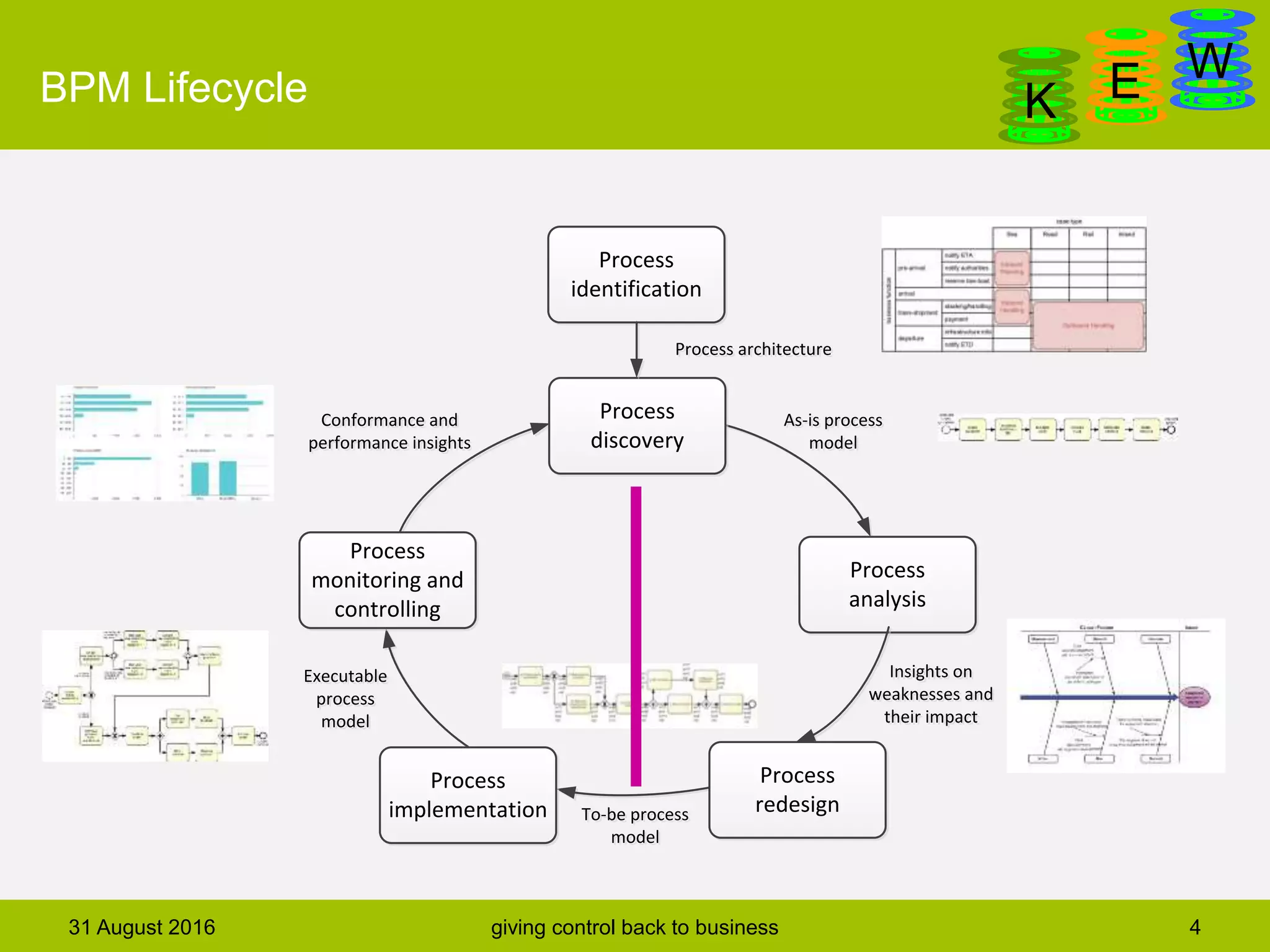
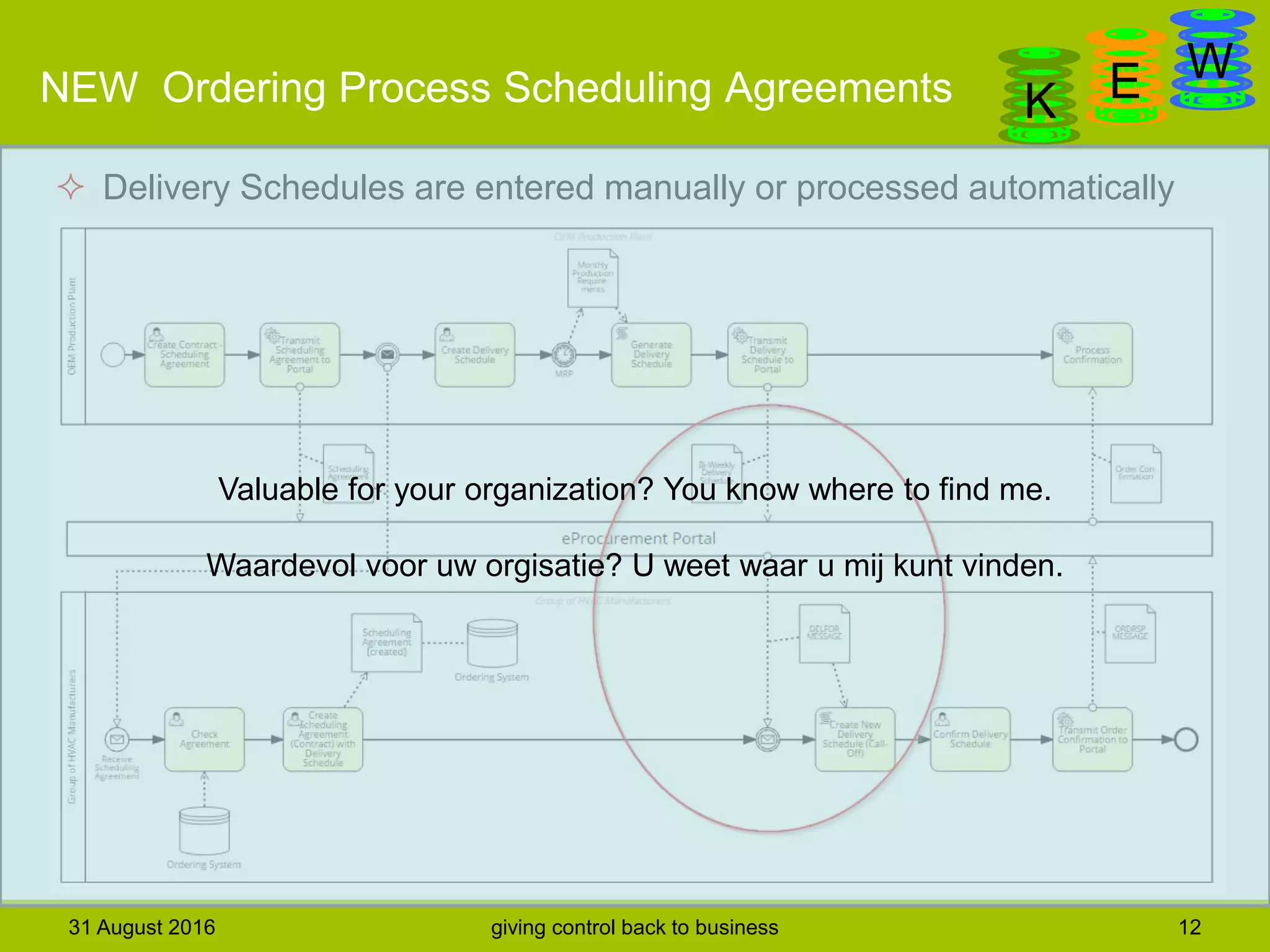
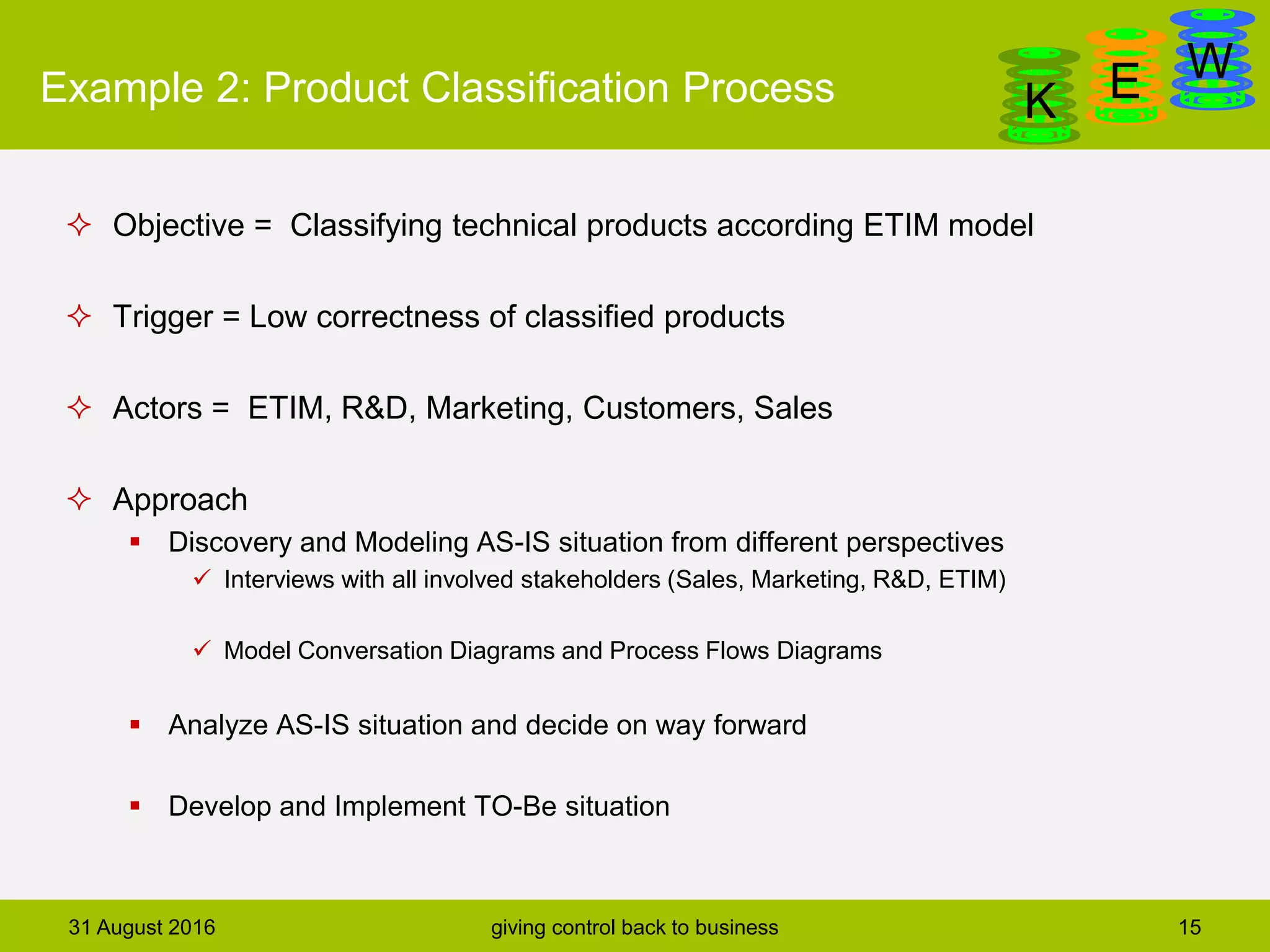
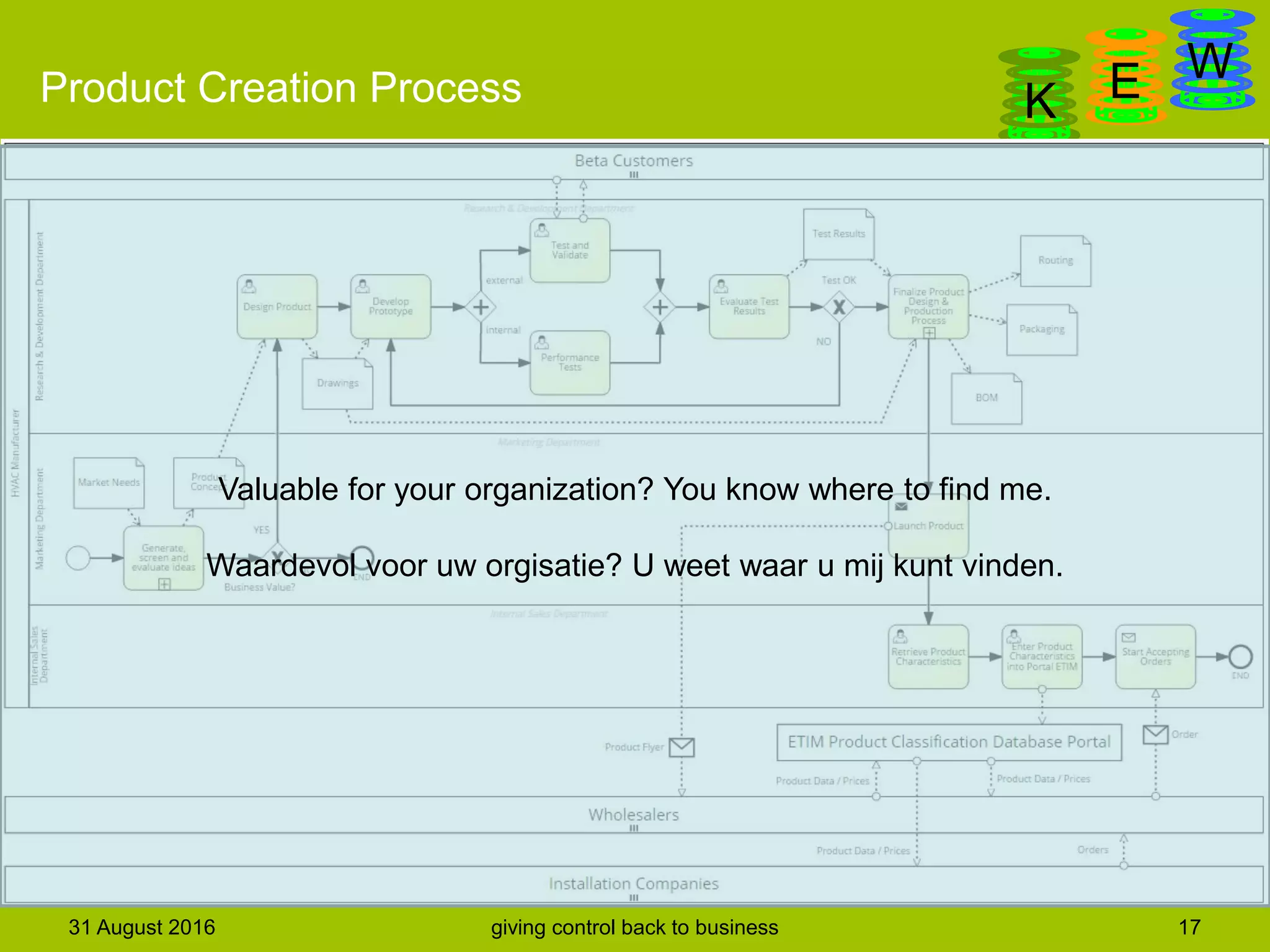
