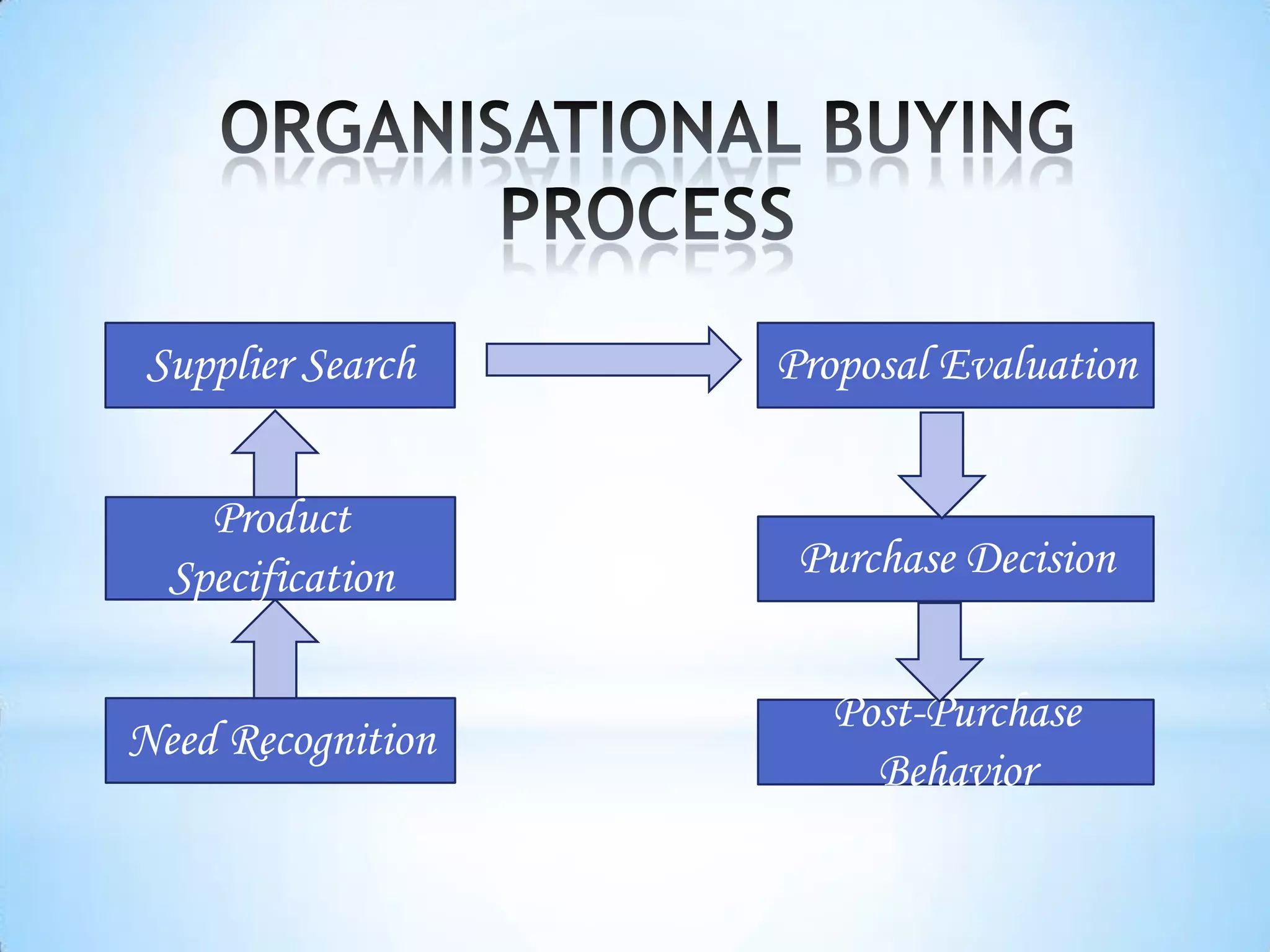
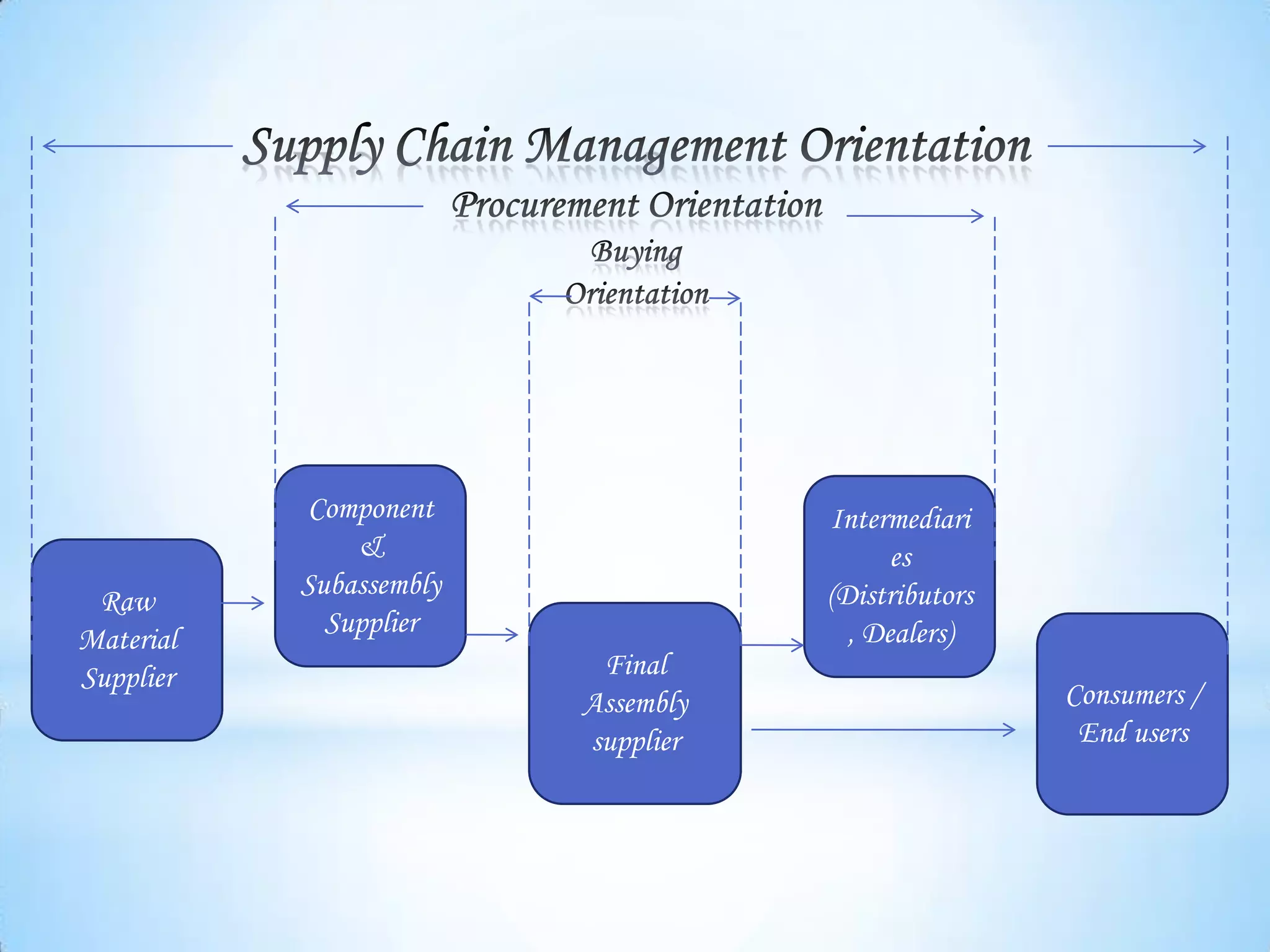
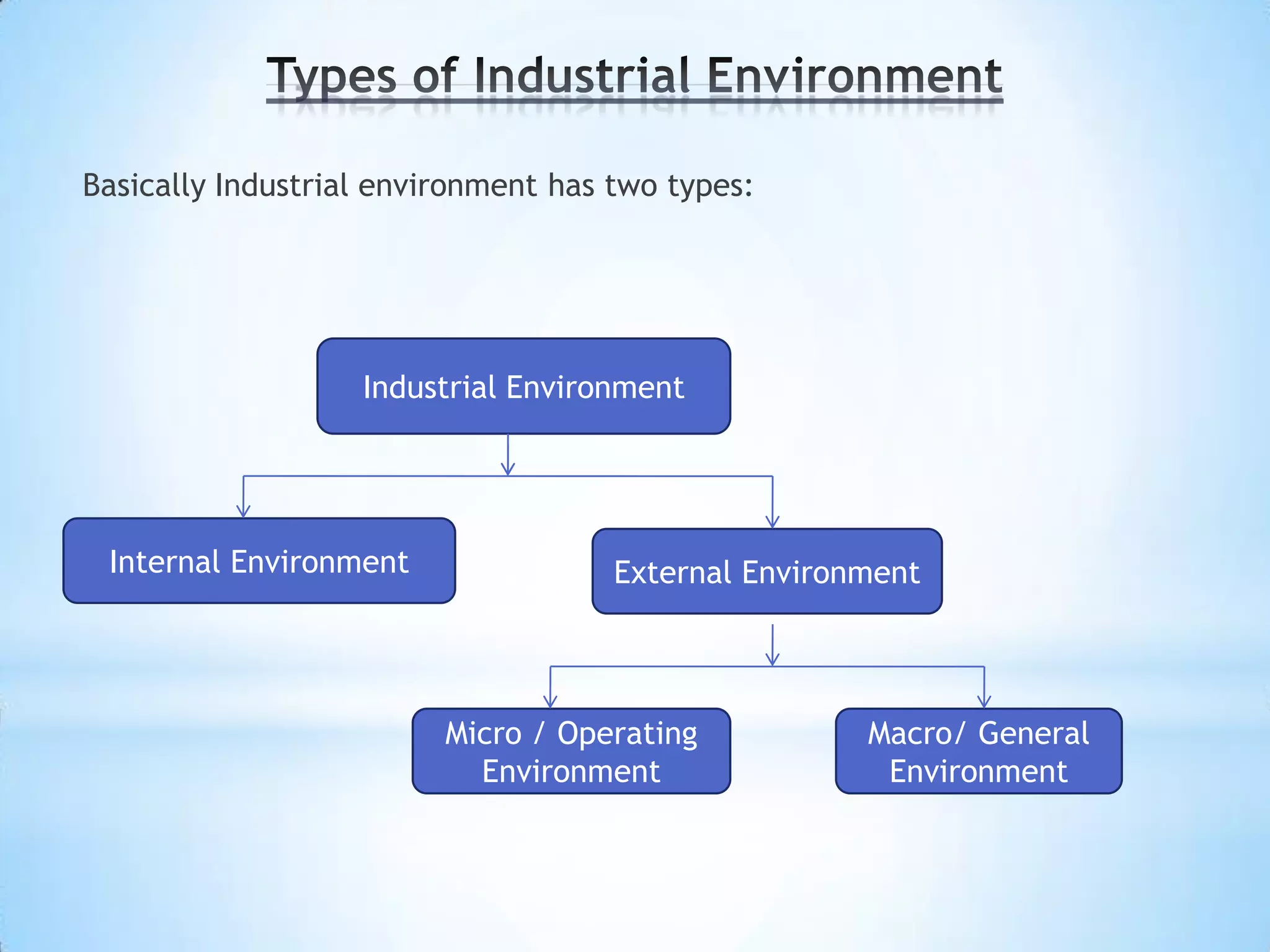
The document provides information on business-to-business (B2B) marketing and industrial customers. It discusses that B2B marketing involves marketing products, services, and solutions to organizations for use in production or to facilitate their operations. Industrial customers include commercial enterprises, government bodies, institutions, and non-profit organizations. The document then describes characteristics of B2B markets, classifications of industrial products and customers, and strategies for marketing to different types of industrial customers like commercial enterprises and government entities.