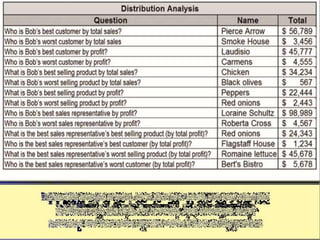
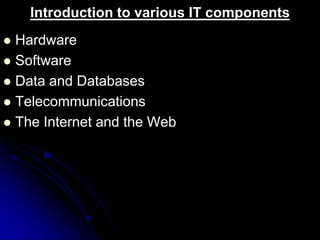
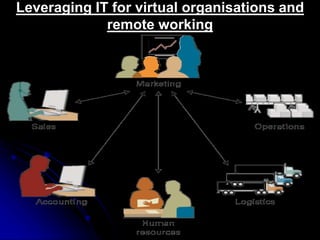
This document provides an overview of an introductory session on information technology for management and business. The session agenda includes introductions, a course outline, assignments, theoretical foundations of IT, and a session review. Key concepts covered are data, information, and business intelligence. The document also defines information technology and its various components. It discusses the importance of understanding IT for business and provides examples of IT applications in different industries.