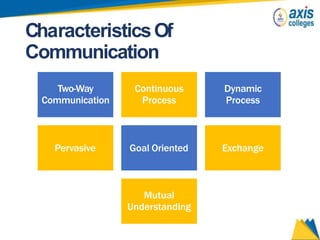
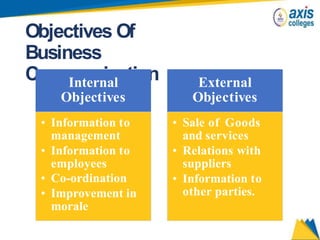
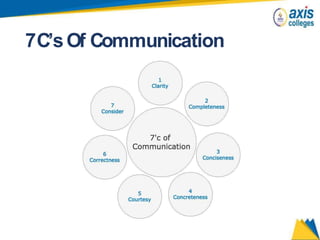
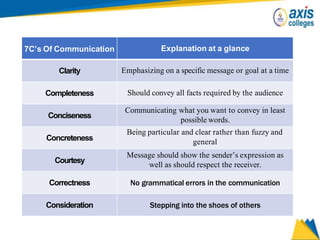
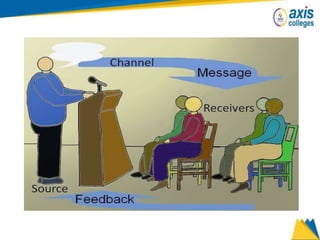
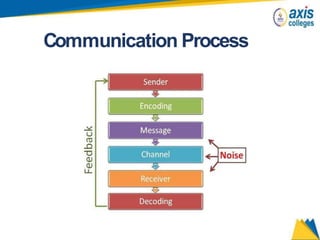
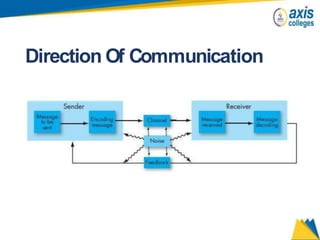
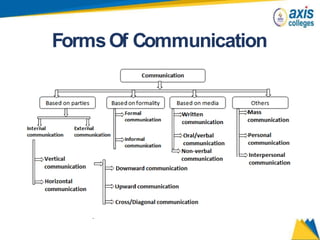
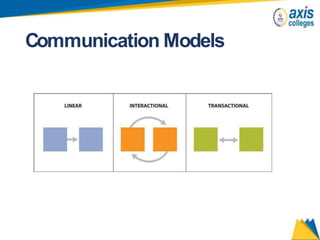
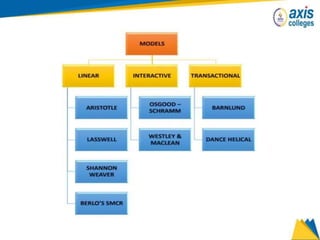
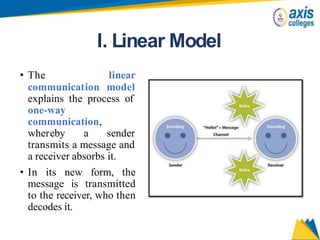
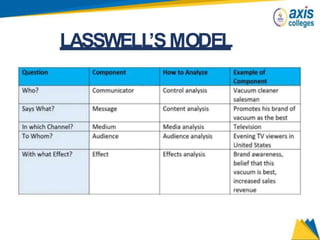
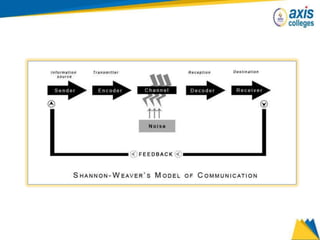
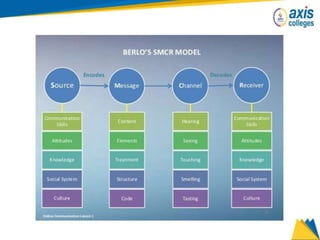
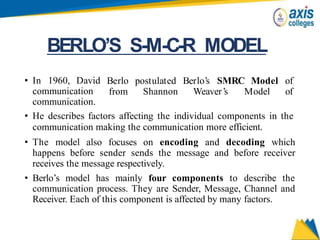
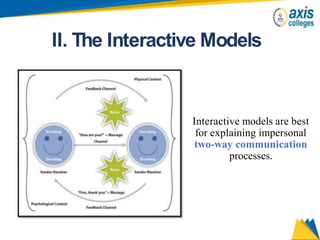
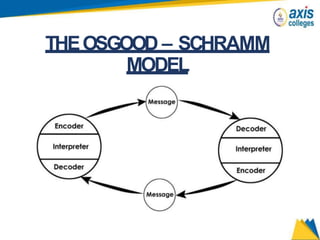
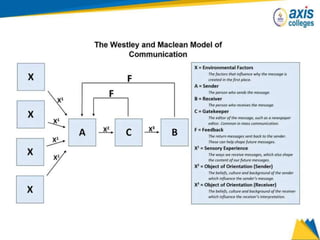
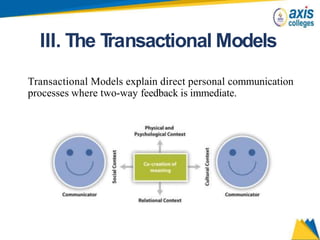
The document provides an overview of business communication including its meaning and objectives. It discusses the importance of business communication for timely decisions, planning, overcoming conflicts, and more. The principles of effective communication are also summarized, including clarity, feedback, consistency, and adequacy. Finally, the communication process and different forms of communication such as internal, external, written, and oral are described at a high level.