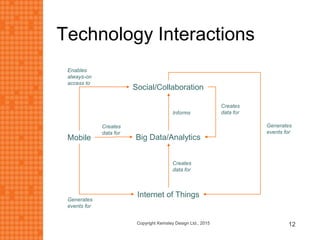
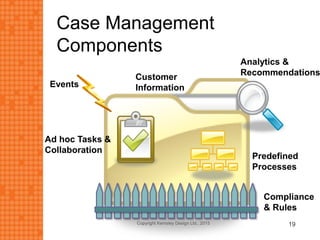
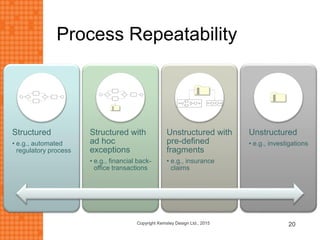
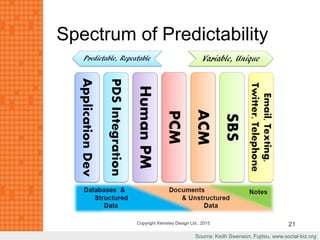
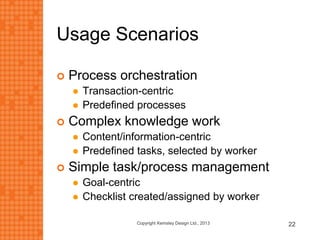
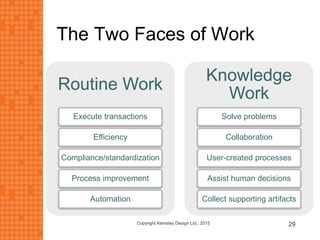
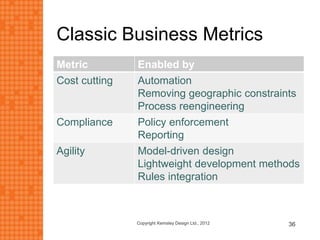
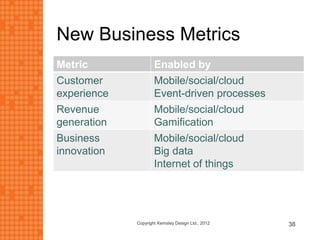
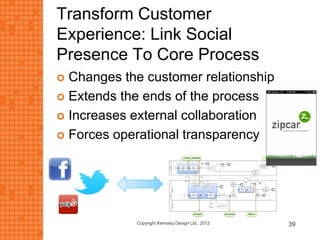
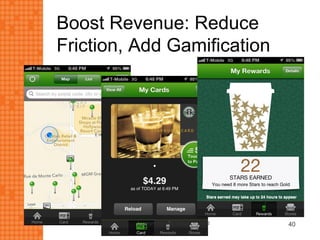
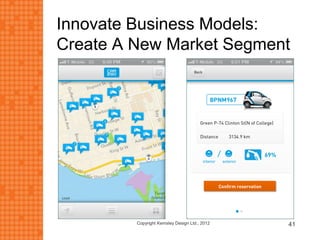
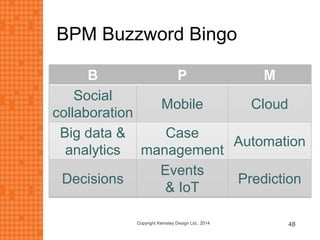
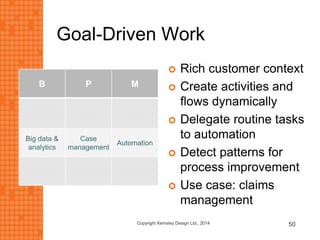
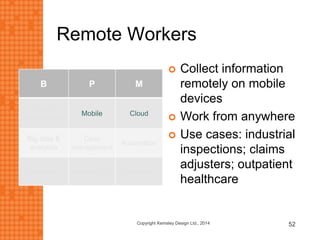
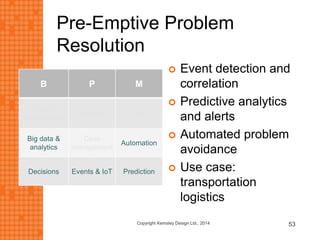
The presentation discusses how new technologies and changing customer and employee attitudes are transforming the future of work. It explores how technologies like social/collaboration tools, mobile devices, cloud platforms, the internet of things, and big data/analytics are driving changes in business models, products, and interactions. It also examines shifting customer expectations around experience, transparency, and influence, as well as changing employee needs around knowledge work, consumer-like tools, and personalization. The presentation argues that businesses must adapt by applying new technologies, creating new business models, and making cultural changes like encouraging collaboration, aligning incentives with goals, and rewarding problem-solving.