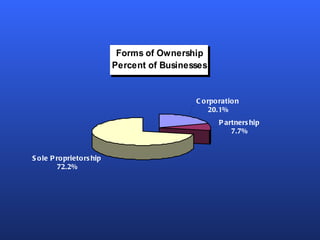
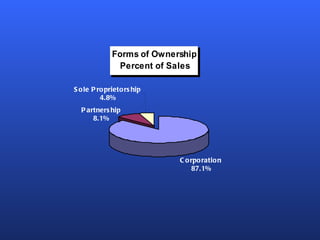
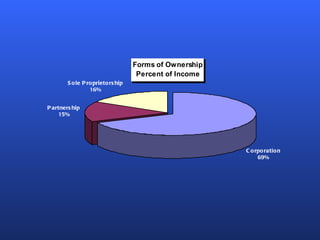
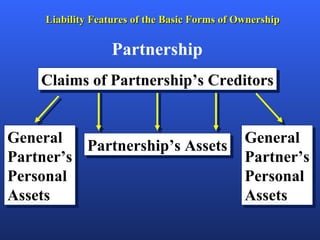
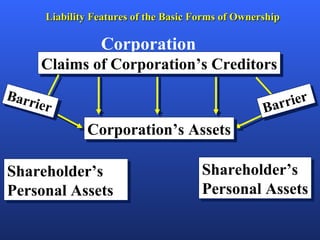
There are several factors to consider when choosing a form of business ownership. The best ownership structure depends on an entrepreneur's specific business and personal circumstances. The key forms of ownership include sole proprietorships, partnerships, limited partnerships, and corporations. Each has advantages and disadvantages related to taxes, liability, capital requirements, and control. The appropriate choice varies based on an entrepreneur's goals, resources, and tolerance for risk.