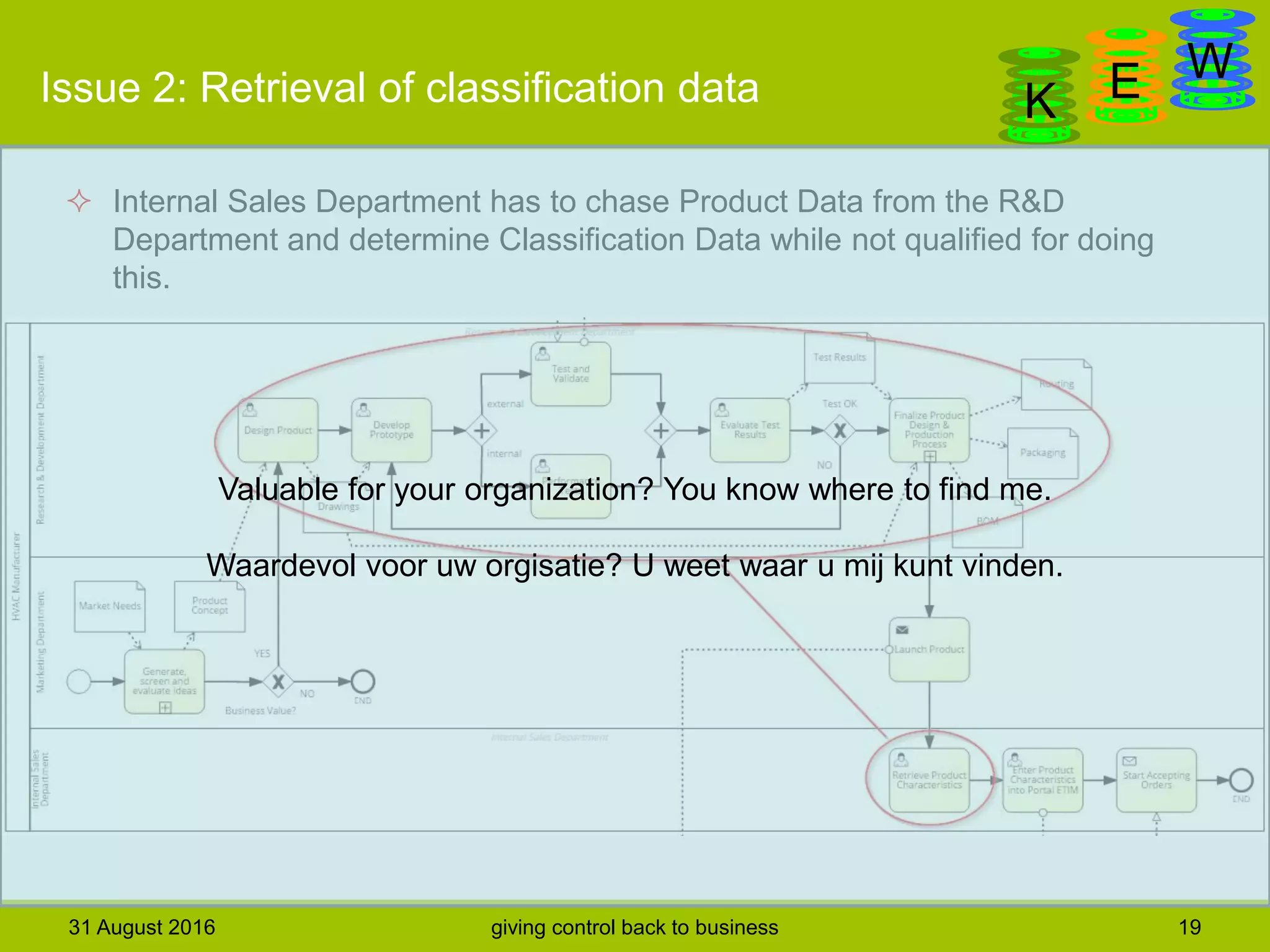
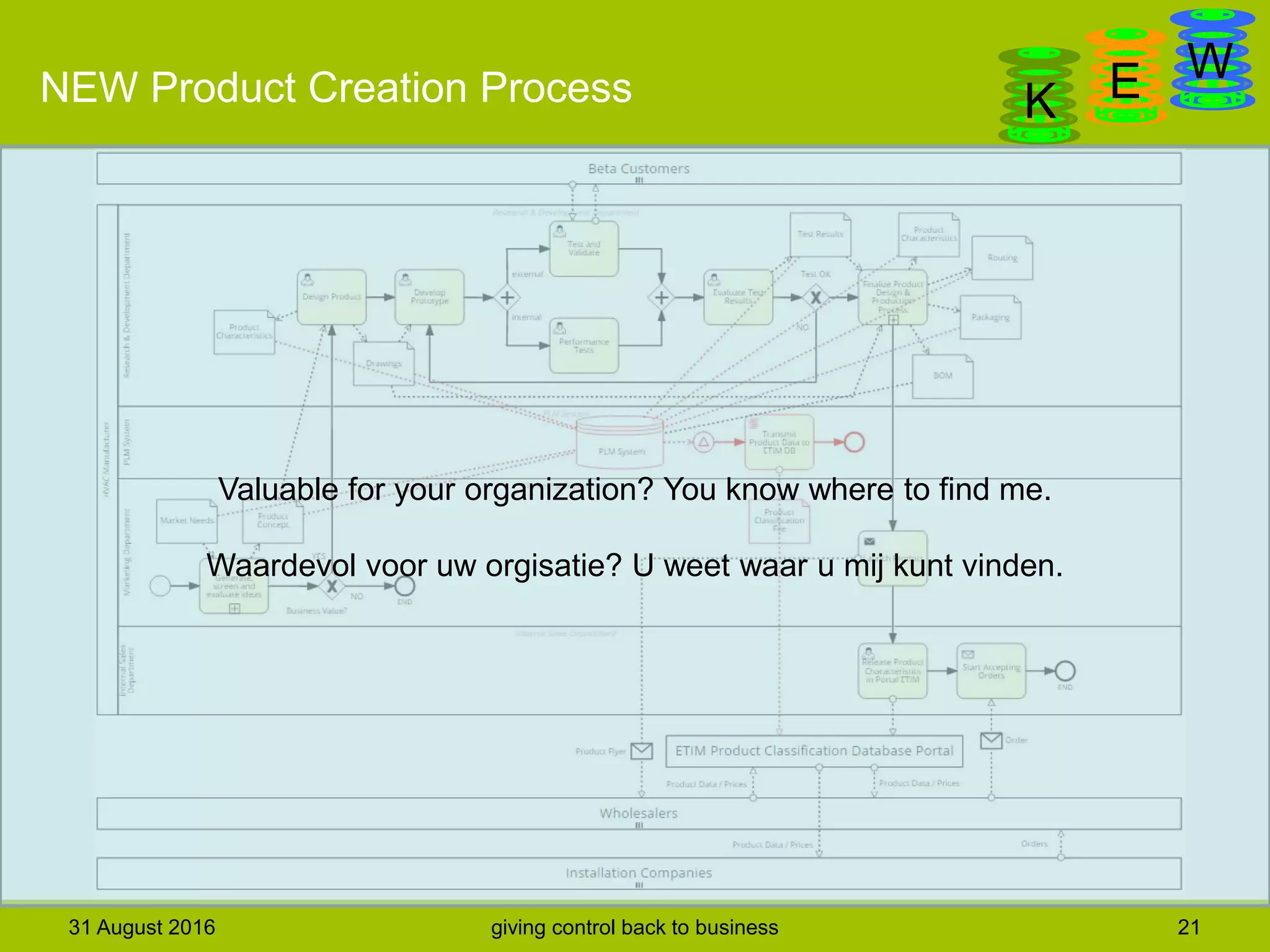
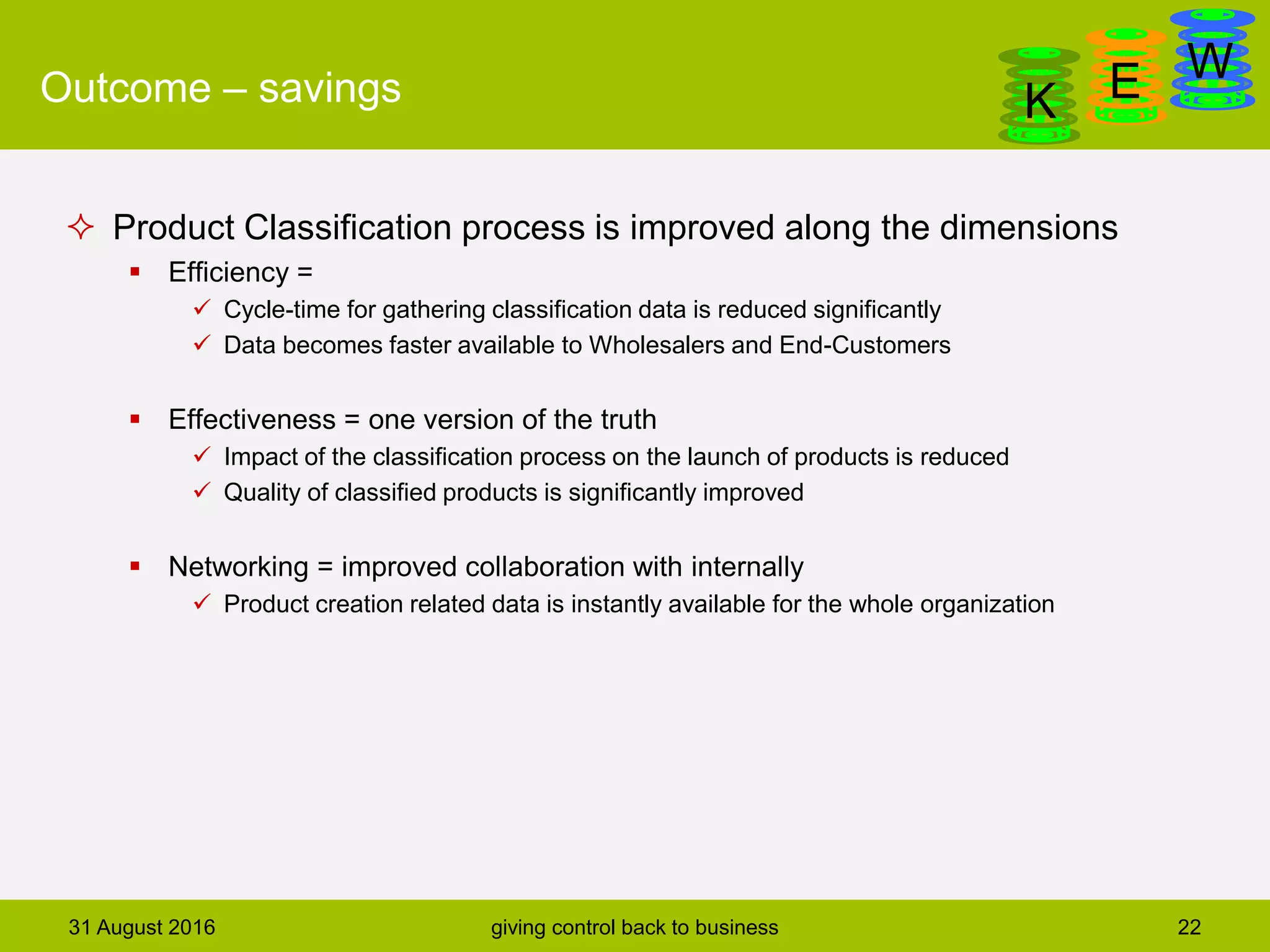
