The document discusses the marketing environment and its various components. It defines the marketing environment as factors and forces that affect a firm's ability to build relationships with customers. The marketing environment has two main parts - the microenvironment and macroenvironment.
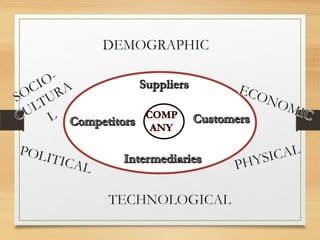
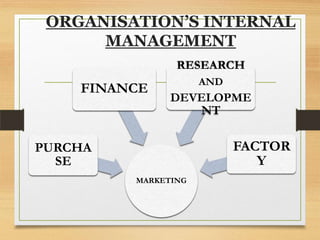
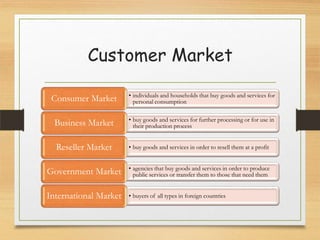
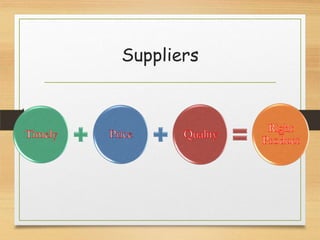
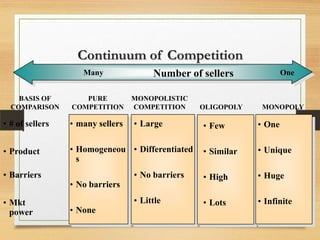
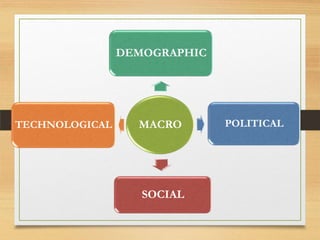
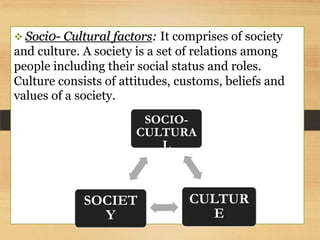
The microenvironment includes customers, competitors, suppliers, marketing intermediaries, and the public. It directly affects the organization. The macroenvironment includes demographic, economic, technological, political/legal, and sociocultural factors. It indirectly affects the organization. Successful companies continuously monitor and adapt to changes in both the micro and macroenvironment.