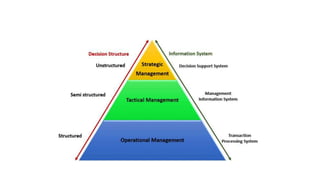
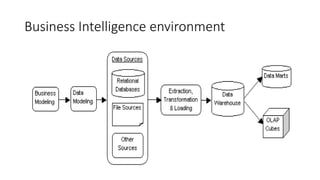
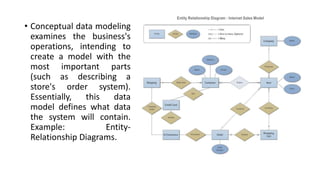
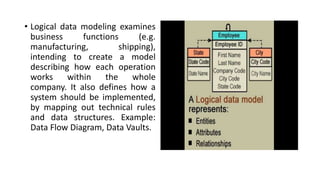
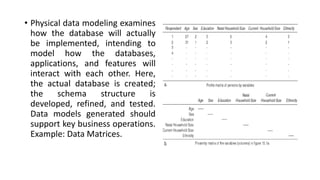
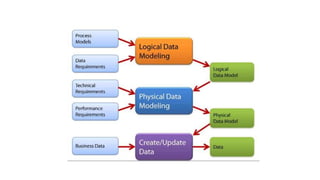
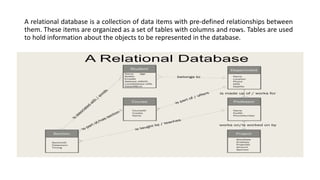
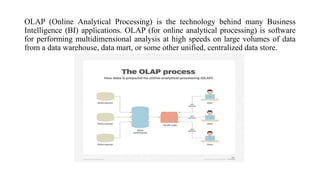
Business intelligence environments involve collecting data from various sources, transforming and organizing it using tools like ETL, and storing it in data warehouses or marts. This data is then analyzed using OLAP and reporting tools to provide useful information for business decisions. Setting up an effective BI environment requires understanding business requirements, defining processes, determining data needs, integrating data sources, and selecting appropriate tools and techniques. Careful planning and skilled people are needed to ensure the BI environment supports organizational goals.