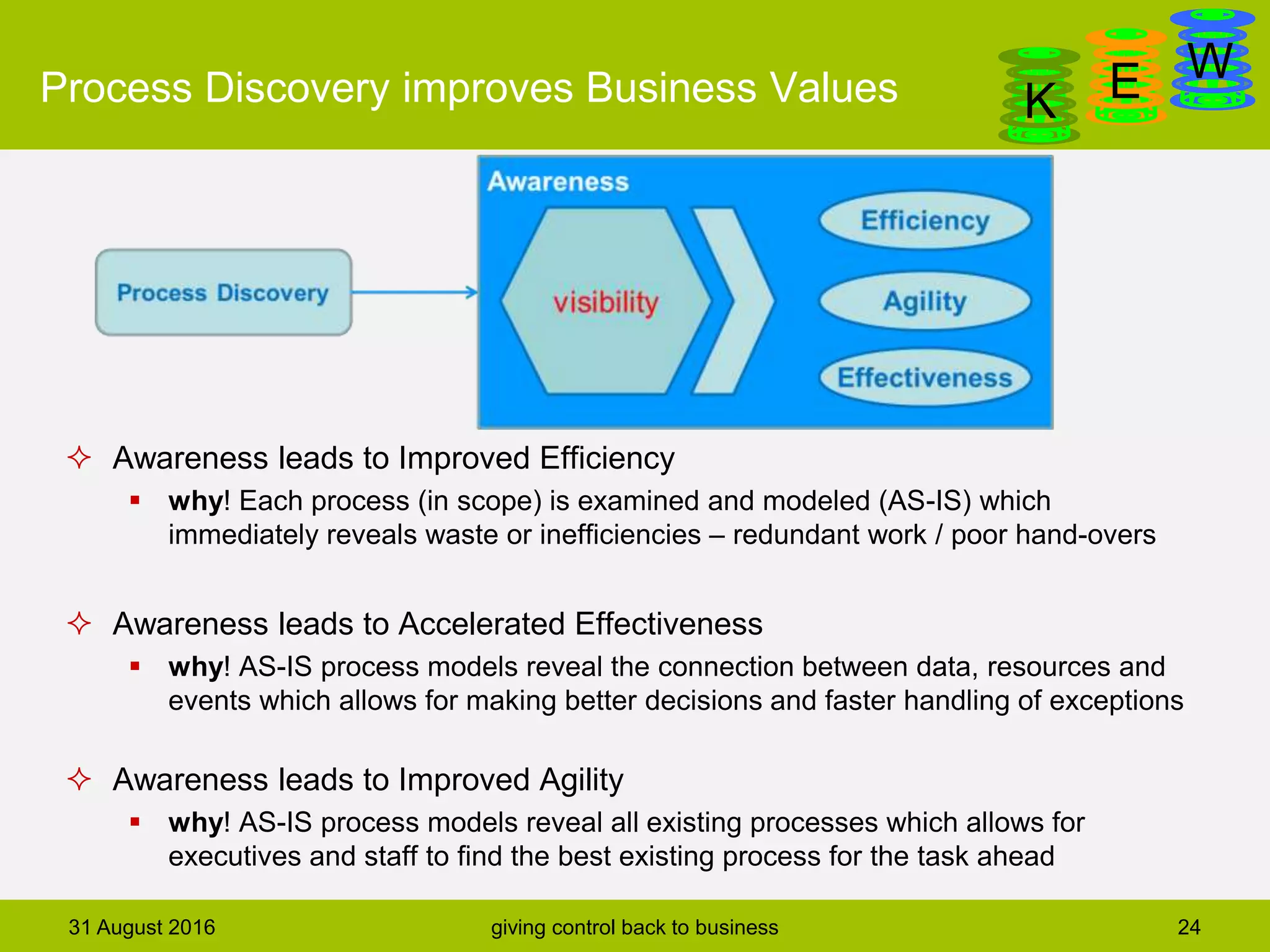
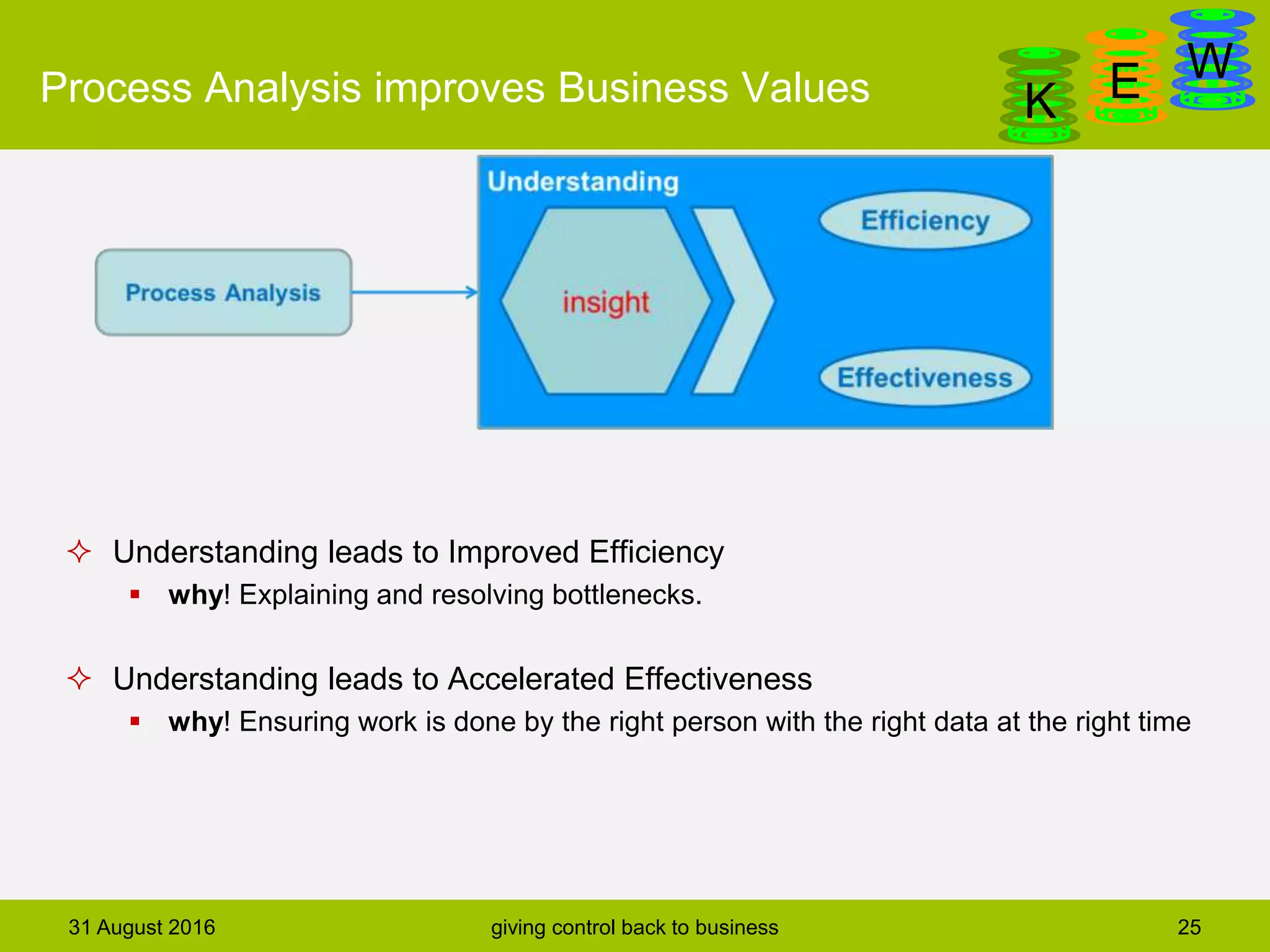
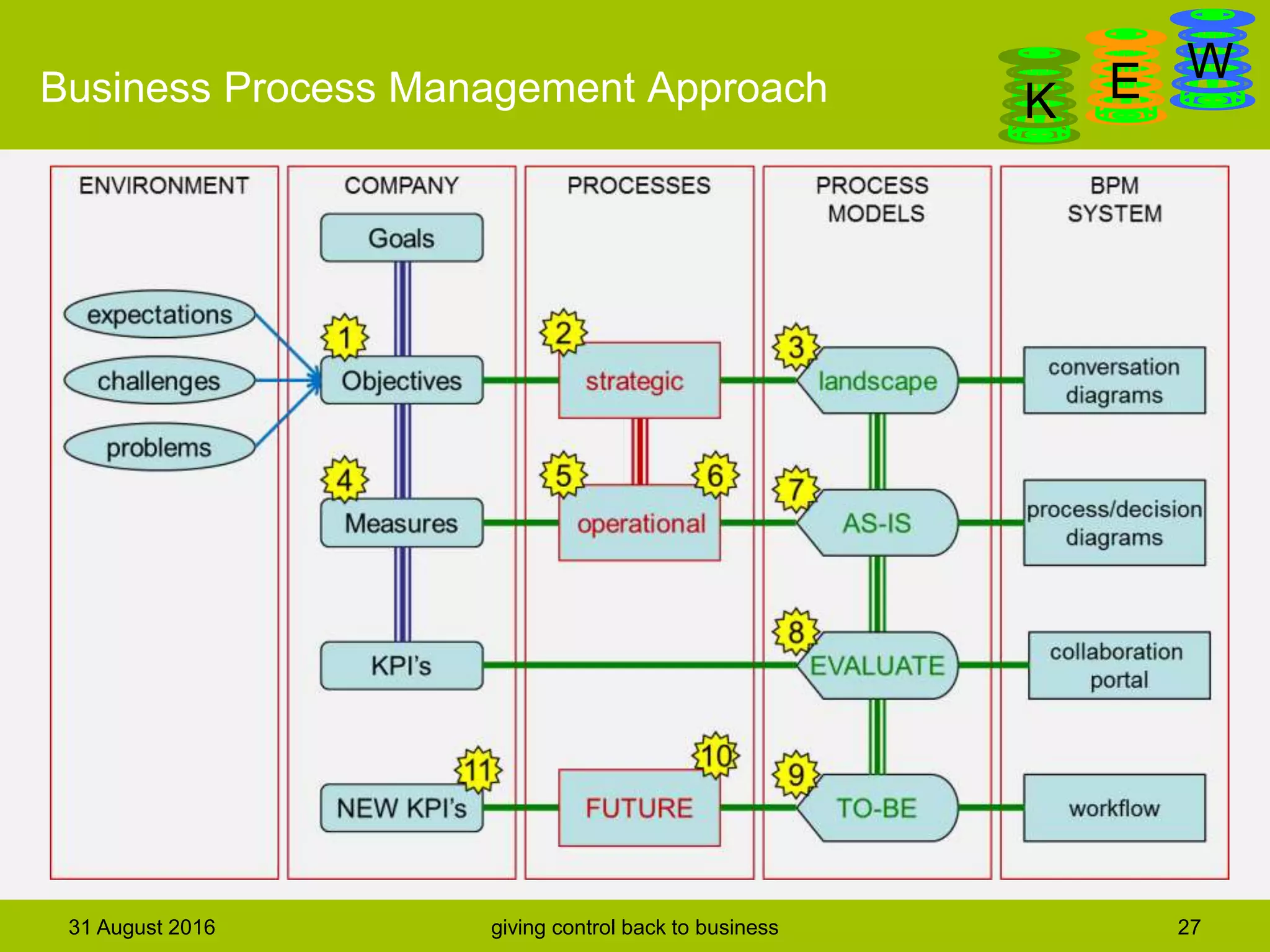
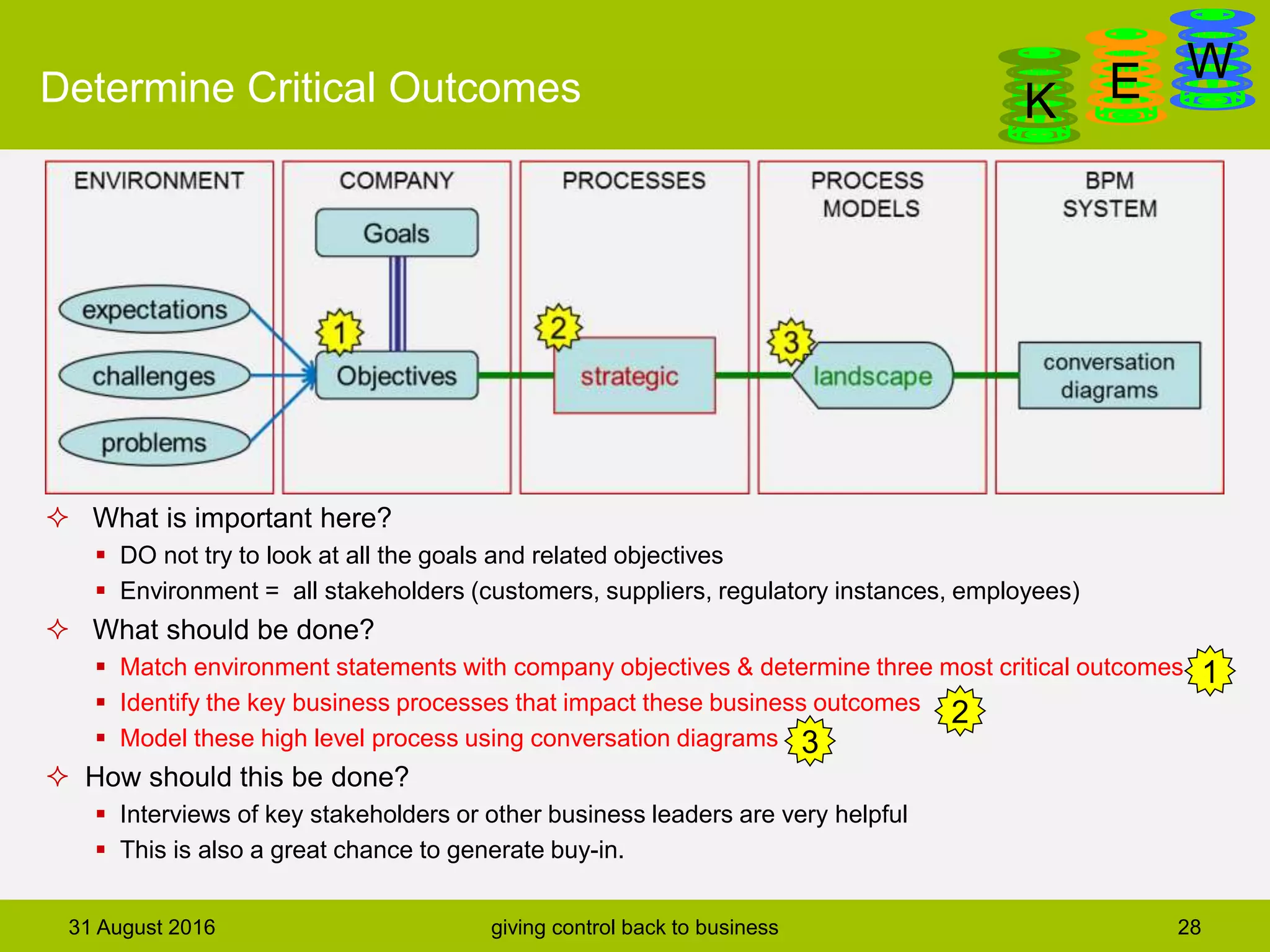
