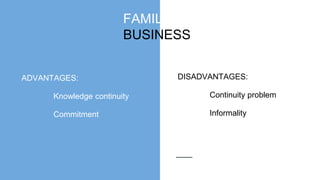
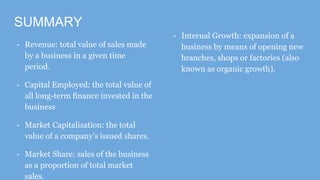
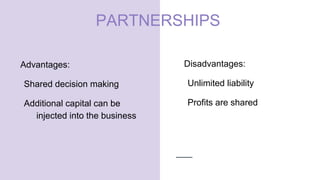
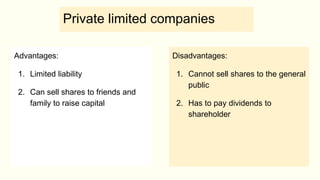
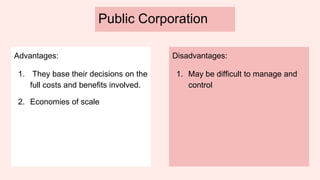
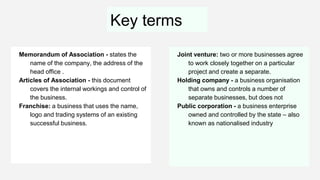
- Sole traders have complete control but unlimited liability, while partnerships allow shared decision making but also shared profit and unlimited liability. Private limited companies provide limited liability but require legal formalities. Public limited companies can sell shares publicly but also face risks of takeover. Franchises receive assistance from franchisers but must share profits. Small businesses are adaptable but have limited financing access, while large businesses benefit from economies of scale but are difficult to manage. [/SUMMARY]