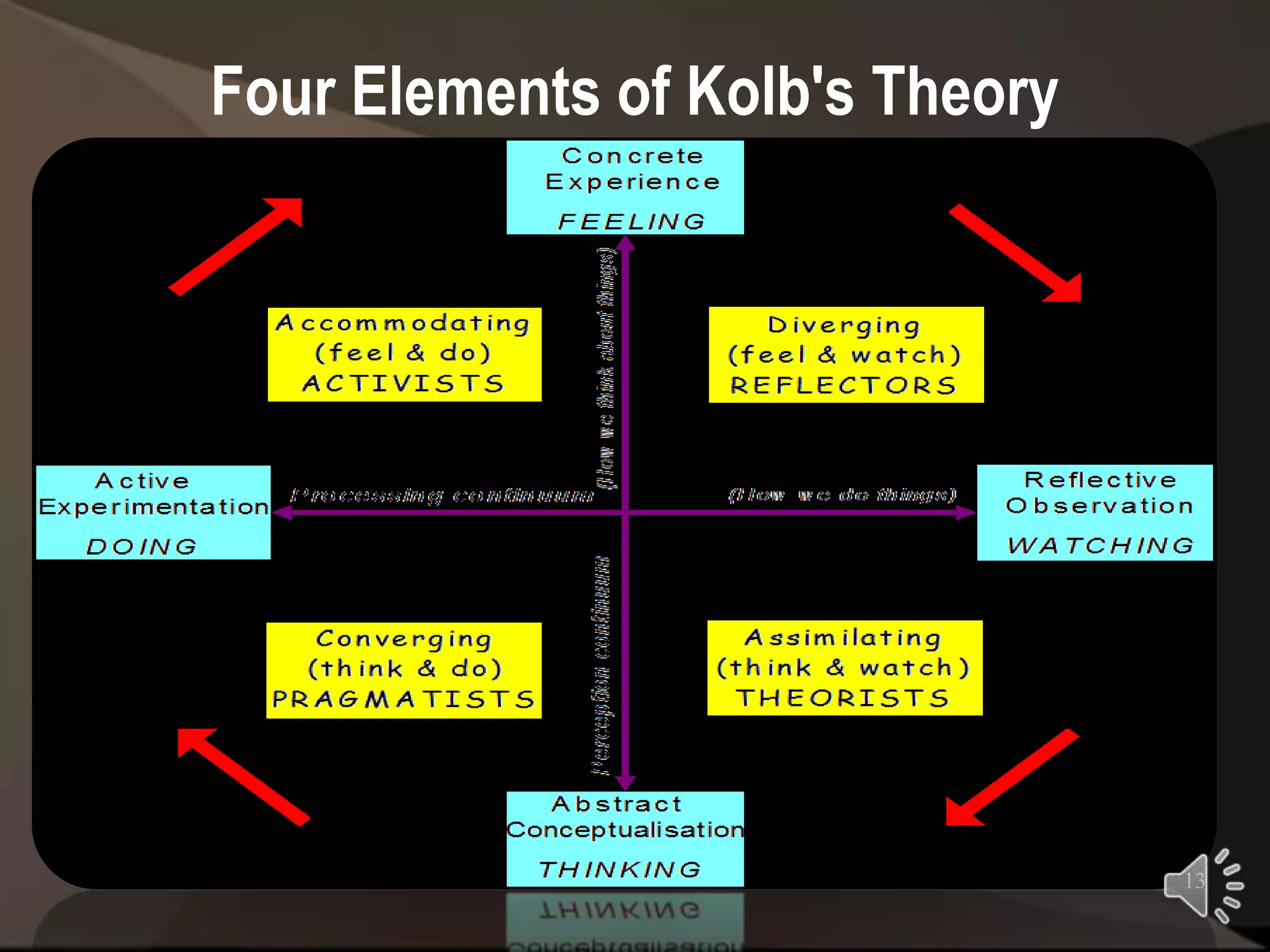
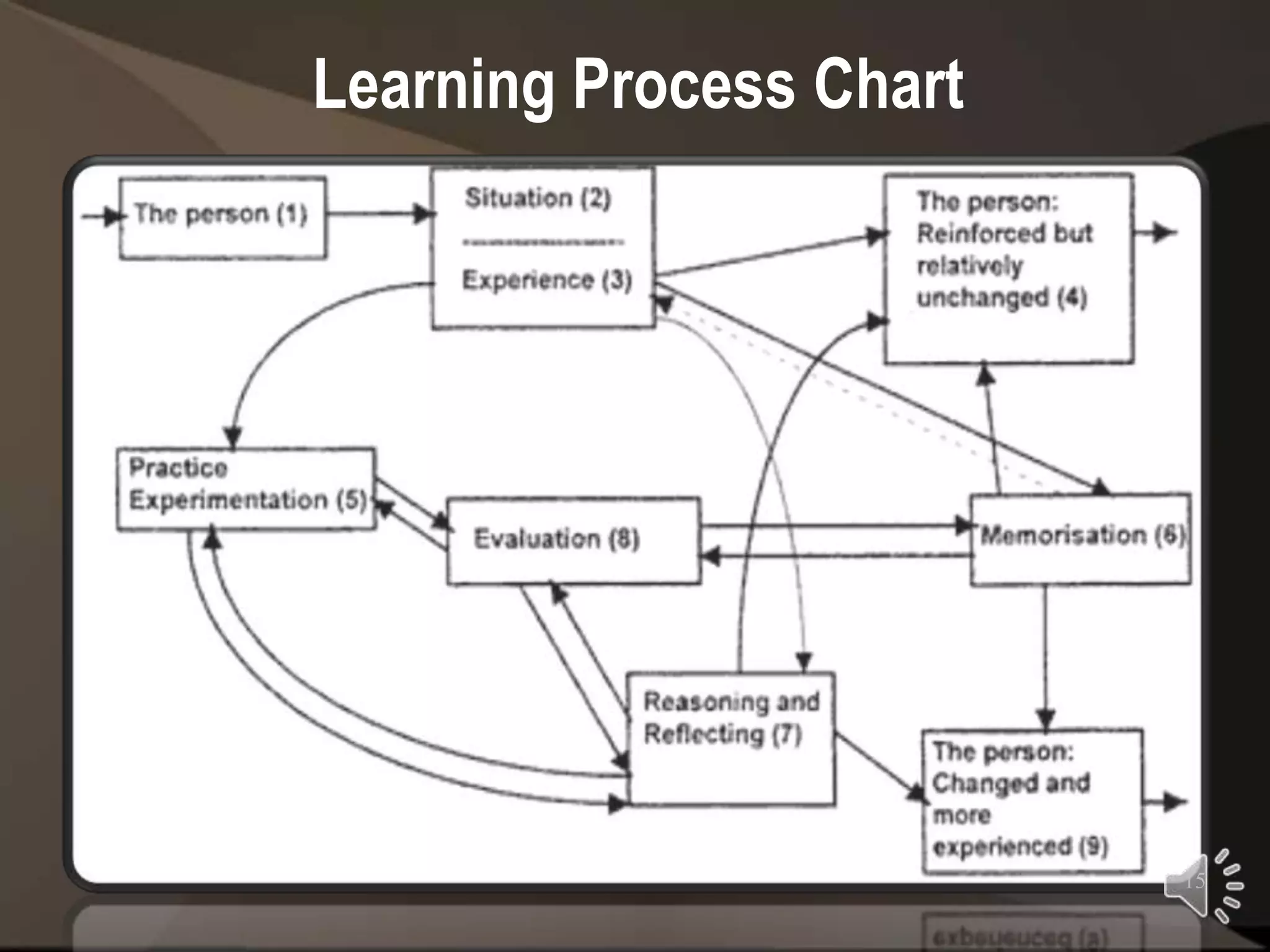
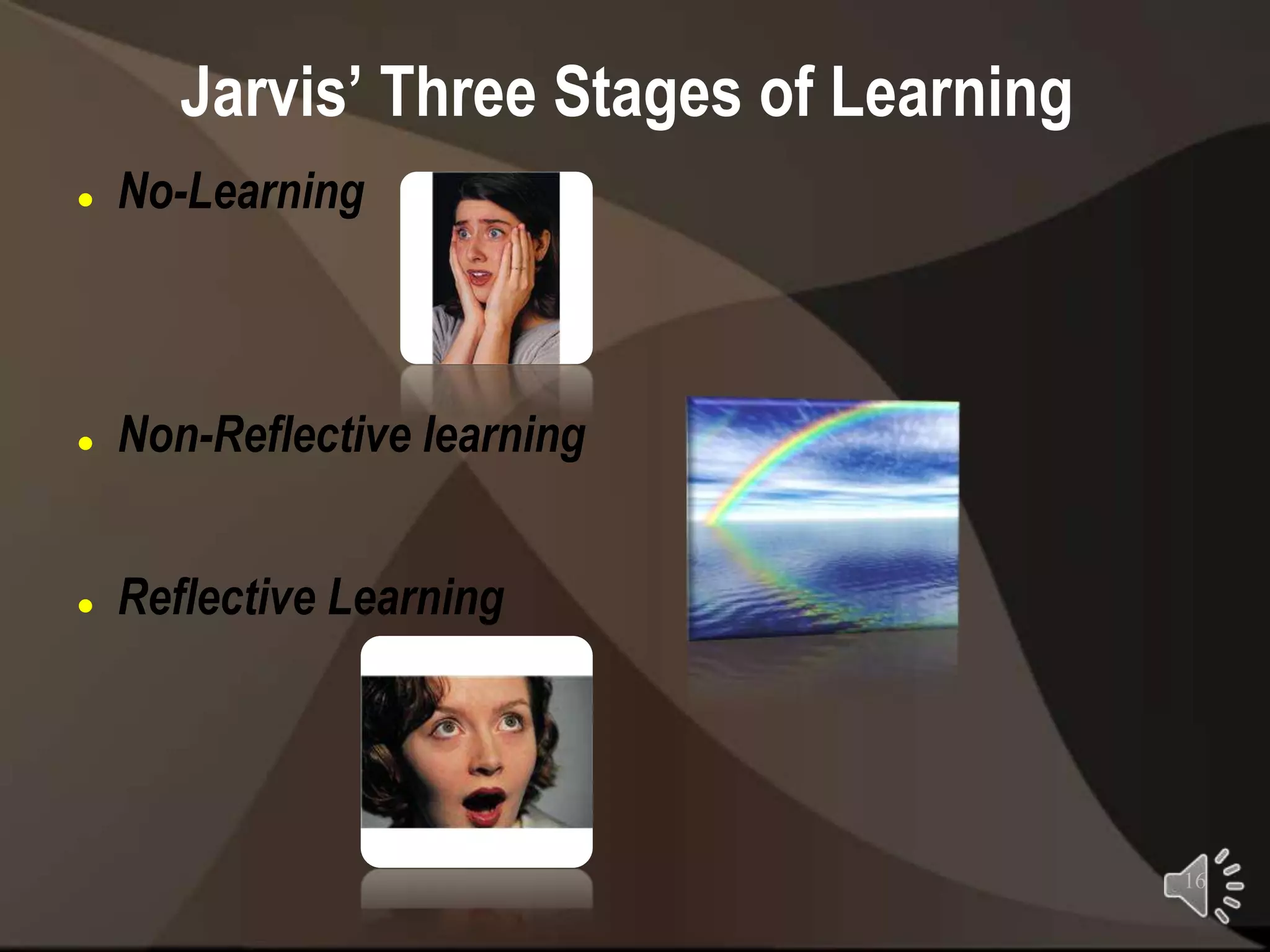
Peter Jarvis developed the Learning Process Theory to explain how adults learn through life experiences. The theory has three stages - non-learning, non-reflective learning, and reflective learning. It is influenced by Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory and sees learning starting with a life situation that causes internal reflection and changes how the adult views themselves and the world. According to Jarvis, adult educators should help learners make sense of their experiences and link lessons to their lives.