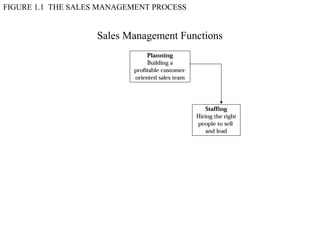
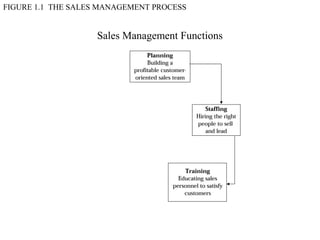
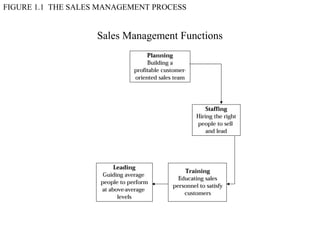
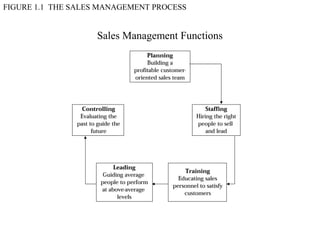
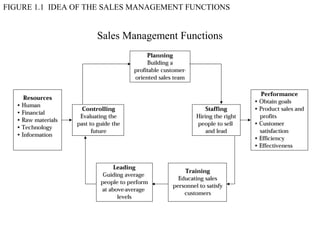
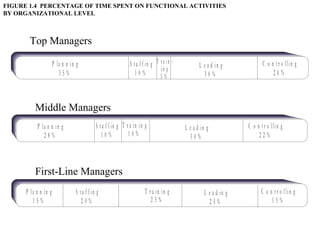
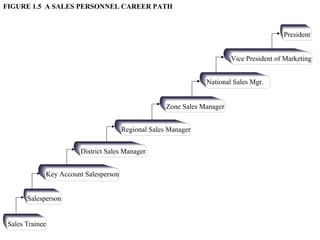
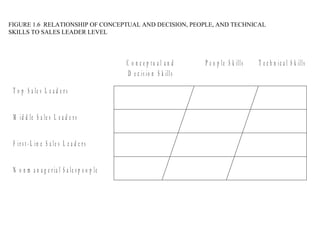
This document provides an overview of sales management, including defining it as planning, directing, and controlling personal selling efforts. It discusses the nature and importance of sales management in achieving organizational goals through relationships between buyers and sellers. The document also outlines the key functions of sales managers as planning, staffing, training, leading, and controlling, and how the skills required vary from conceptual to technical depending on the management level. Finally, it addresses the experience of being promoted from salesperson to sales manager.