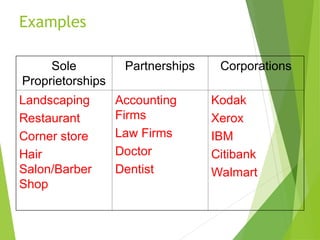
The document outlines different types of business organizations, highlighting definitions, advantages, and disadvantages for each type, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, franchises, cooperatives, and nonprofits. It emphasizes the operational structures, financial implications, and legal liabilities associated with each form of business. Additionally, examples of each type are provided to illustrate their practical applications in the business world.













![3 types of Mergers
Horizontal Merger: combination of 2 or more corporations who
provide the same good or service (ex. Cingular and AT&T)
Vertical Merger: combine 2 or more firms involved in different
stages of producing a good or service (ex. Carnegie Steel
owned the Iron mines and Steel Refineries)
Conglomerate: a combination of 3 or more businesses making
unrelated products. [ex. AOL (internet) Time (news magazines)
Warner (TV and Movies]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/businessorganization-241218150213-768d0b81/85/Business_Organization-Classic-Presentation-14-320.jpg)