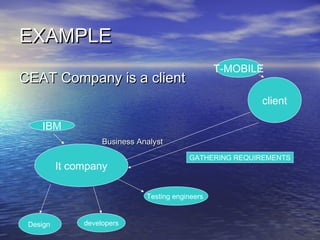
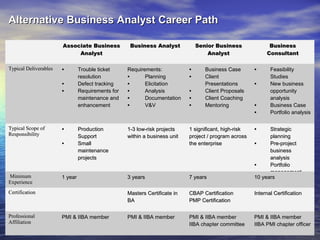
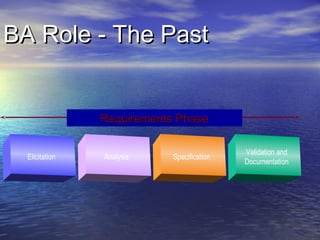
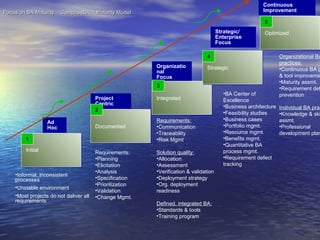
A Business Analyst is responsible for identifying business needs, developing and managing requirements, and acting as a liaison between business stakeholders and technical teams. Specifically, they elicit, analyze, validate and document organizational requirements without predetermining solutions, which may include systems development, process improvement, or organizational change. Business Analysis involves tasks like requirements gathering and management throughout a project's life cycle to help ensure effective business systems are developed.