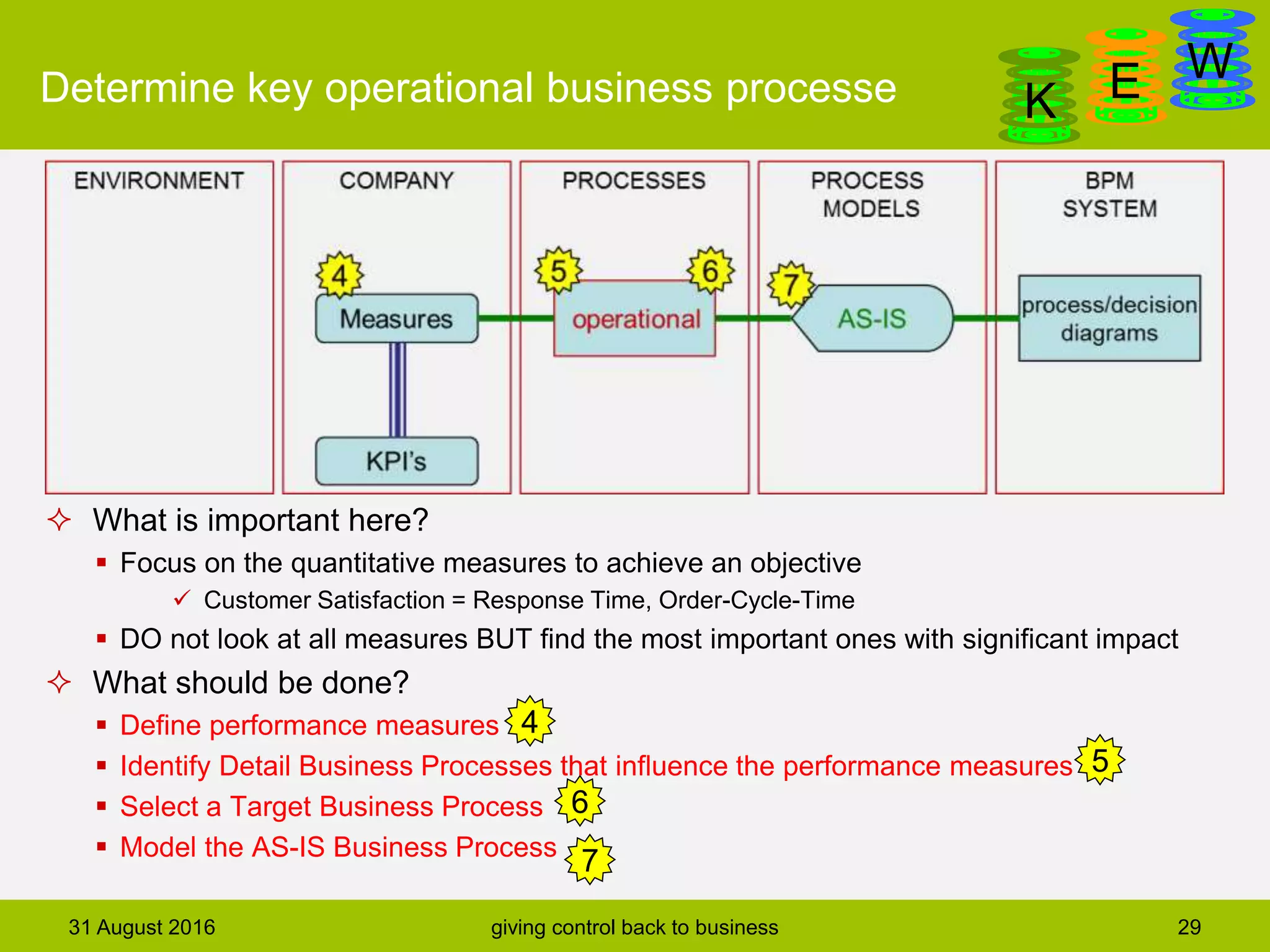
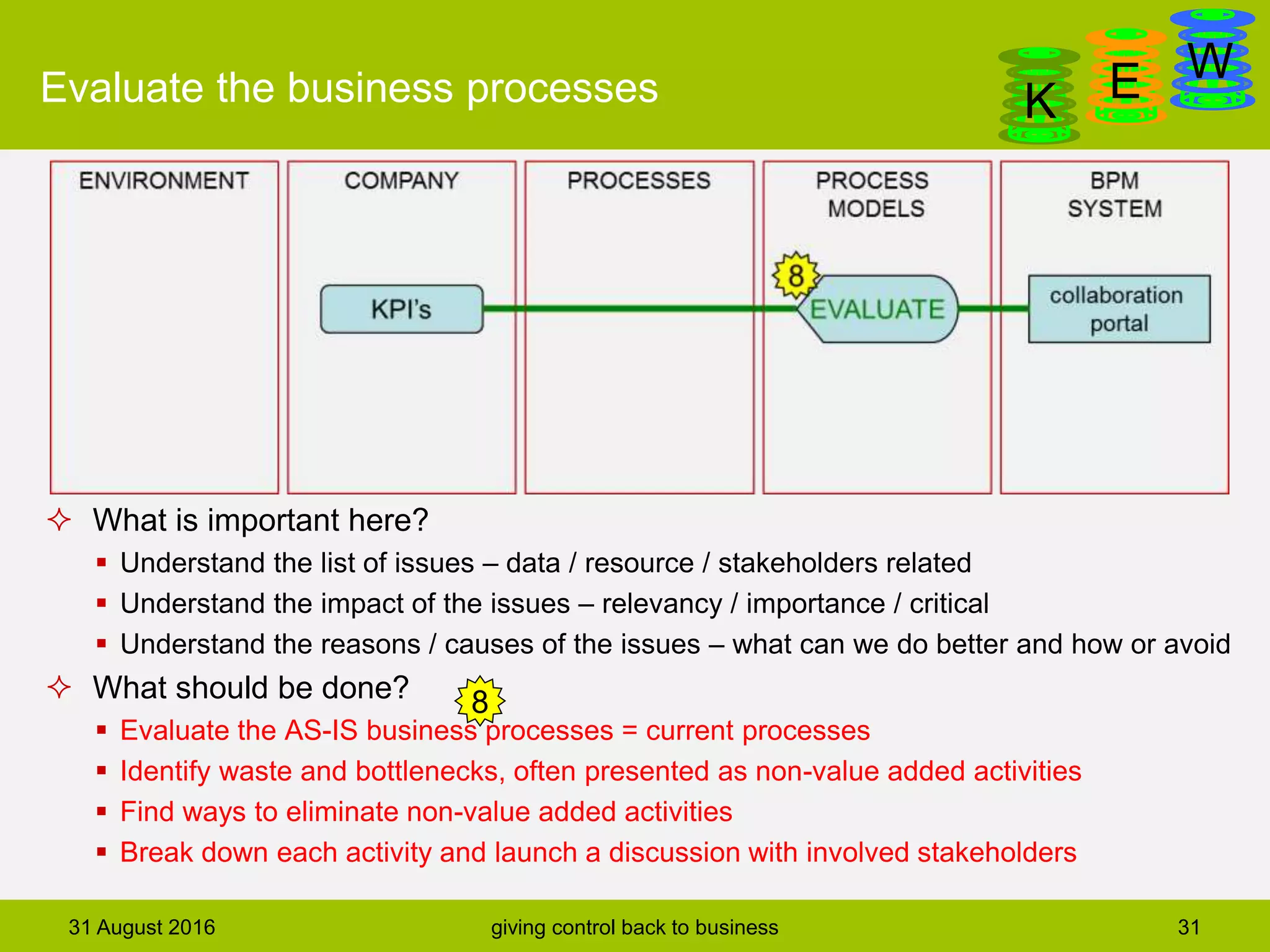
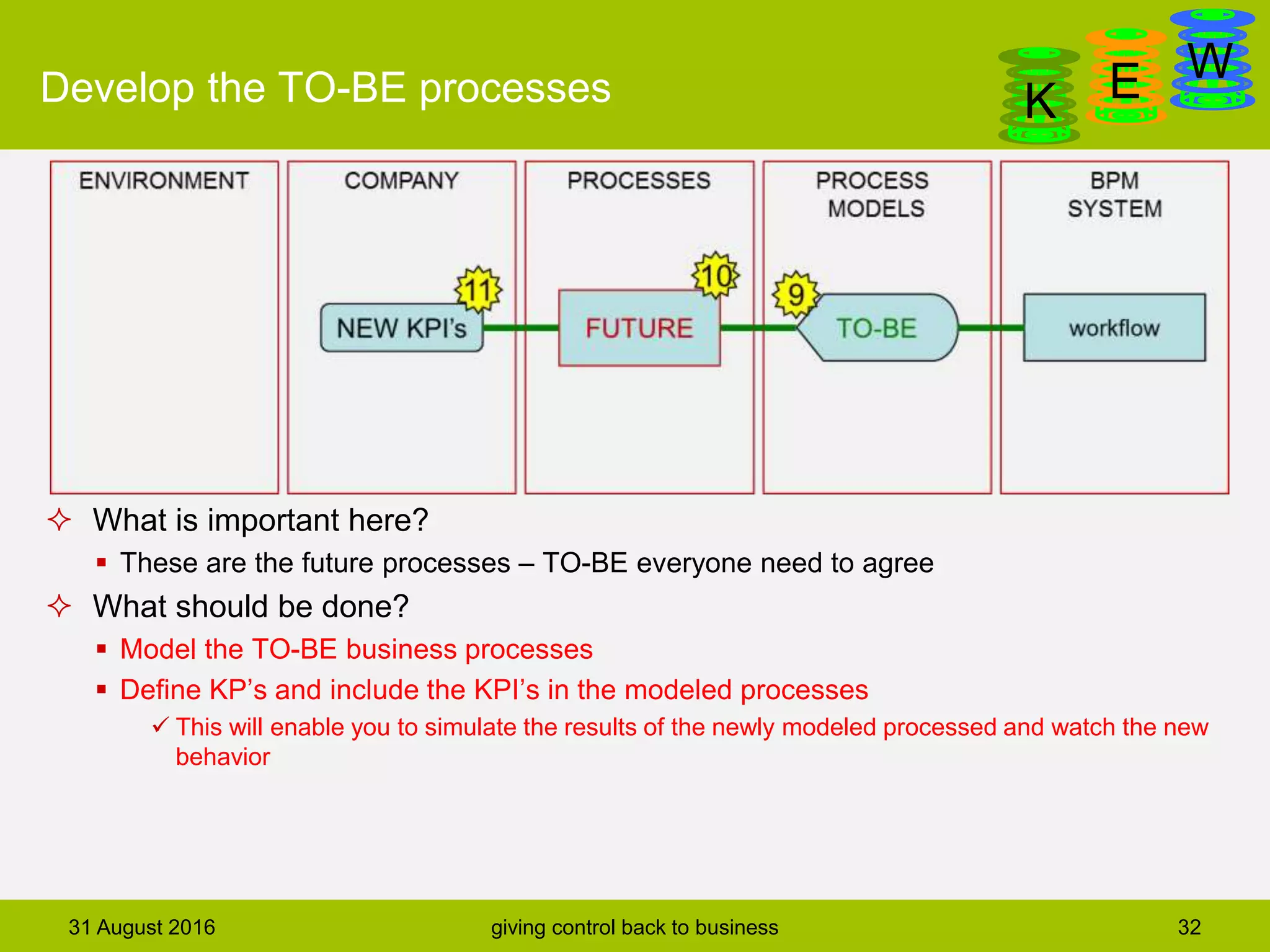
