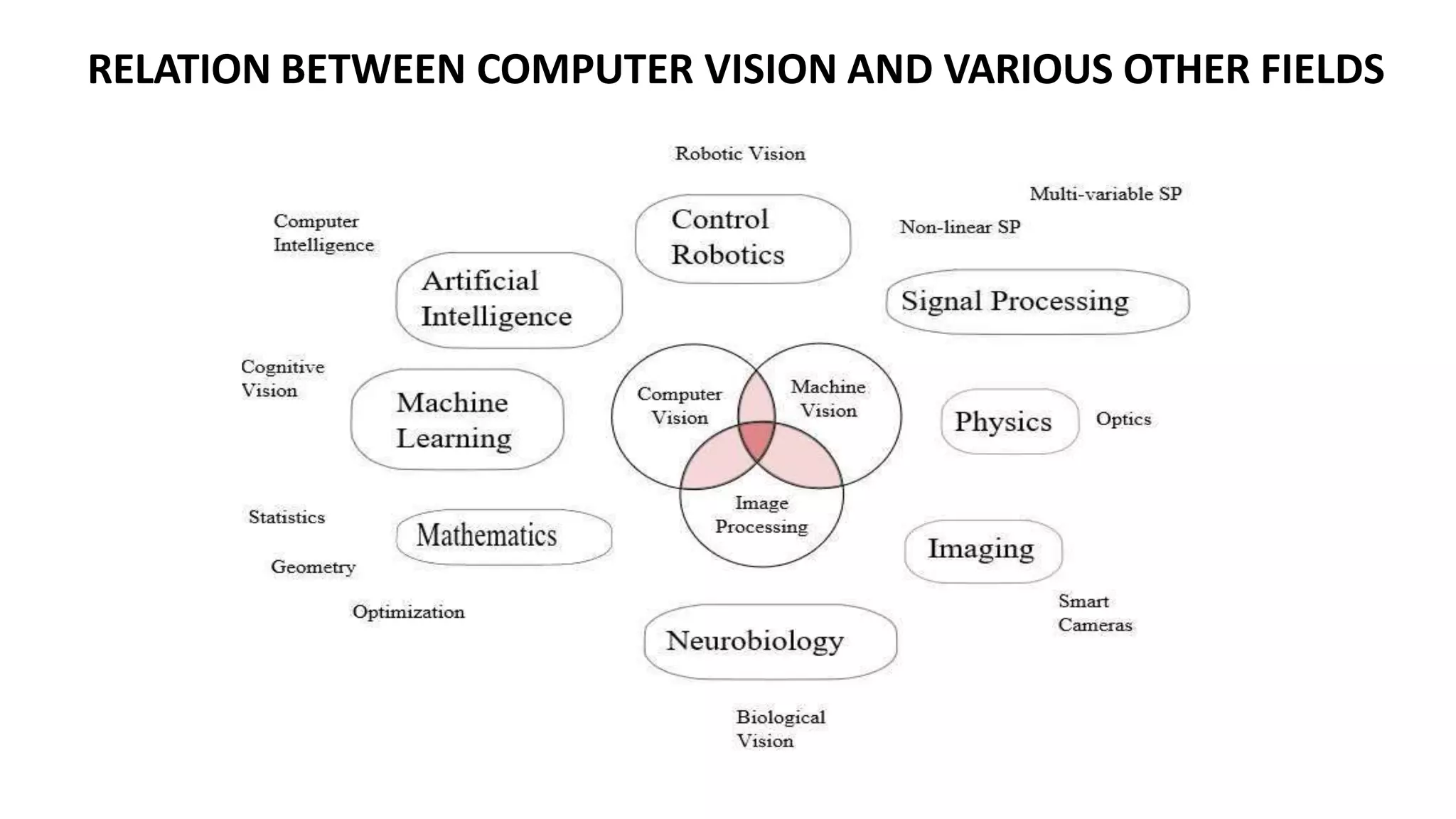
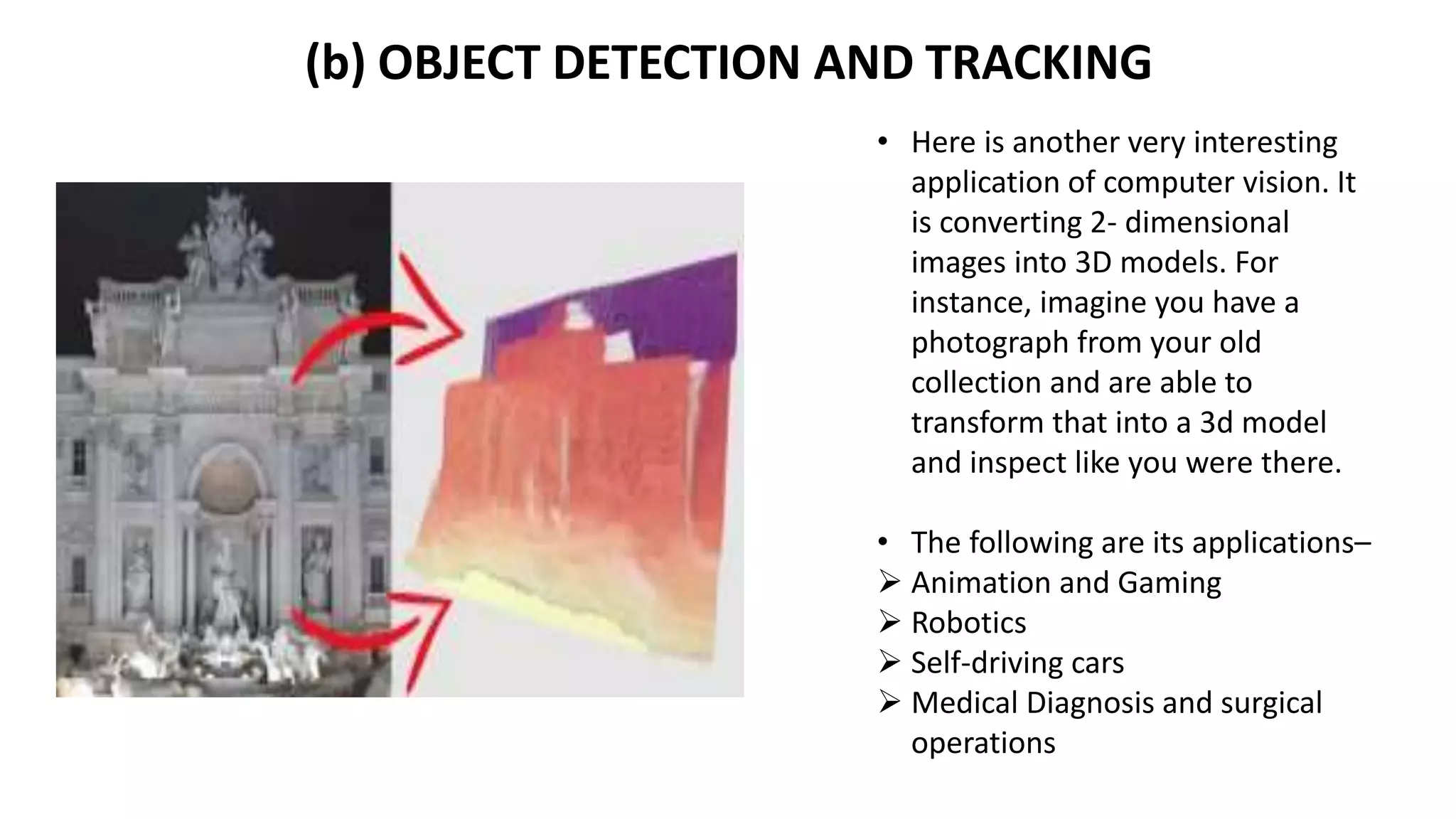
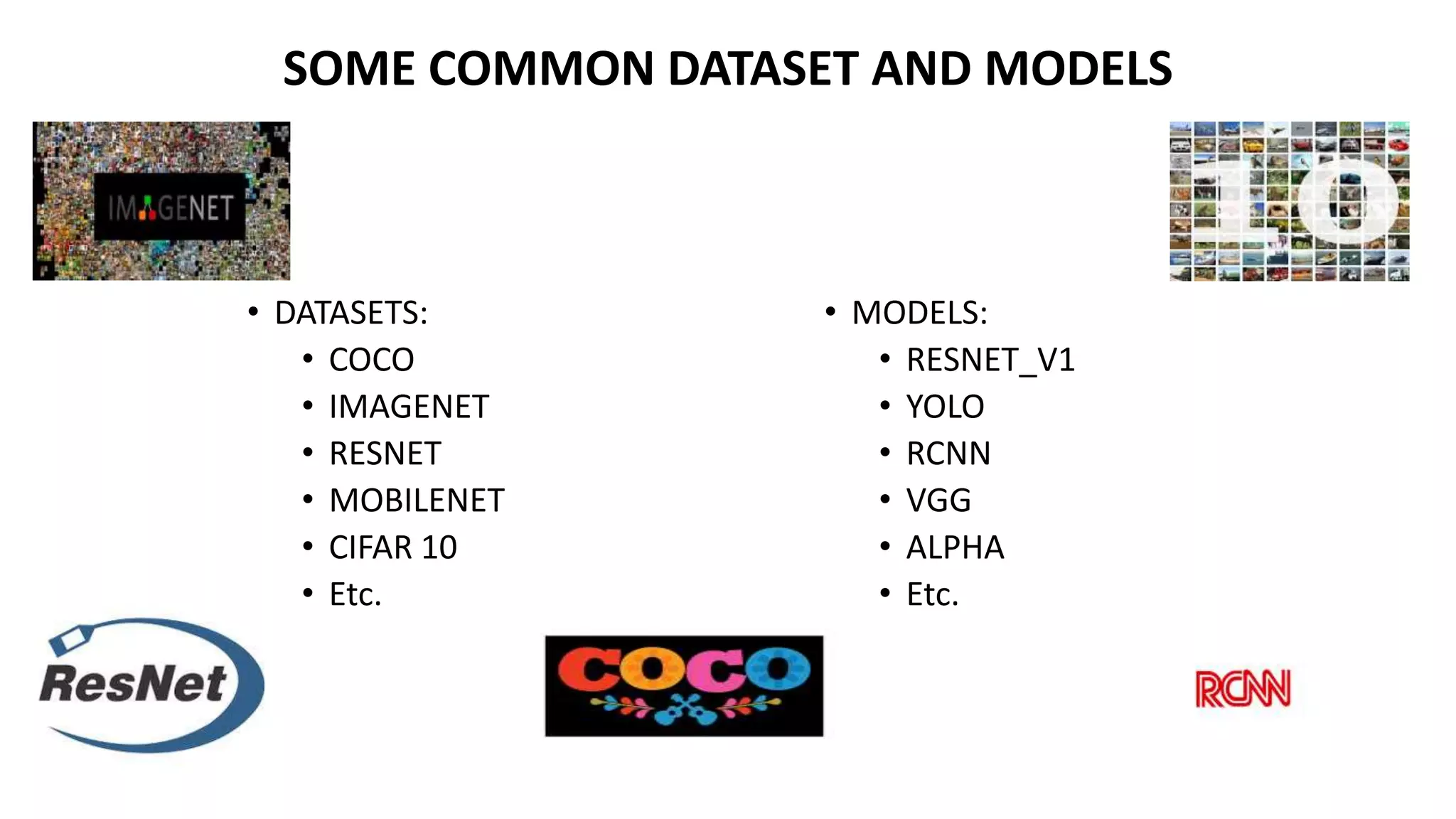
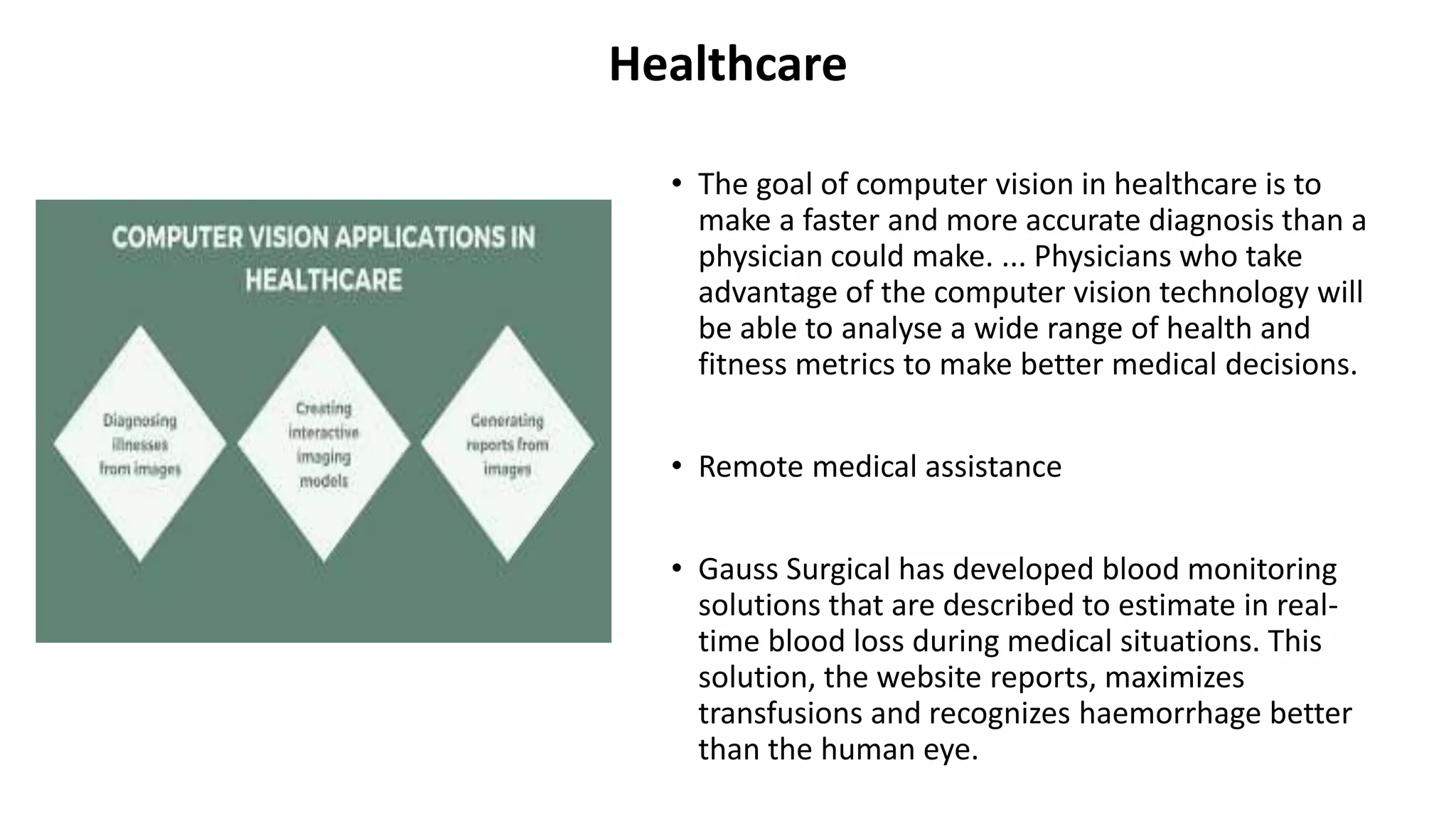
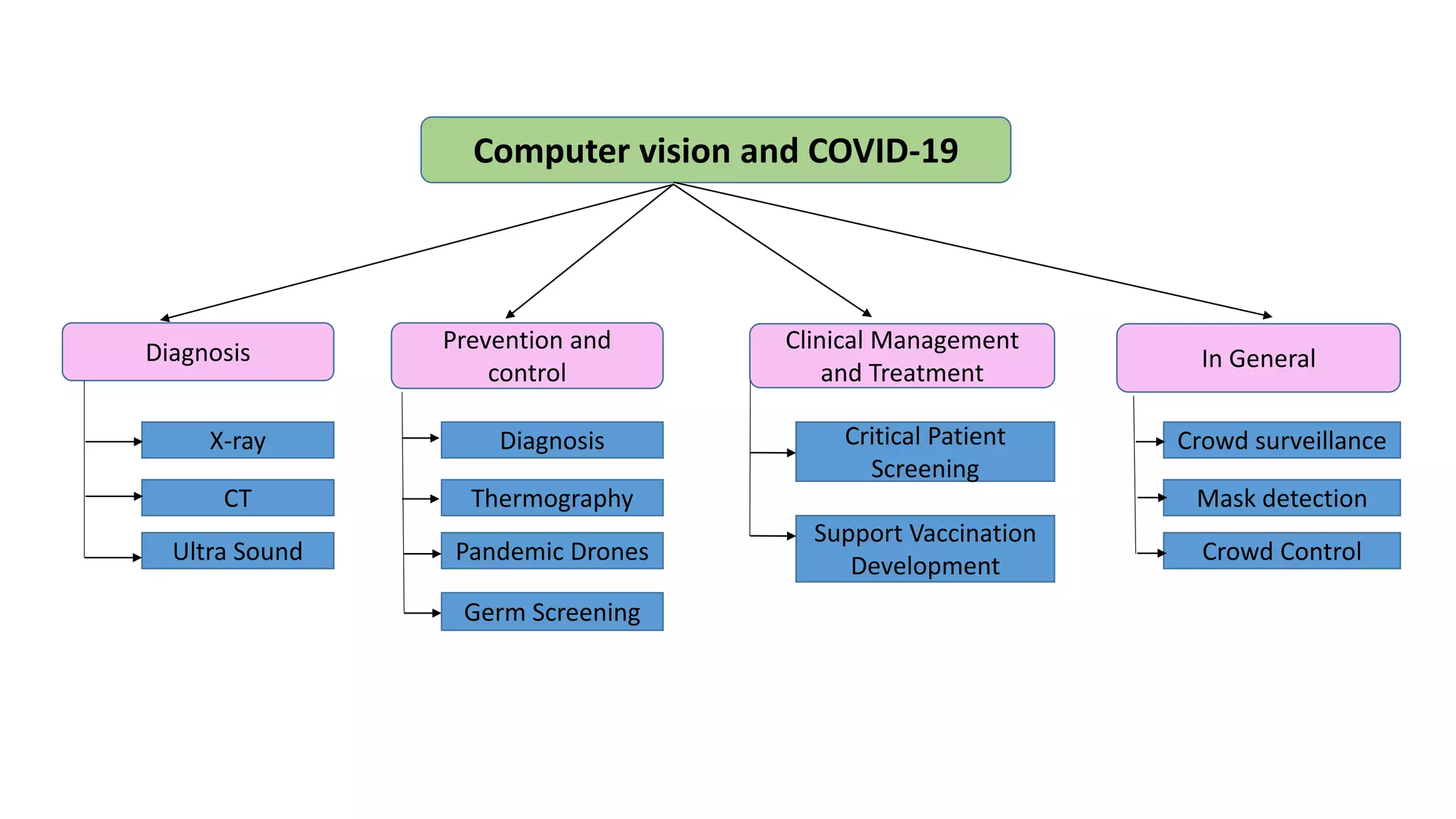
This document provides an overview of computer vision including its definition, applications, working concepts, popular models and datasets, advantages, and disadvantages. Computer vision is a field that uses computer algorithms to gain a high-level understanding from digital images or videos. It has applications in areas like face detection, object detection and tracking, developing social distancing tools, and medical image analysis. Popular computer vision models include ResNet, YOLO, and MobileNet, and datasets include COCO, ImageNet, and CIFAR10. Advantages are faster and more reliable processing while disadvantages include needing specialists and potential failures in image processing. The document also discusses uses of computer vision for COVID-19 response and in areas like healthcare, automotive, and retail