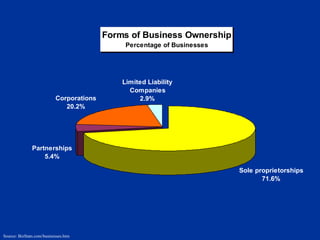
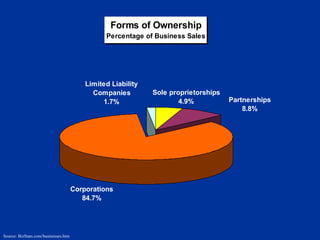
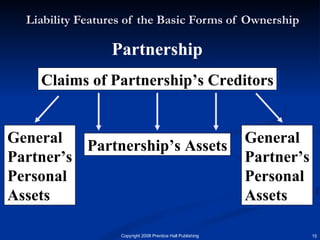
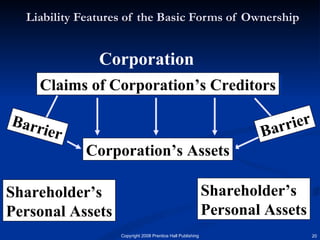
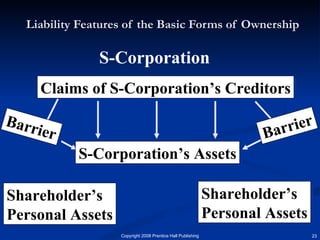
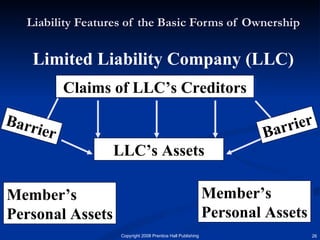
The document discusses the major forms of business ownership including sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, S-corporations, and limited liability companies. For each form of ownership, it covers characteristics like liability, tax implications, control structure, and costs. Choosing the best structure depends on an entrepreneur's goals, capital needs, and tolerance for risk. The key is understanding how each form matches their specific business and personal circumstances.