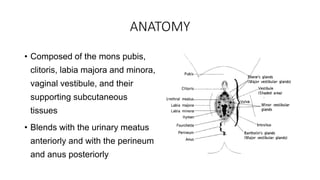
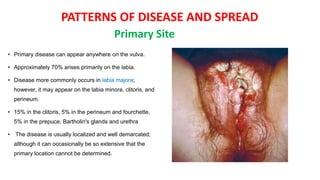
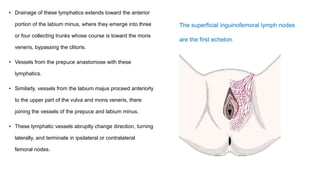
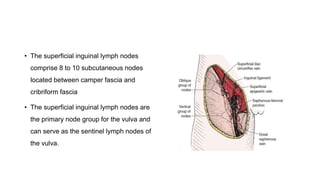
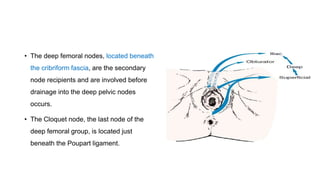
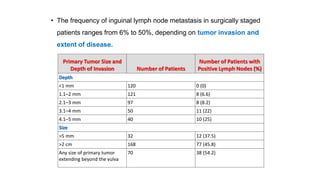
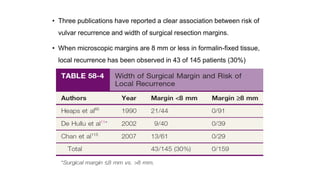
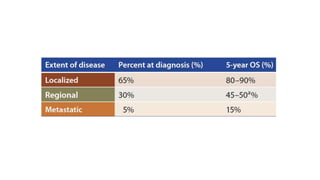
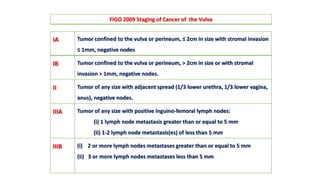
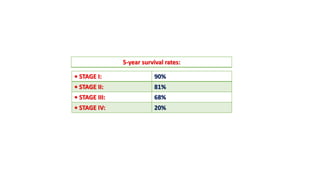
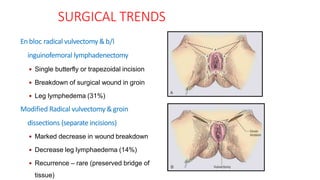
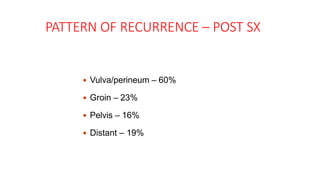
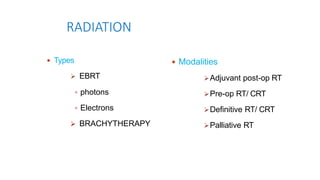
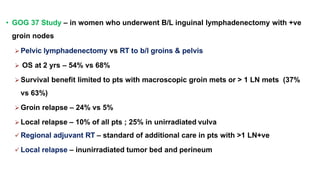
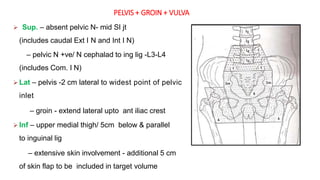
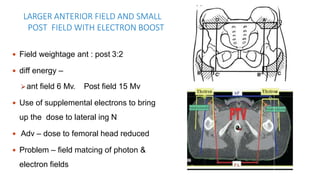
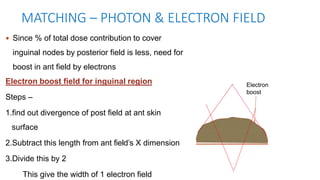
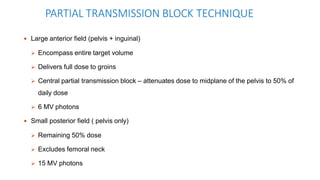
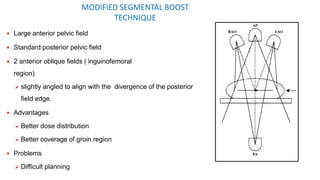
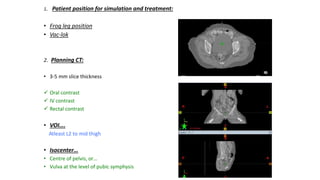
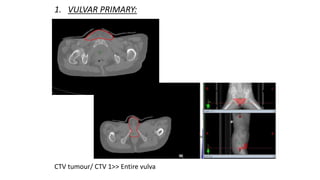
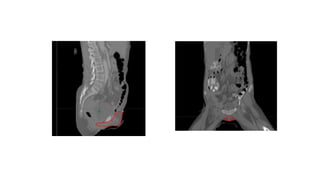
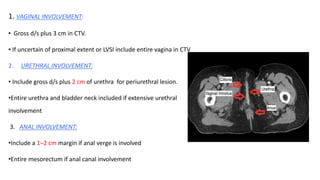
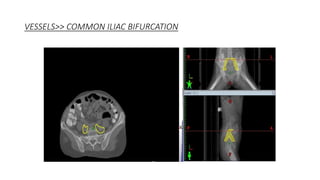
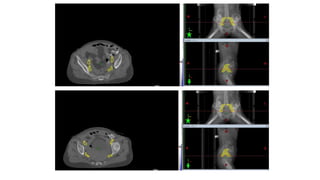
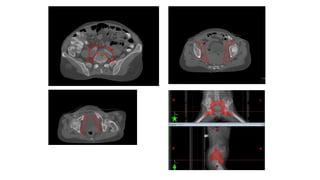
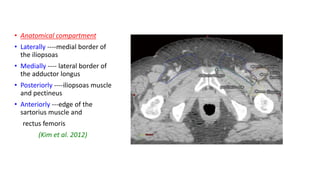
