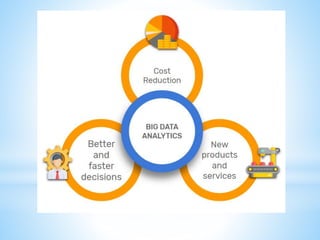
Big data analytics is used to extract meaningful insights from data through identifying hidden patterns, correlations, trends, and customer preferences. It provides advantages like better decision making and preventing fraud. Business intelligence encompasses technologies, applications, and practices for collecting, integrating, analyzing, and presenting business information and is data-driven to support decision making. Business intelligence tools allow users to identify actionable information from raw data to facilitate data-driven decision making.