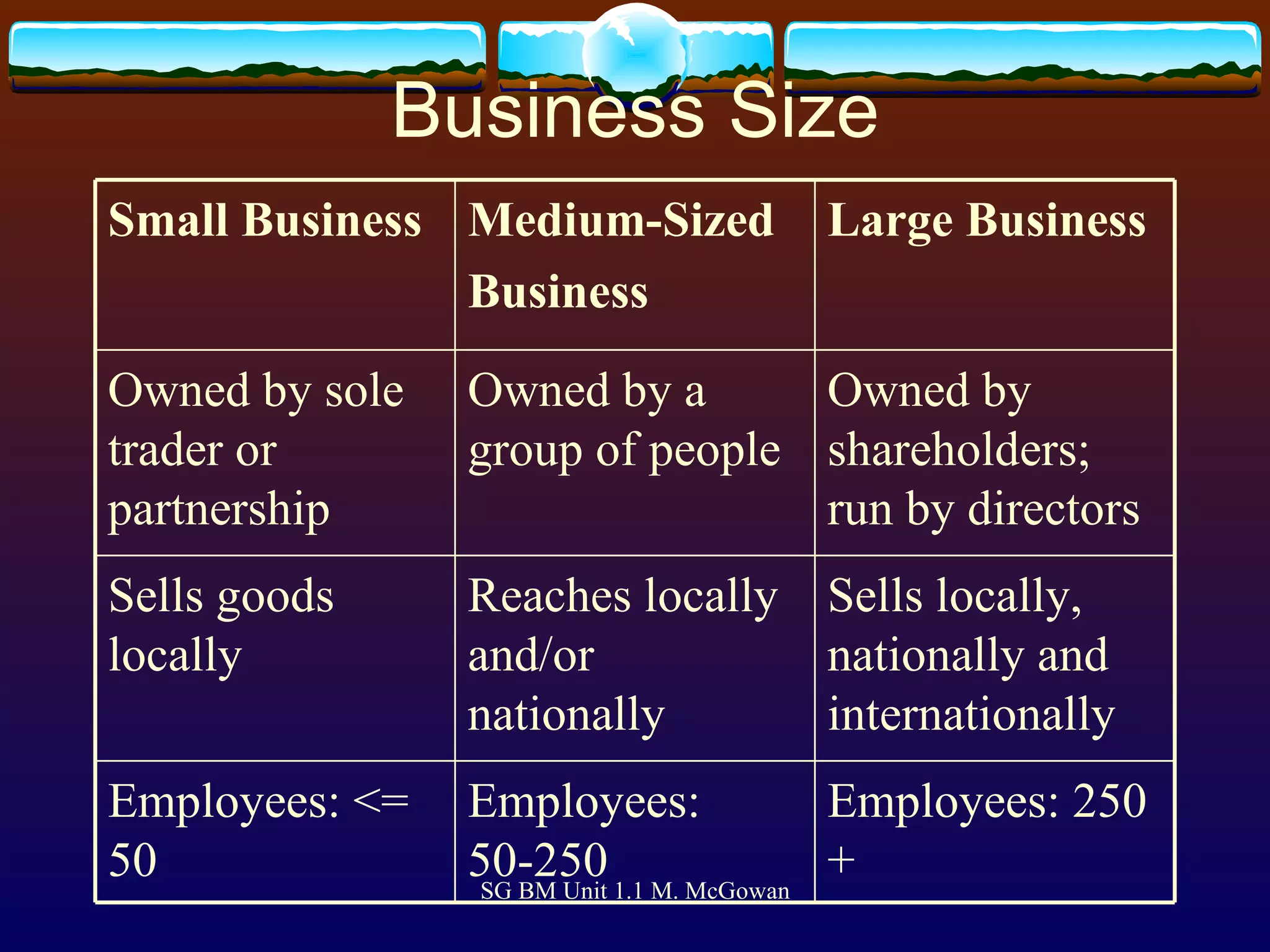
Businesses provide goods and services to satisfy human needs and wants. They can be small, medium, or large businesses. Goods are physical products that can be touched, while services are non-physical and provided by others. Businesses operate in the private, public, or voluntary sectors. Common types of businesses include sole traders, partnerships, private limited companies, public limited companies, franchises, co-operatives, and government-owned organizations. Factors of production include land, labor, capital and enterprise. Production involves transforming raw materials through primary, secondary and tertiary sectors to create finished goods and services.