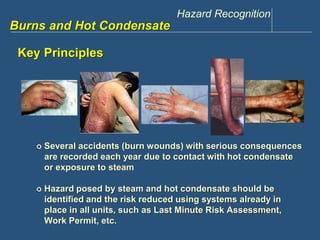
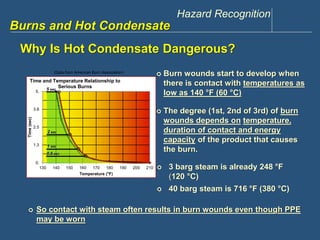
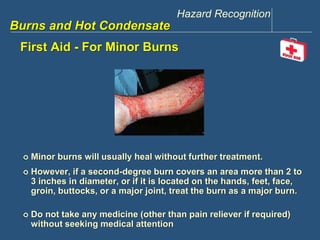
This document discusses hazards related to burns and hot condensate. It outlines objectives to recognize hazards from steam and hot condensate, identify potential consequences, describe control actions, and identify burn severity and first aid treatments. Examples of incidents involving burns from condensate and steam are provided. Precautions to prevent contact with hot condensate include guiding it away from occupied areas, barricading, and properly securing discharge hoses. The document also reviews different levels of burn severity and first aid treatments for minor and major burns.