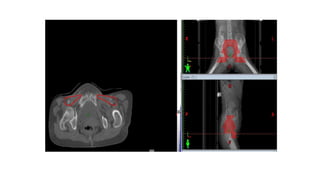
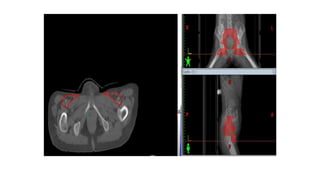
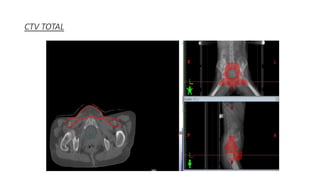
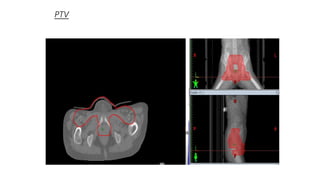
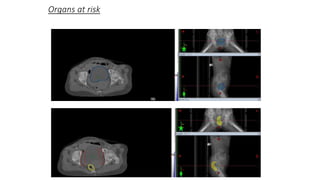
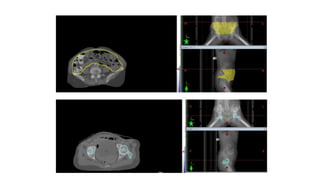
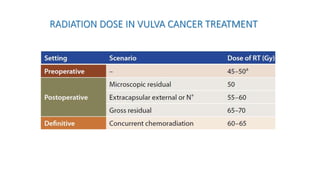
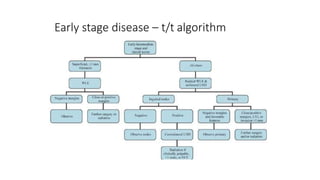
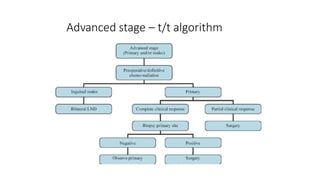
Vulvar cancer is a rare malignancy that represents less than 1% of cancers in women. It occurs most commonly in two age groups - younger women who smoke and are HPV-positive, and older women who may have epithelial dystrophies as risk factors. Lymphatic drainage is primarily to the superficial inguinal lymph nodes, with potential spread to deep femoral and pelvic nodes. Positive lymph nodes, particularly those over 5mm or with extracapsular spread, are the strongest prognostic factors and reduce 5-year survival by 50%. Surgical margins of at least 8mm are also important to reduce the risk of local recurrence after resection. Radiation may help reduce recurrence risk when margins are close. Distant metastases generally occur