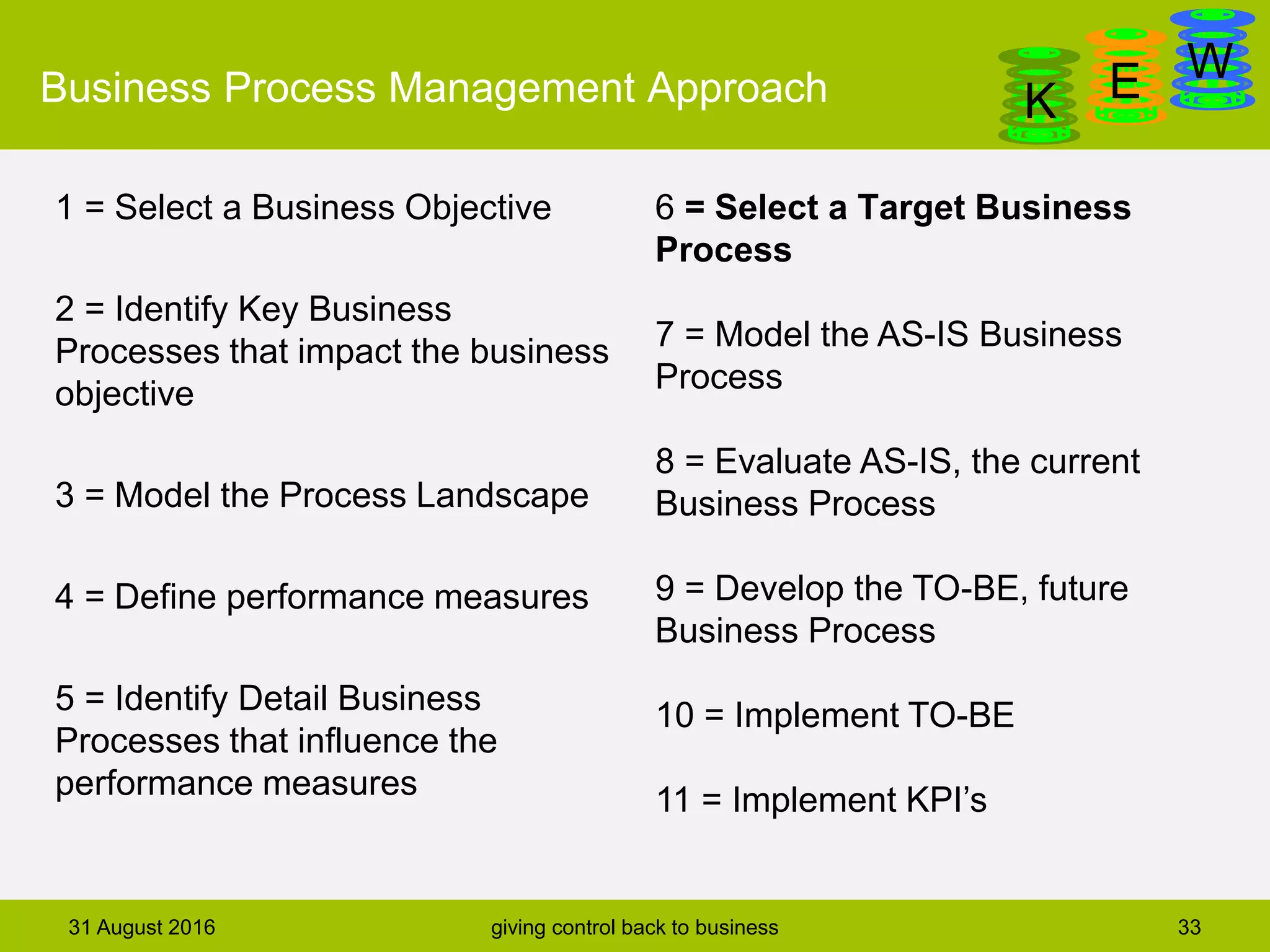
The document discusses business process modeling and automation aimed at enhancing control within organizations, detailing a defined BPM lifecycle that includes stages such as process discovery, analysis, redesign, and implementation. It provides case studies on optimizing ordering and product classification processes, highlighting improvements in efficiency, effectiveness, and customer satisfaction. The importance of stakeholder involvement in identifying and modeling key business processes is emphasized as a means of achieving better organizational outcomes.