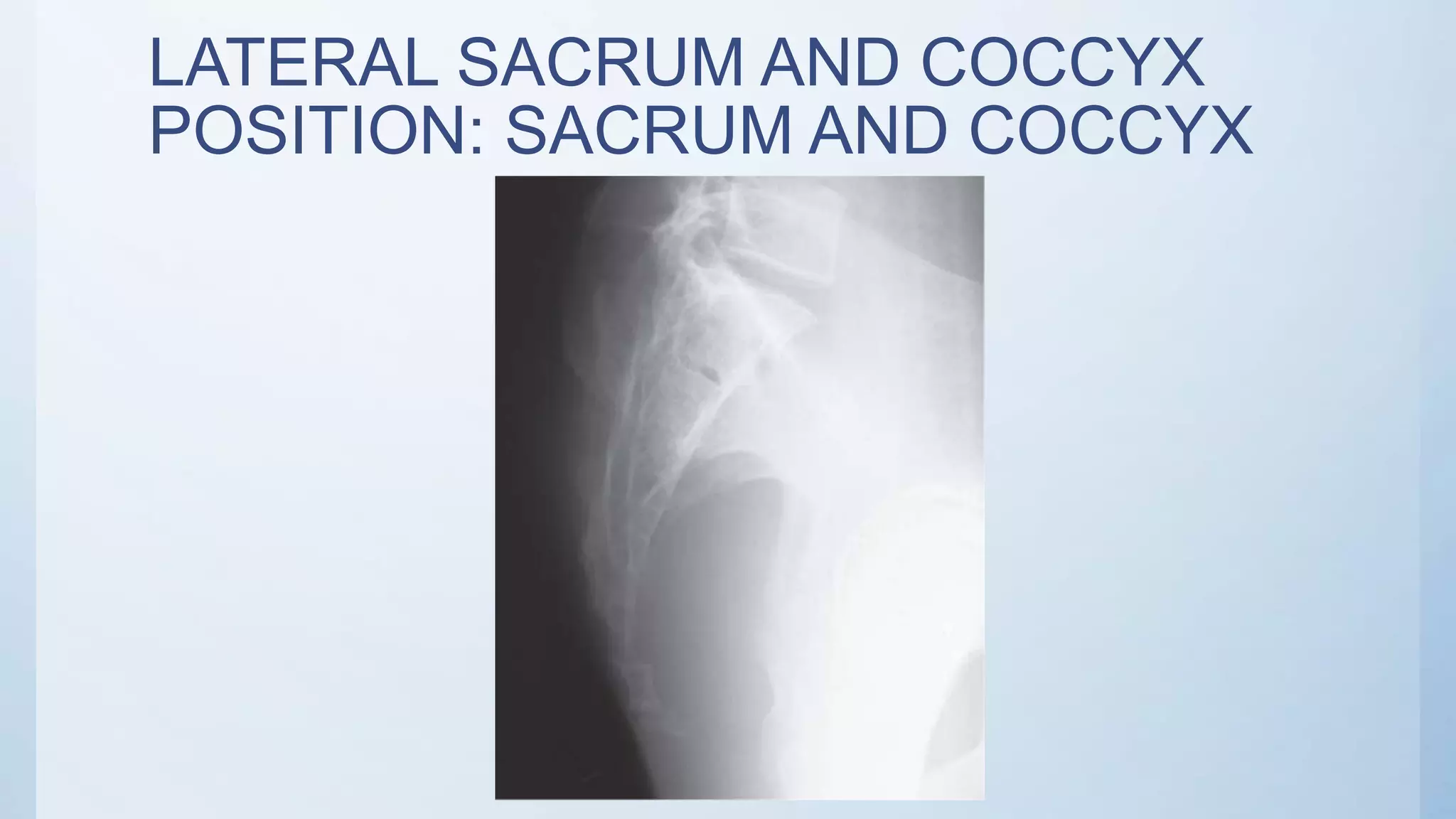

The document describes the positioning and technique for three common radiographic views of the sacrum and coccyx: 1) AP axial sacrum projection is taken with the patient supine and the central ray angled 15 degrees cephalad and directed 2 inches superior to the pubic symphysis to view pathology of the sacrum, including fractures. 2) AP axial coccyx projection similarly has the patient supine but with the central ray angled 10 degrees caudad and directed 2 inches superior to the pubic symphysis. 3) Lateral sacrum and coccyx projection is done with the patient in a lateral recumbent position and the central ray perpendicular to the image receptor and directed 3







